3D Texture Synthesis算法
Procedural texture synthesis
Procedual:过程式,用函数表达纹理
方法论
Use 3D functions to define texture properties of objects
• Non‐trivial programming
• Flexibility
• Parametric control
• Unlimited resolution, antialiasing possible
• Low memory requirements
• Low‐cost visual complexity
• Adapts to arbitrary geometry

第一步:构造纹理特征
- Analytic scalar function of world coordinates (x, y, z)
- Texturing: evaluation of function on object surface
- Ray tracing: 3D intersection point with surface
- Textures of natural objects
- Similarity between different patches
- Repetitiveness, coherence
- Similarity on different resolution scales
- Self-similarity
- But never completely identical
- Additional disturbances, turbulence, noise
- Similarity between different patches
- Procedural texture function
- Mimics statistical properties of natural textures
- Purely empirical approach
- Looks convincing, but has nothing to do with material's physics
第二步:Perlin’s Noise生成随机纹理
[Perlin, Siggraph 1985]
- Noise (x,y,z)
- Statistical invariance under rotation
- Statistical invariance under translation
- Narrow bandpass limit in frequency
- Integer lattice (i, j,k)
- Random number at each lattice point (i, j,k)
- Look-up table or hashing function
- Gradient lattice noise
- Random gradient vectors
- Random number at each lattice point (i, j,k)
- Evaluation at (x,y,z)
- Tri-linear interpolation
- Cubic interpolation (Hermite spline \(\to\) later)
- Unlimited domain
- Lattice replicated to fill entire space
- Fixed fundamental frequency of \(\sim\) 1 Hz over lattice
- Smooth interpolation of interim values

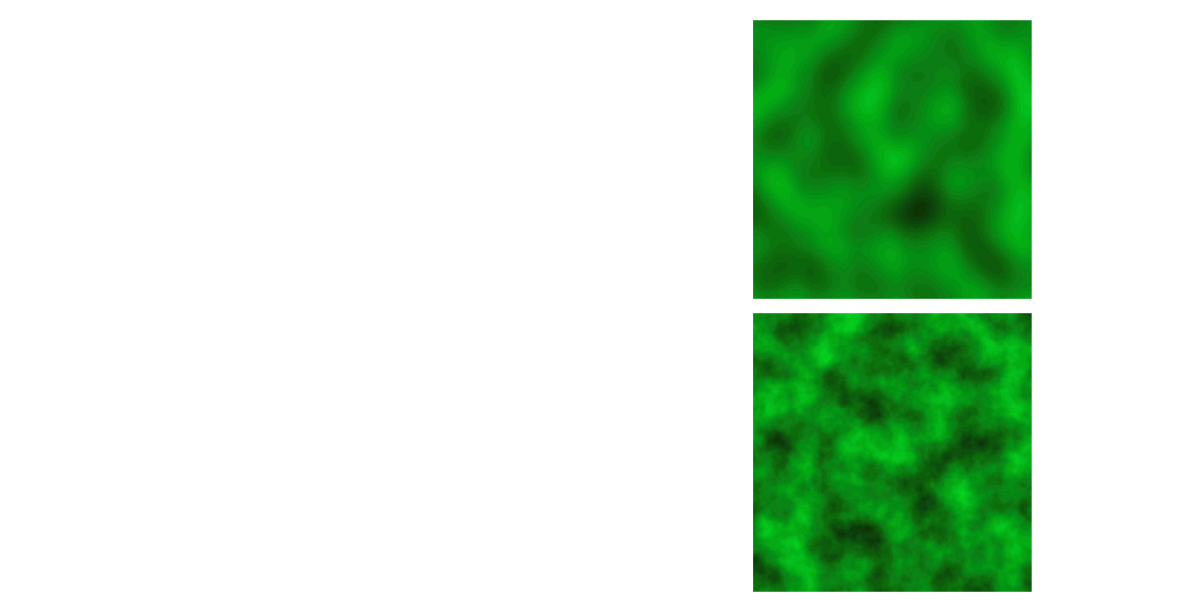
噪声转化为纹理
-
Noise function
- “White” frequency spectrum
-
Natural textures
- Decreasing power spectrum towards high frequencies
-
Turbulence from noise
- Turbulence \((x)=\sum_{i=0}^{k}\) abs ( noise \((2^i x ) / 2^{i}\))
- Summation truncation
- \(1 / 2^{k+1}\) < size of one pixel (band limit)
-
- Term: noise (x)
-
- Term: noise (2 x) / 2
- \(\dots\)
- Power spectrum: 1 / f
- (Brownian motion: \(1/f^2\))
应用
Reaction Diffusion Based Method
[Turk, Siggraph 1991]
Solid Textures
[Peachey, Siggraph 1985]
- Solid texture functions in 3D space
- Nonhomogeneous materials
• wood and stone
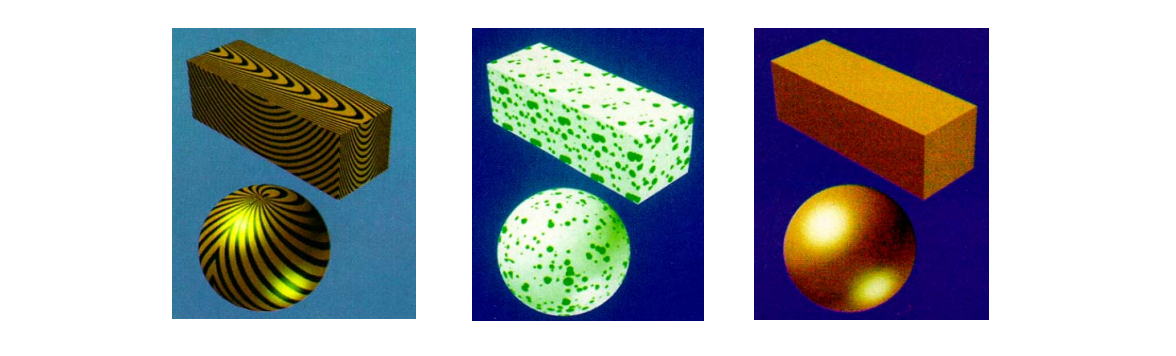
切开之后里面的体素也有纹理
Sample‐based texture synthesis
Methodology
- Synthesize a surface texture by coloring mesh vertices
- Extensions from 2D texture synthesis
- Key issues
- Resampling
- 邻域信息:Size、Orientation

纹理只定义在mesh顶点上,这种算法常于mesh加密的情况
Vertex colors on three levels in the mesh hierarchy
例子
以下是mesh上某个点的邻域信息
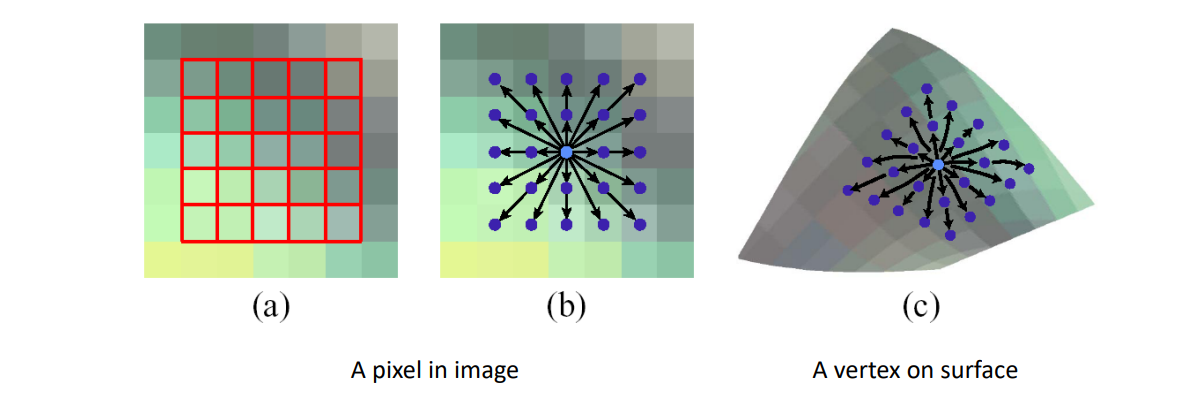
第一步:把点的邻域参数化
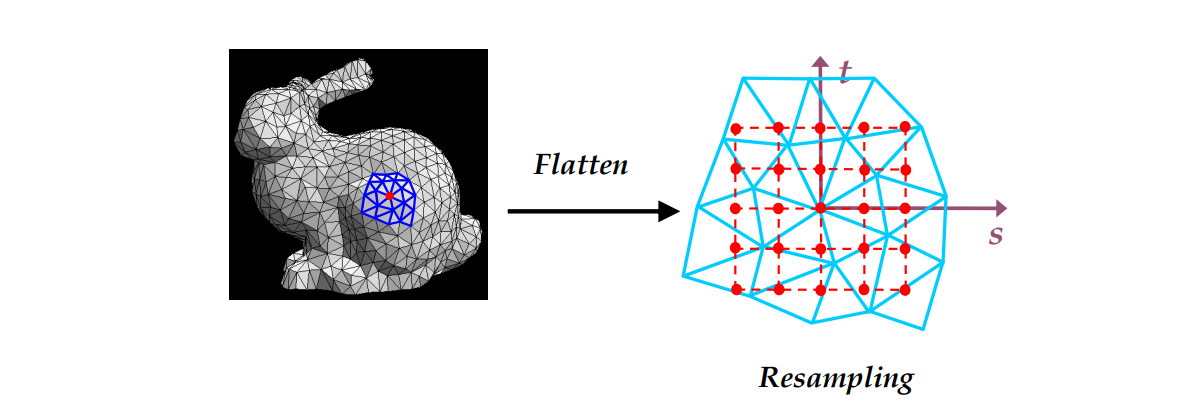
第二步:采样
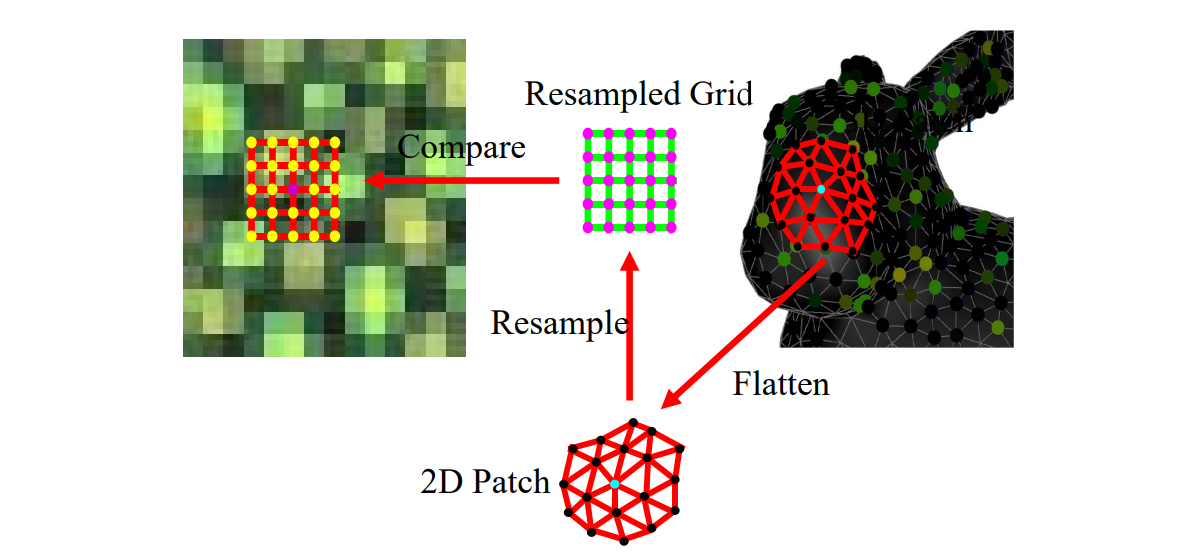
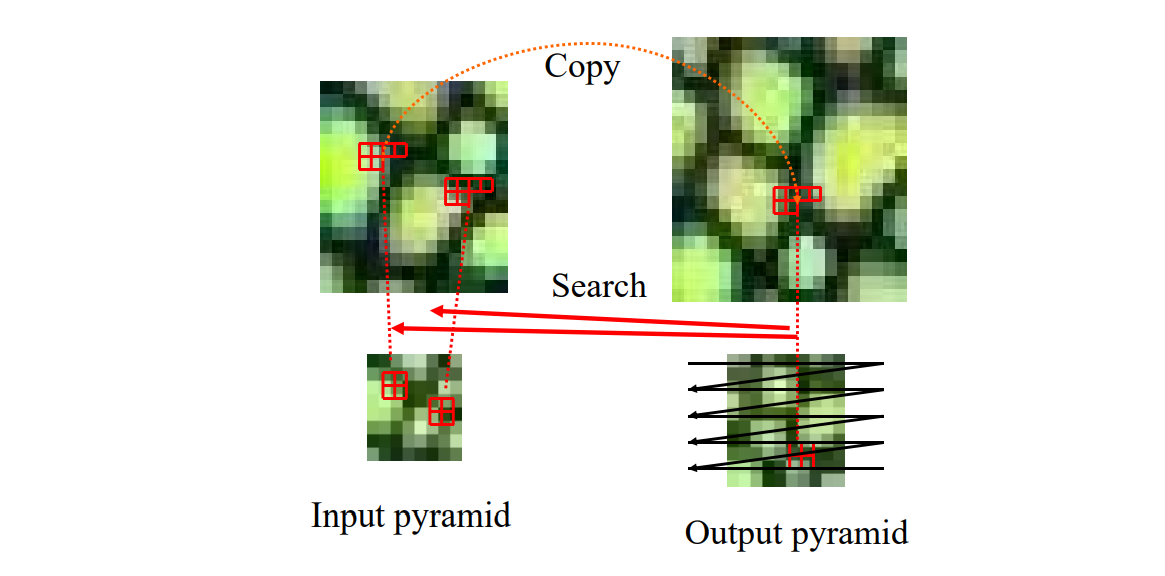
Recap: Texture Synthesis by Neighborhood Search
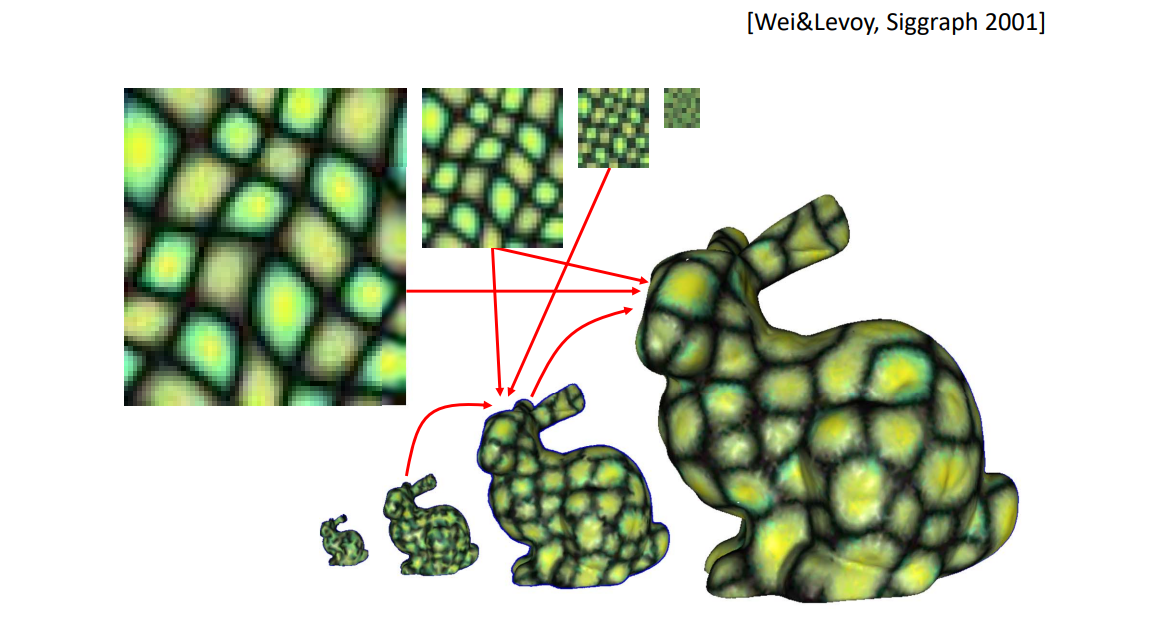
用多分辨率的方法实现上面过程,可以同时捕捉不同大小的特征
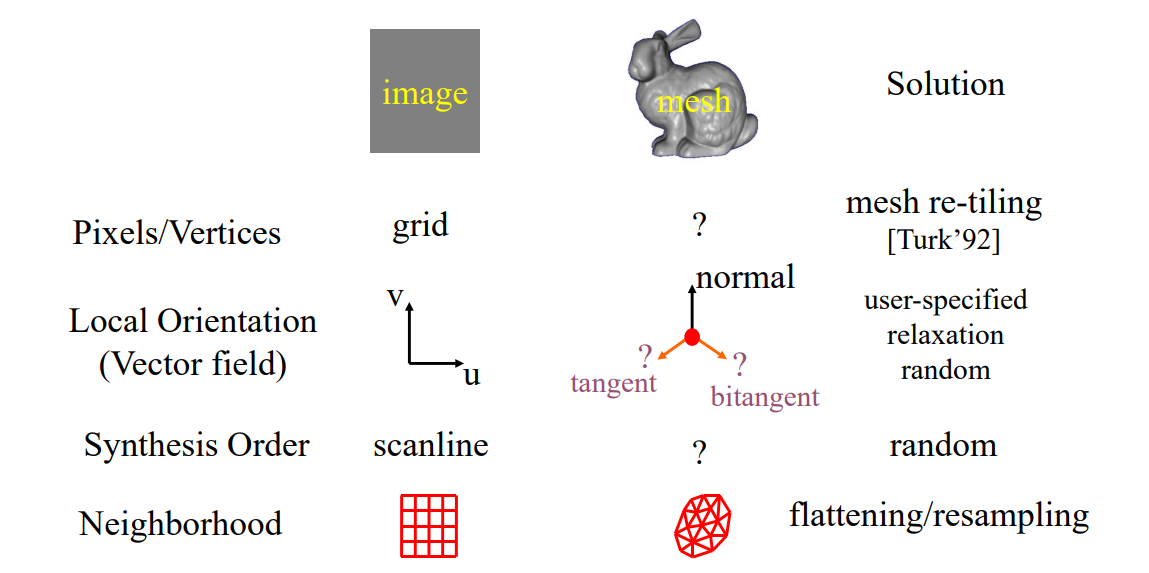
Differences between 2D and 3D
Texture Orientation
Methodology中提到这类算法需要使用某点邻域的方向,获取方向的方法有:
- user‐specified
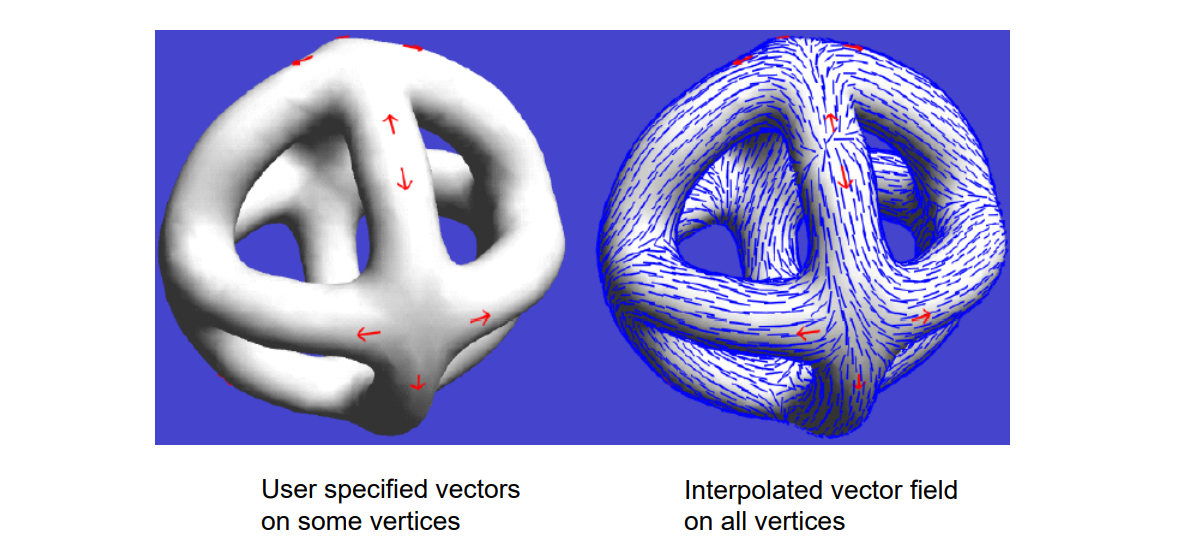
- random (for isotropic textures)
- smooth or symmetric (for anisotropic textures)
- by relaxation
不同orientation对纹理结果的影响:
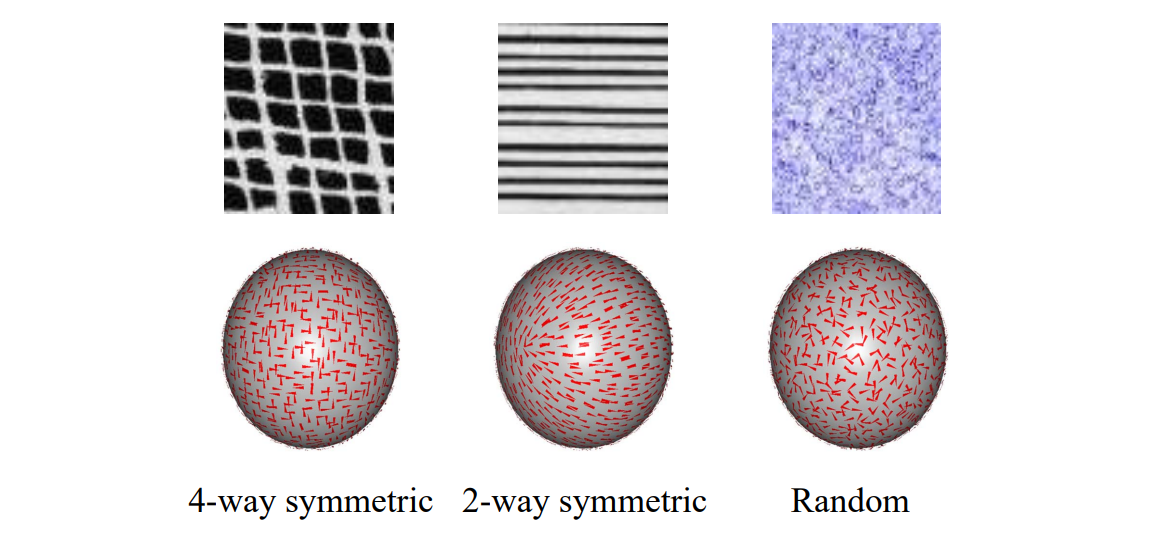
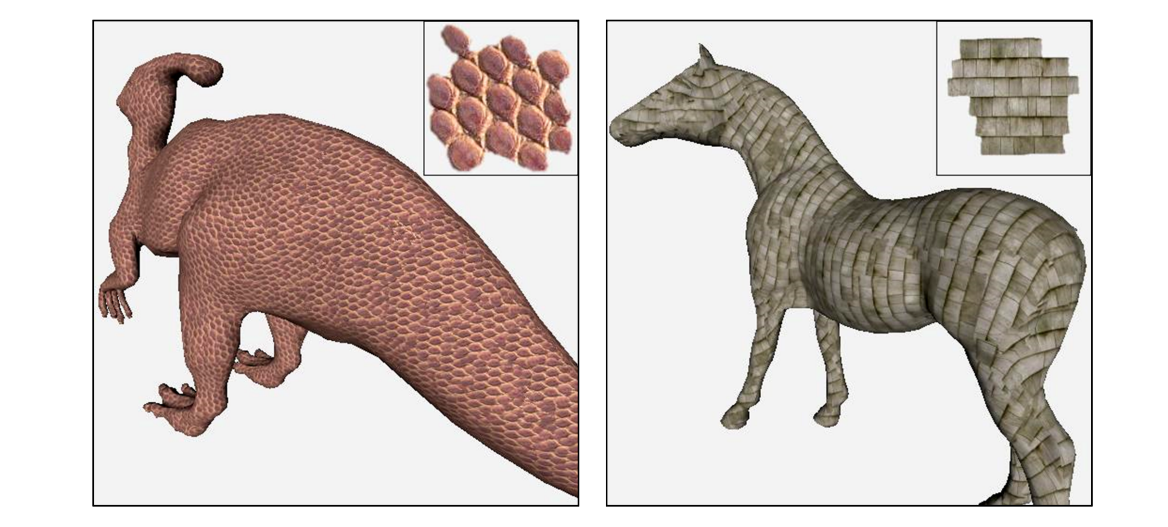
Patch‐based Synthesis
[Praun et al., Siggraph 2001]
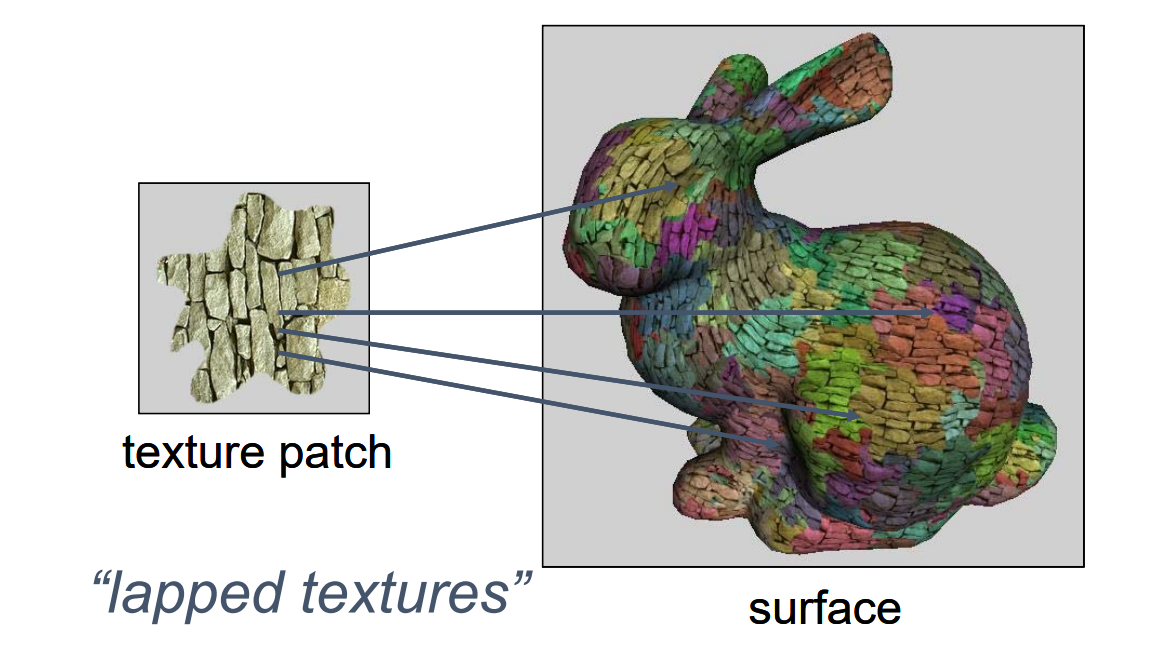
每贴一块就是这一块的参数化
大块贴完没贴满的部分,用周边的颜色产生一个patch
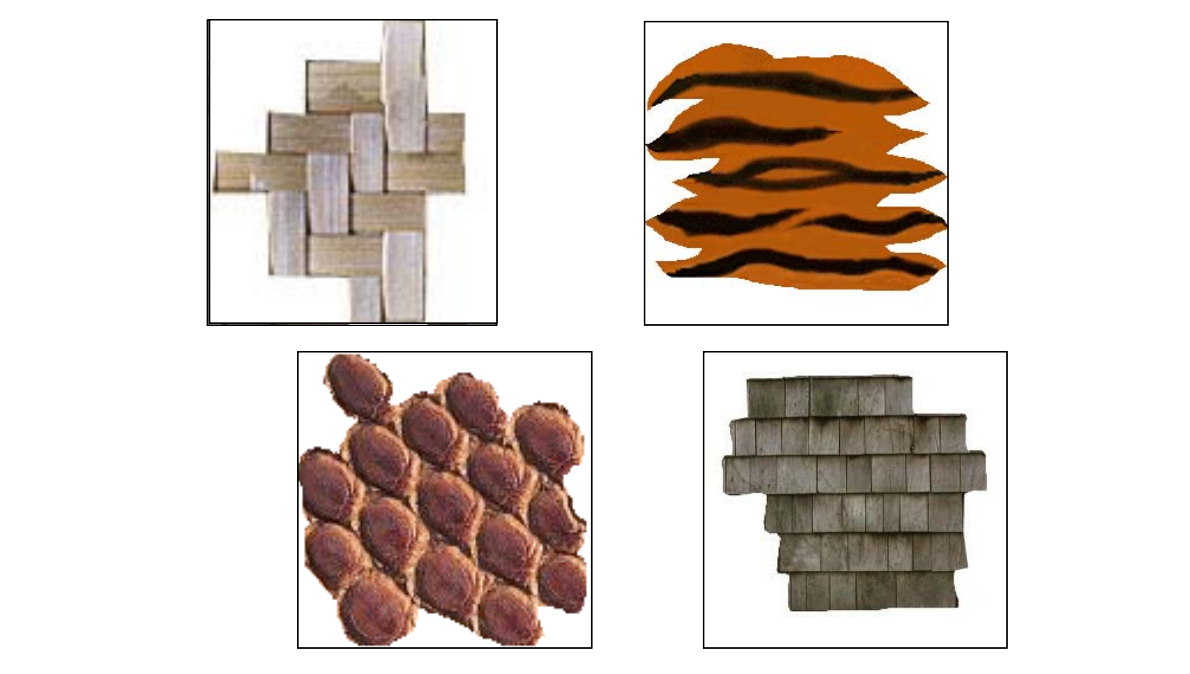

一个patch一般不是整块,而是基于基本元素的边界,这样是为了保证纹理特征的完整性
如果没有结构,可以随机设置边界
Patch Growth
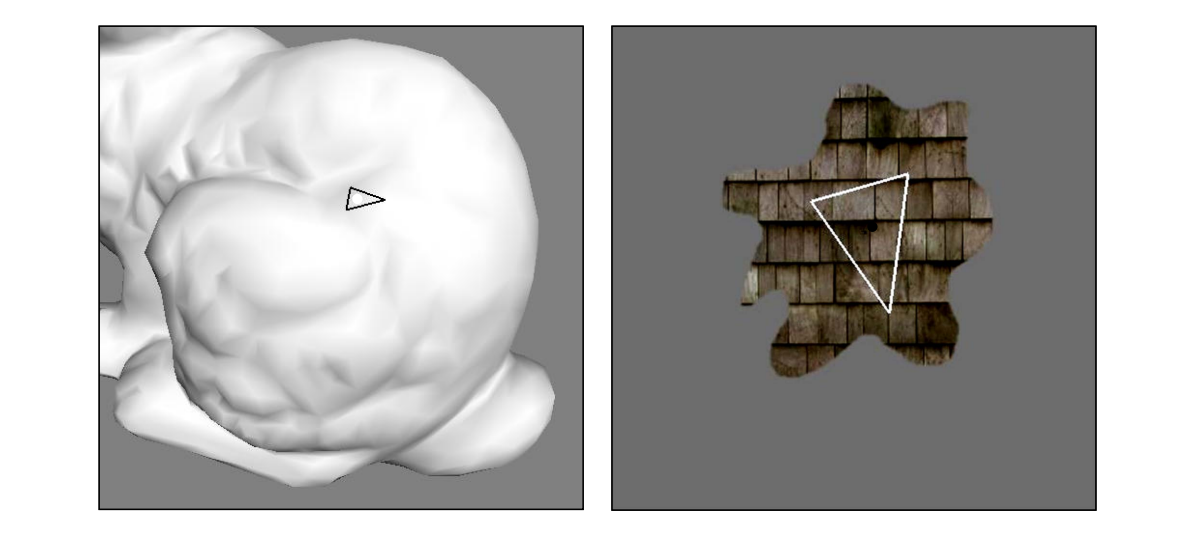 |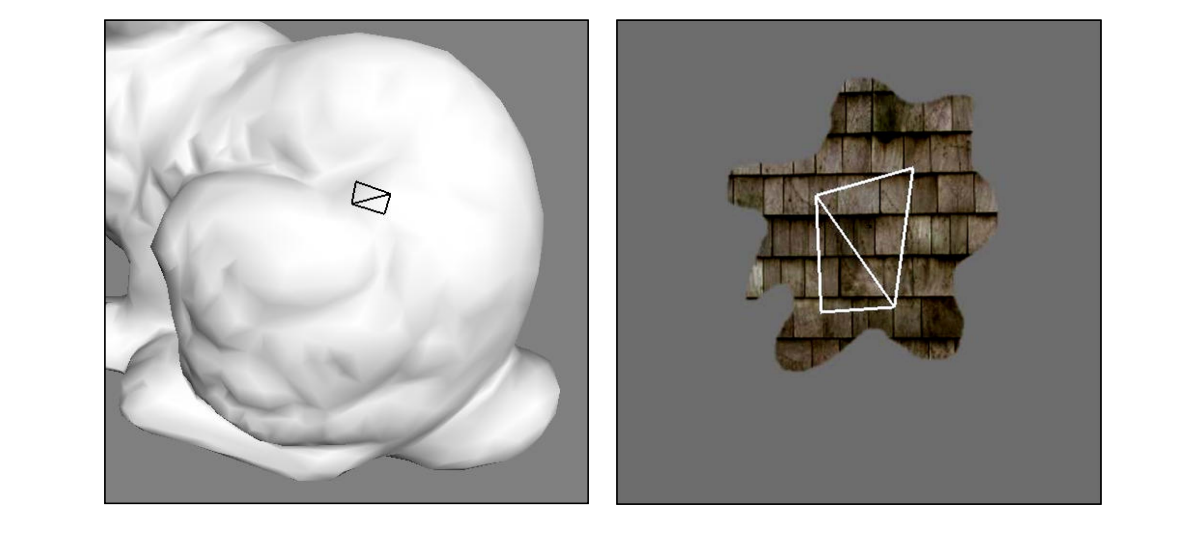  | 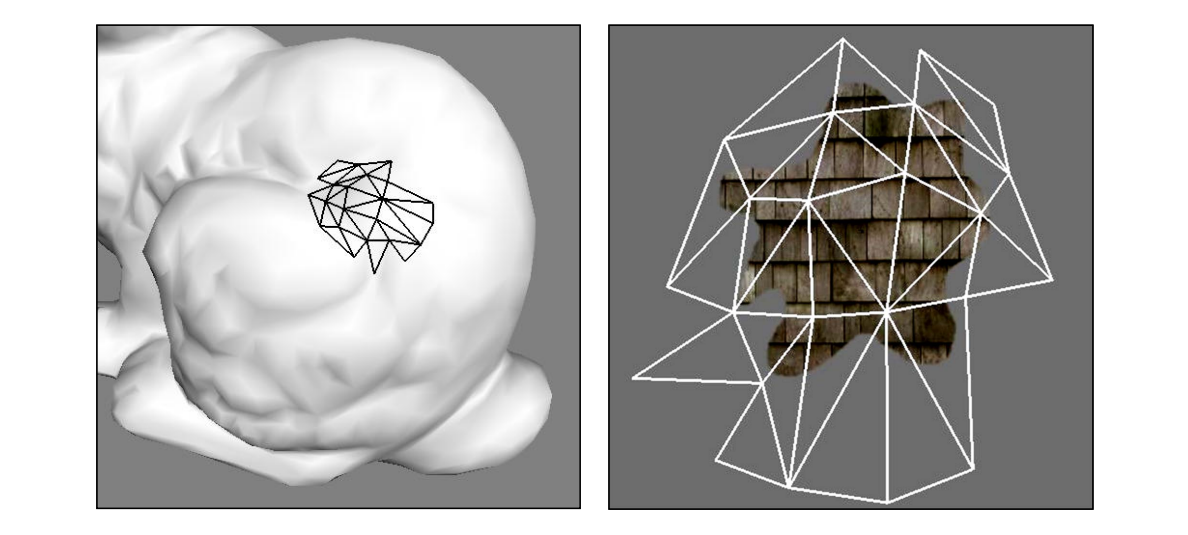 |
Results: Splotches
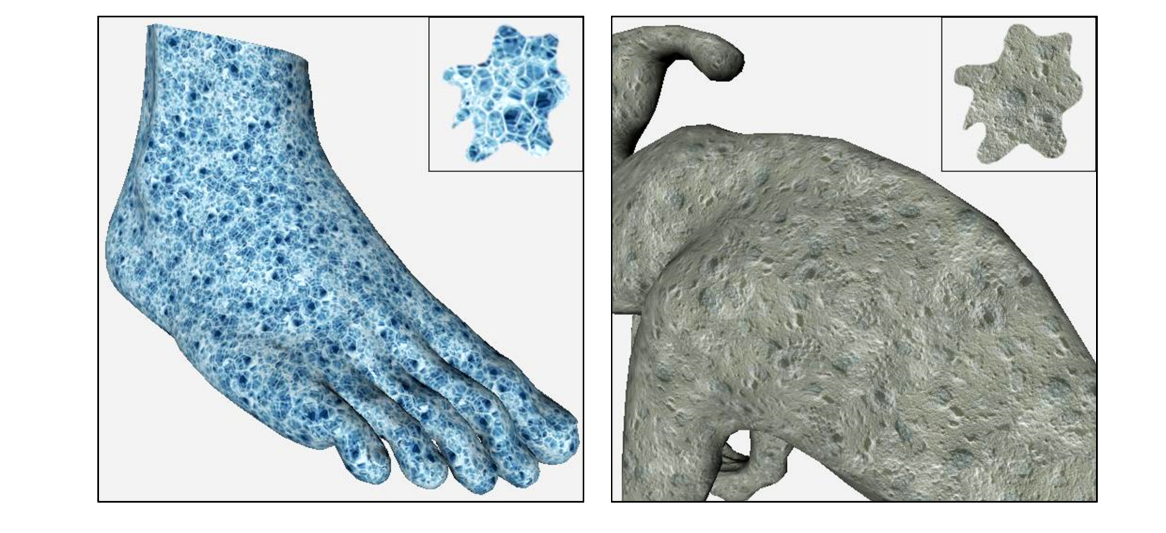
(completely automatic: no direction field)
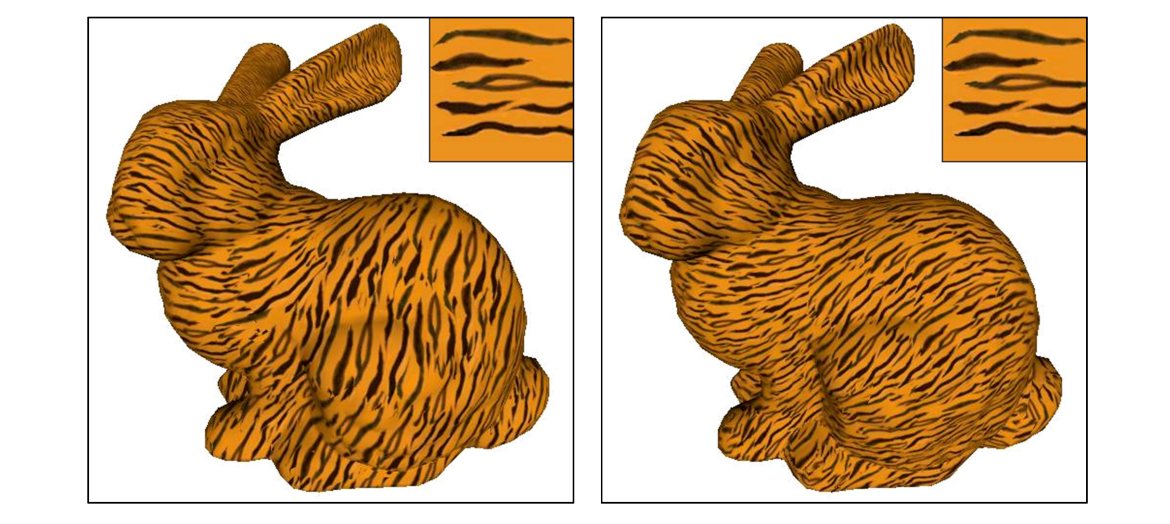
Controlling Direction and Scale
各向同性可以随机nomral,各向异性必须定义normal
Controlling Direction and Scale
| 各向同性 | 各向异性 |
|---|---|
 |  |
Limitations
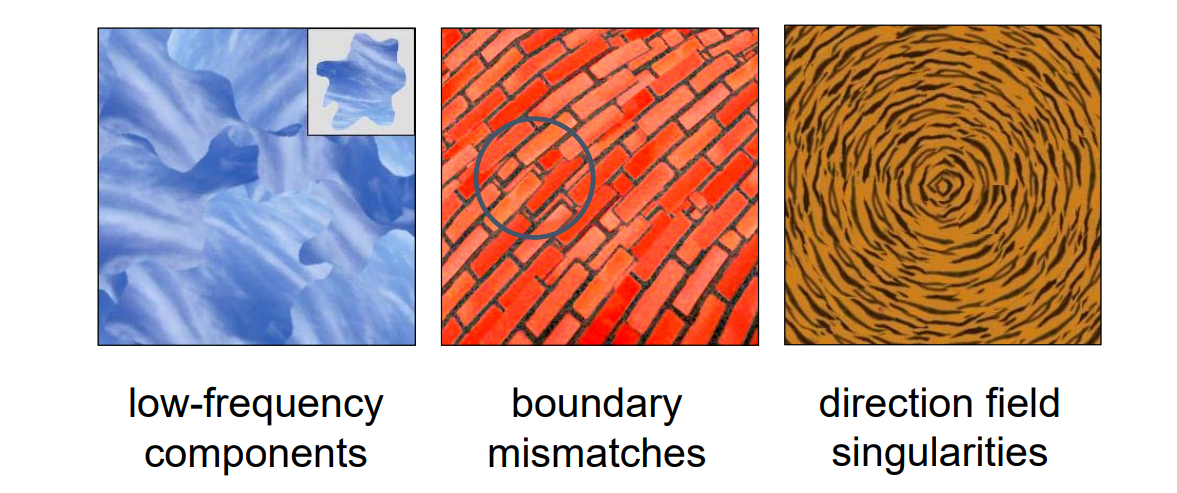

Feature‐aligned Texture Synthesis
[Xu et al., Siggraph Asia 2009]
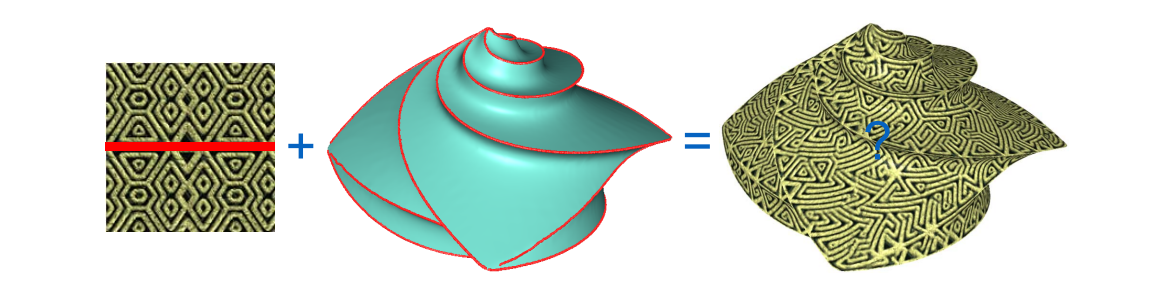
第一步:提取边界特性和方向,把起点集中到一个不显眼的地方
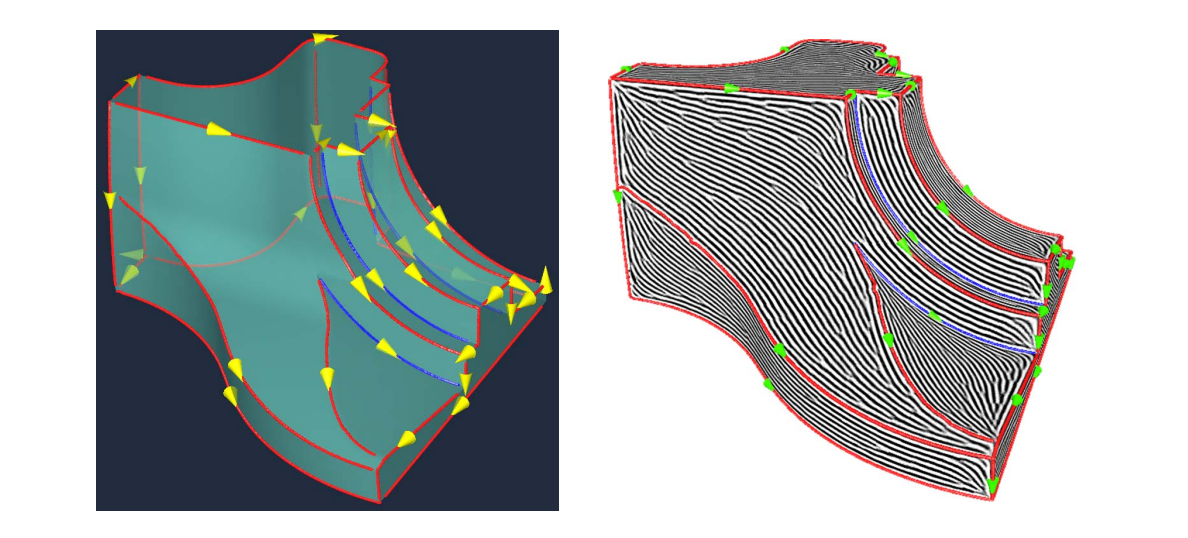
结果对比:
| 不基于特征 | 基于特征 |
|---|---|
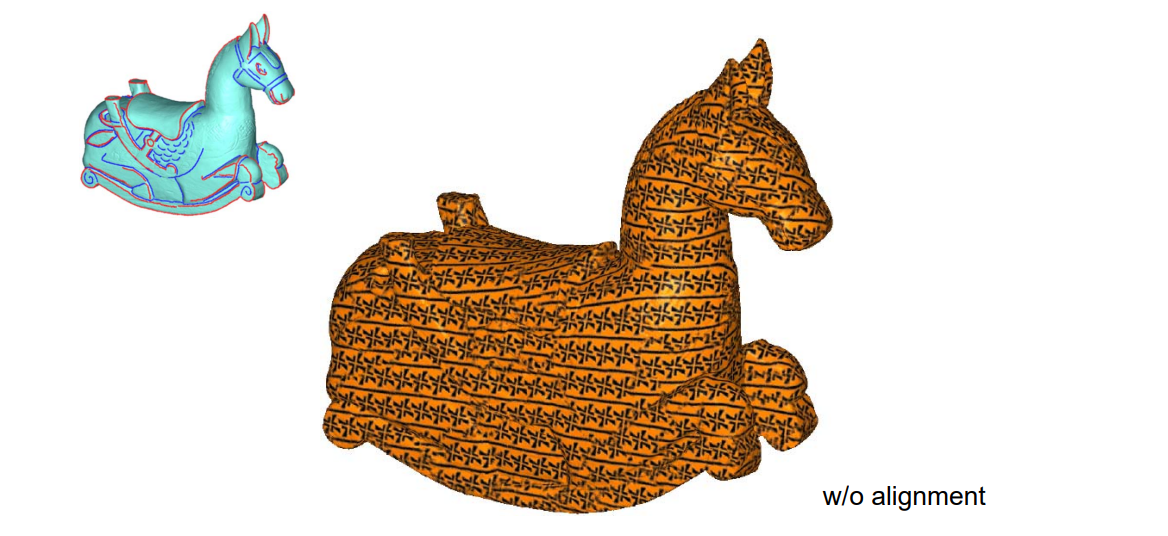 |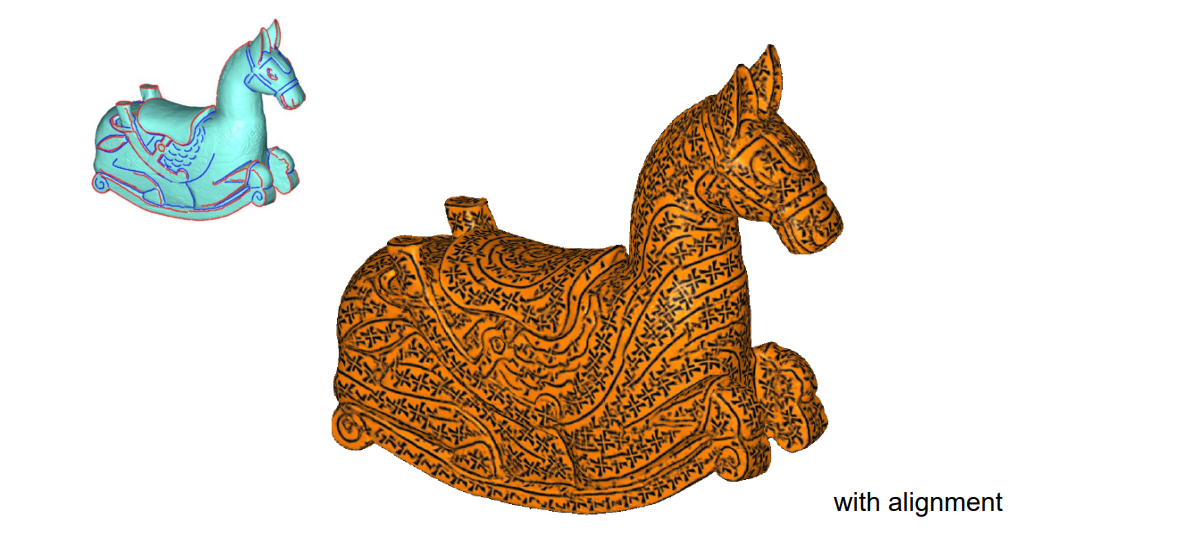  |
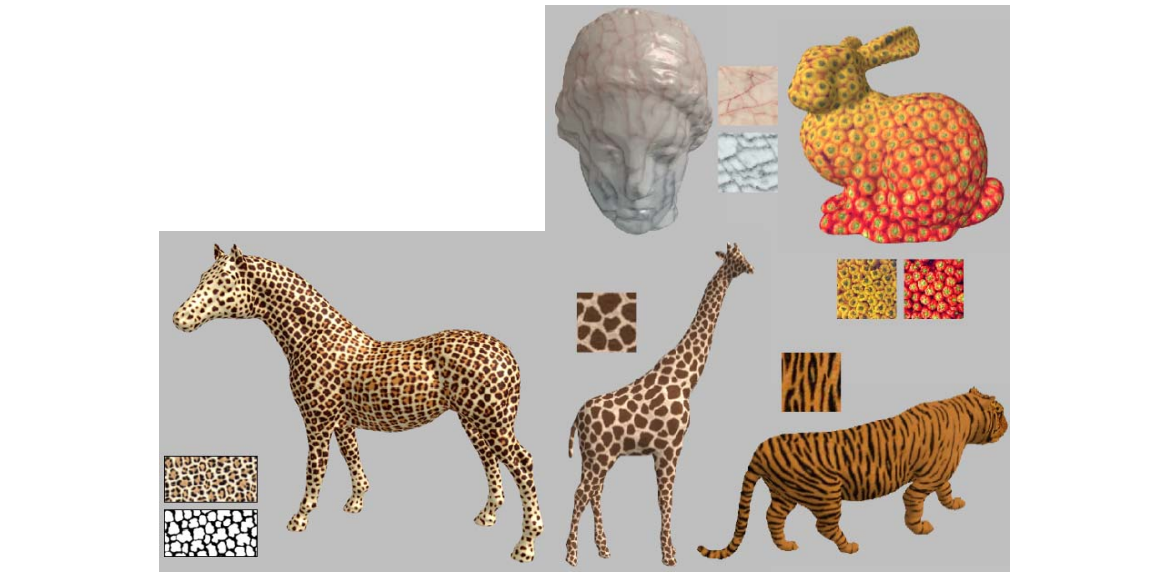
Progressively‐Variant Texture Synthesis
[Zhang et al., Siggraph 2003]

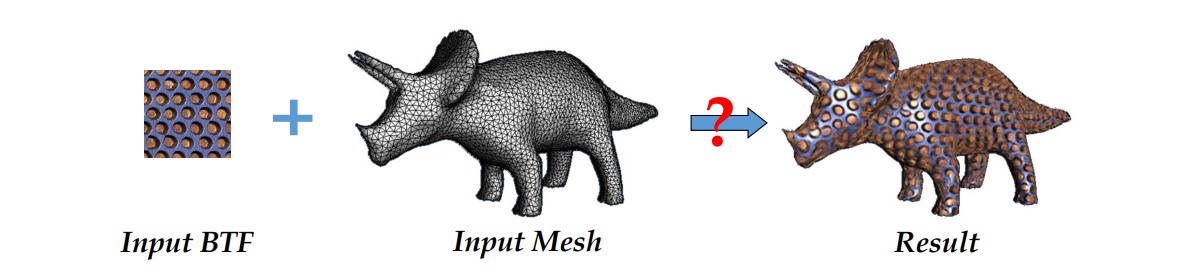
BTF Synthesis
[Tong et al., Siggraph 2002]
纹理效果与光照方向有关,这样合成效果更有立体感
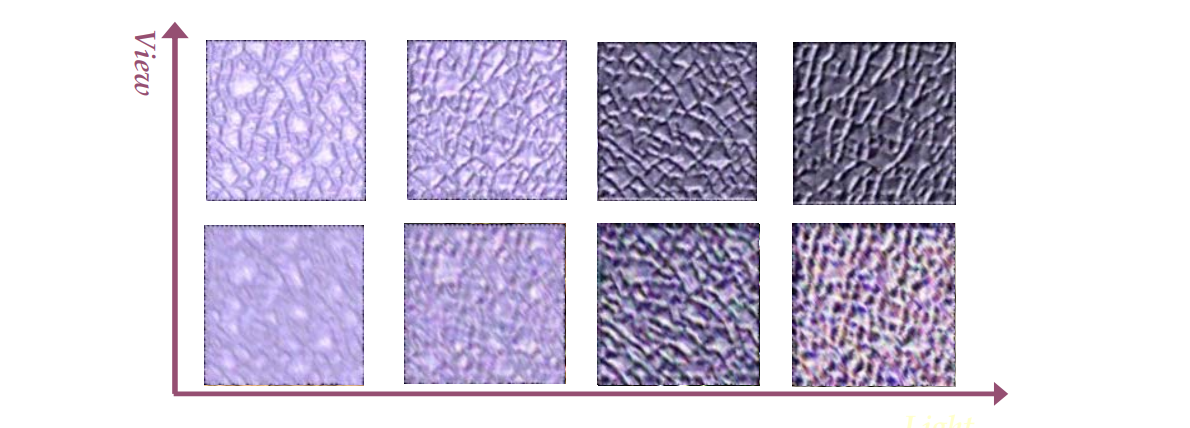
Bidirectional Texture Functions (BTF): A collection of images of the same surface under different lighting and viewing directions.
✅ 6D Function ( \(x, y, l_θ, l_φ, v_θ, v_φ\) )
✅ Dense Sampling in Viewing/Lighting Directions
✅ Capturing Appearance of Real World Surface
Real World Texture from CuRet
•Geometry Details (Mesostructure) on Surface
•Self-Occlusion, Self-Shadow, and Specularity
学习
Treating BTF as a 2D Texture Map
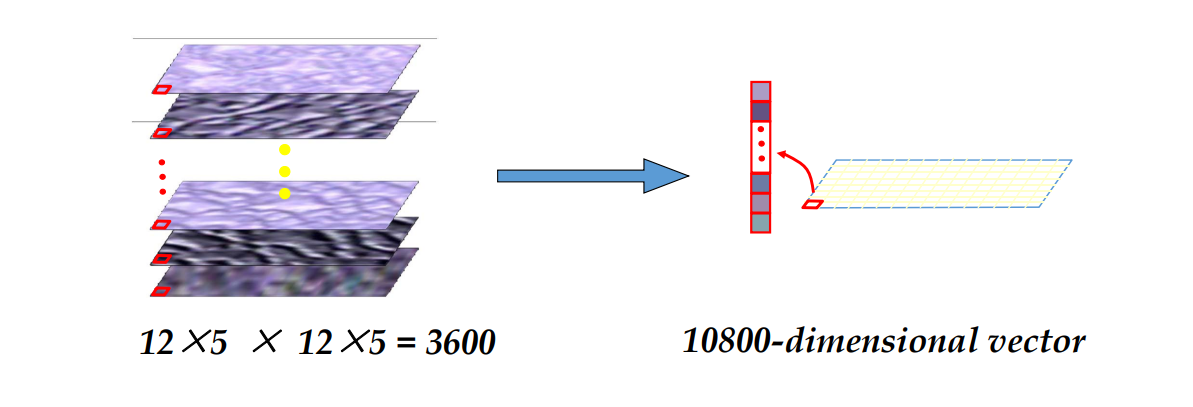
一个像素有多个对应点,每个对应点是这个像素在不同光线下的特征。
把左图特征转化为右图特征,用右图特征来做匹配。
特征转化的过程可以用网络或传统方法,本文用的是滤波。
左右维数越高,能抓到的信息的越多。❓ 上限不就是3600吗?为什么需要10800?
Surface Texton
使用
Surface Texton Map & Rendering
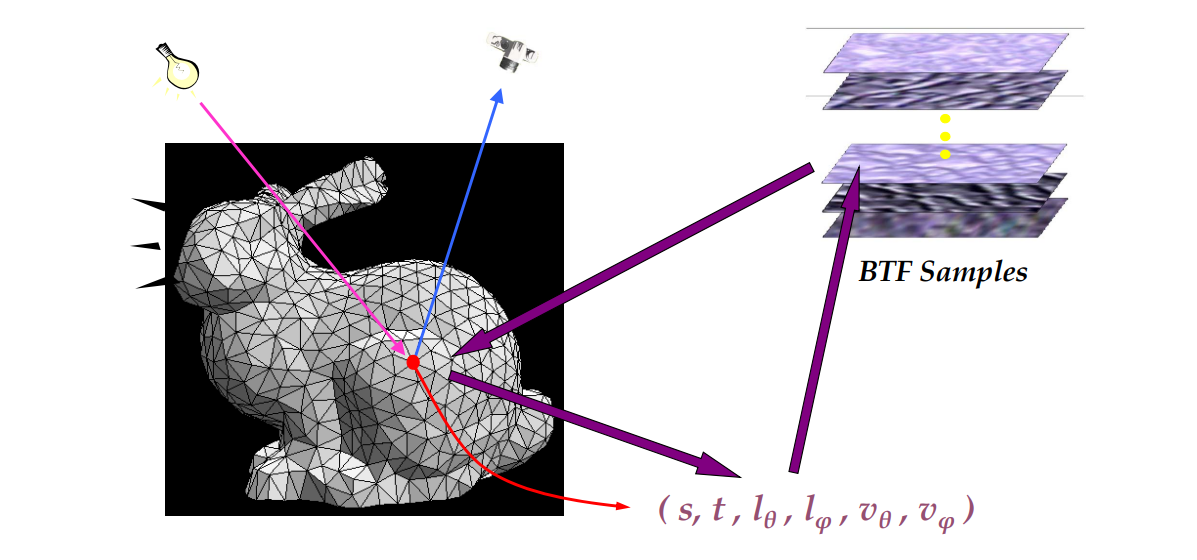
每个点根据它的实际情况,从源里面匹配出合适的纹理效果。
💡 需要提前采好这个兔子的各个角度的数据?
K‐Coherent Search:通过匹配找到最好的K个,从里面随机选择一个
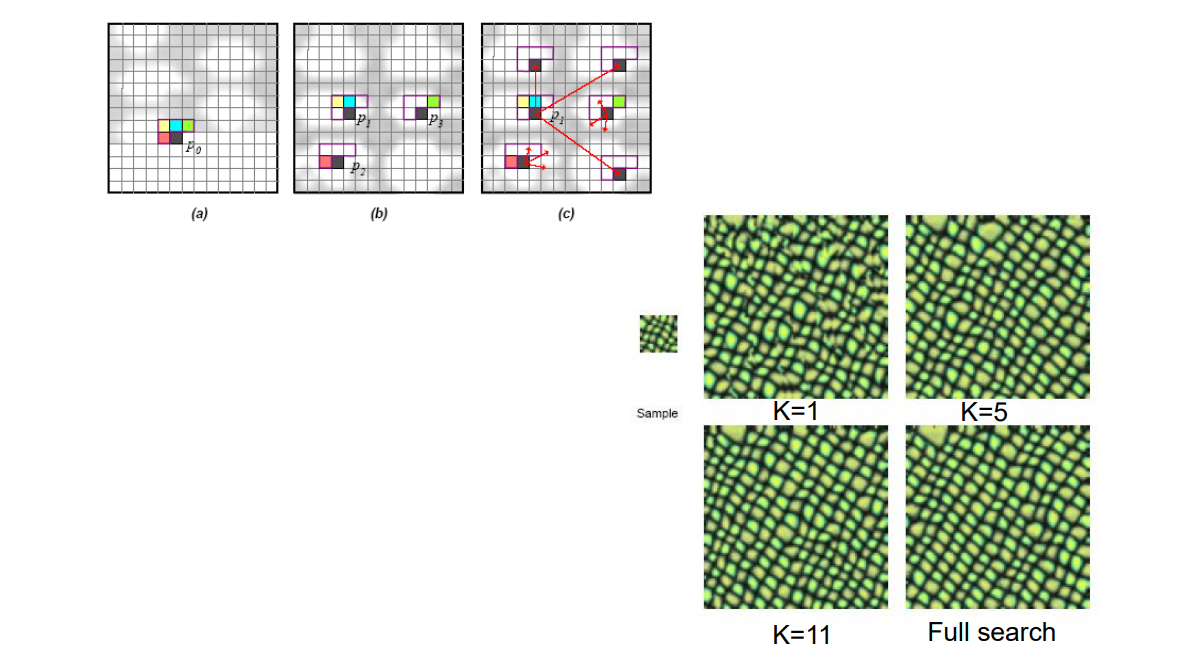
Comparison
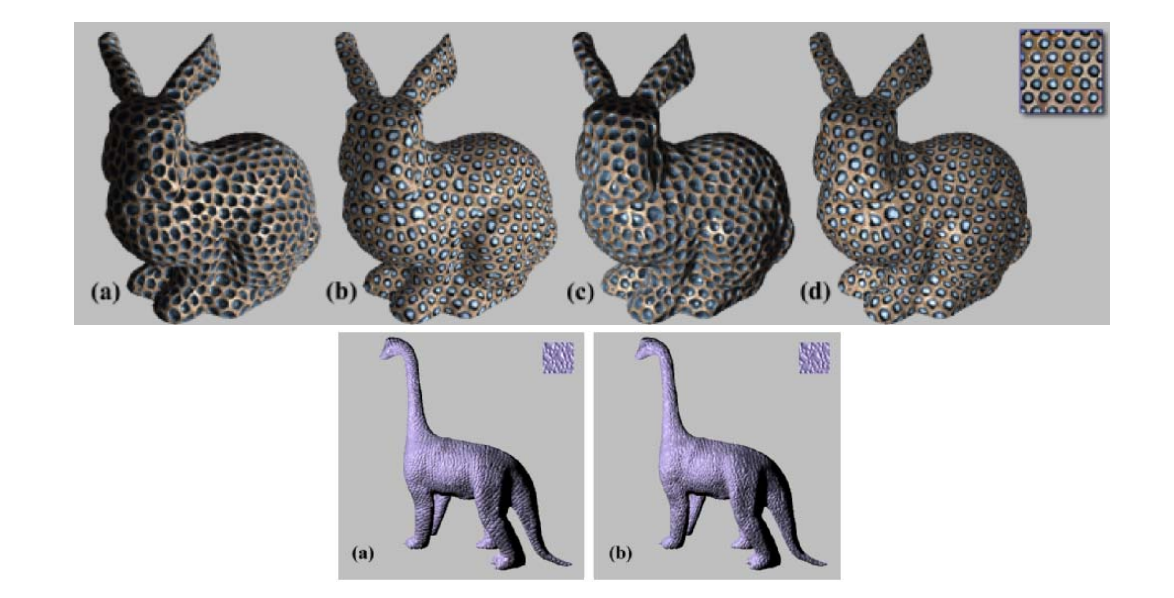
Geometry synthesis
要解决的问题:Generating geometry over surfaces by texture (geometry) samples,例如:
| 体素合成 | 风格合成 | 基于几何匹配的拼接 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 效果 | 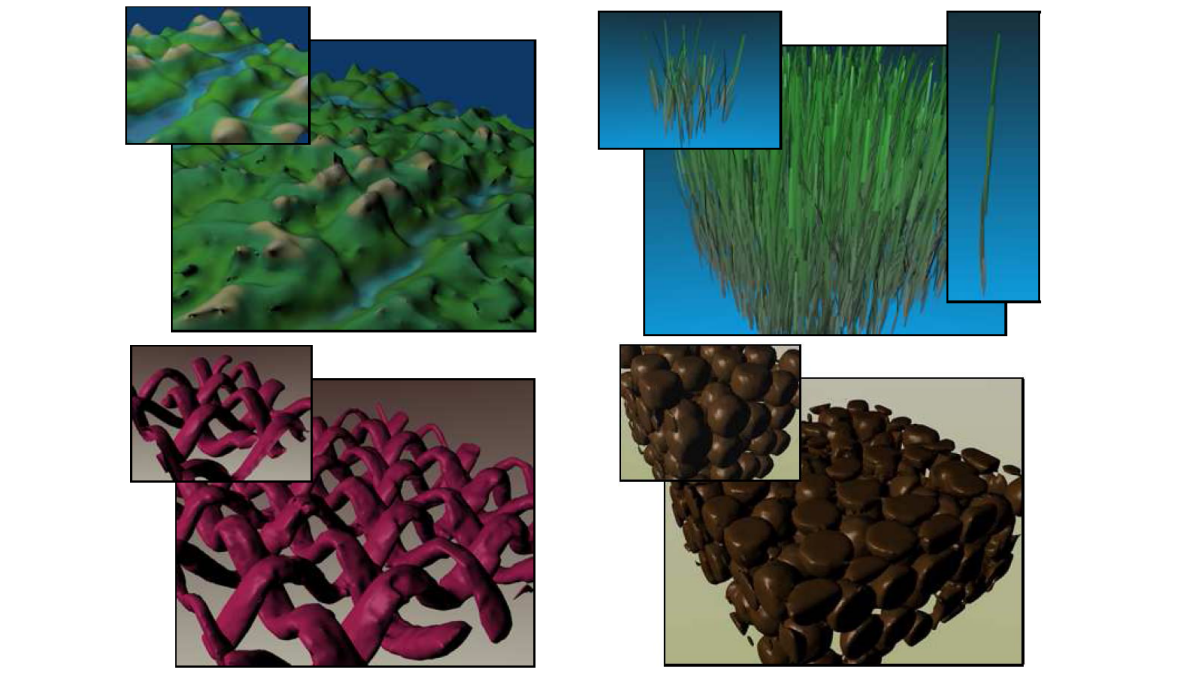 | 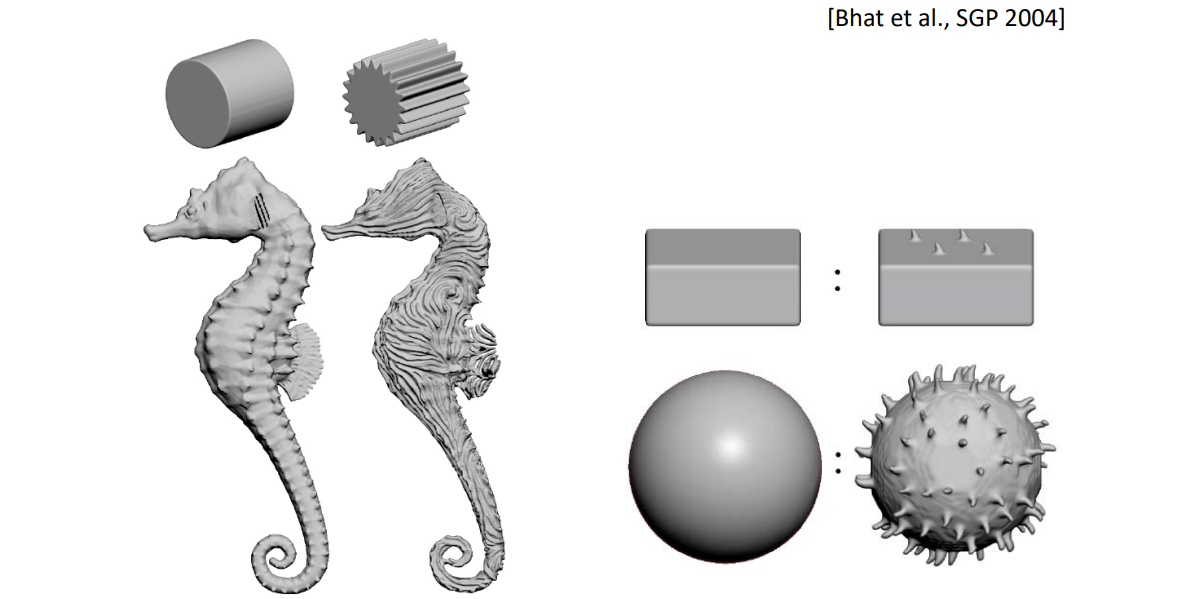 | 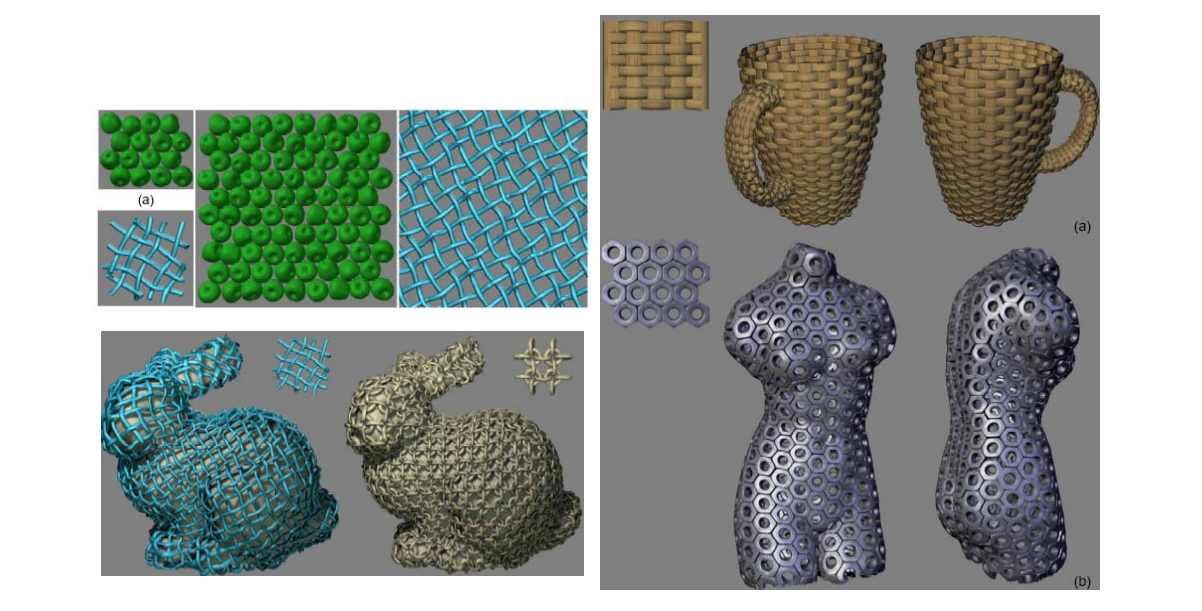 |
| 方法 | 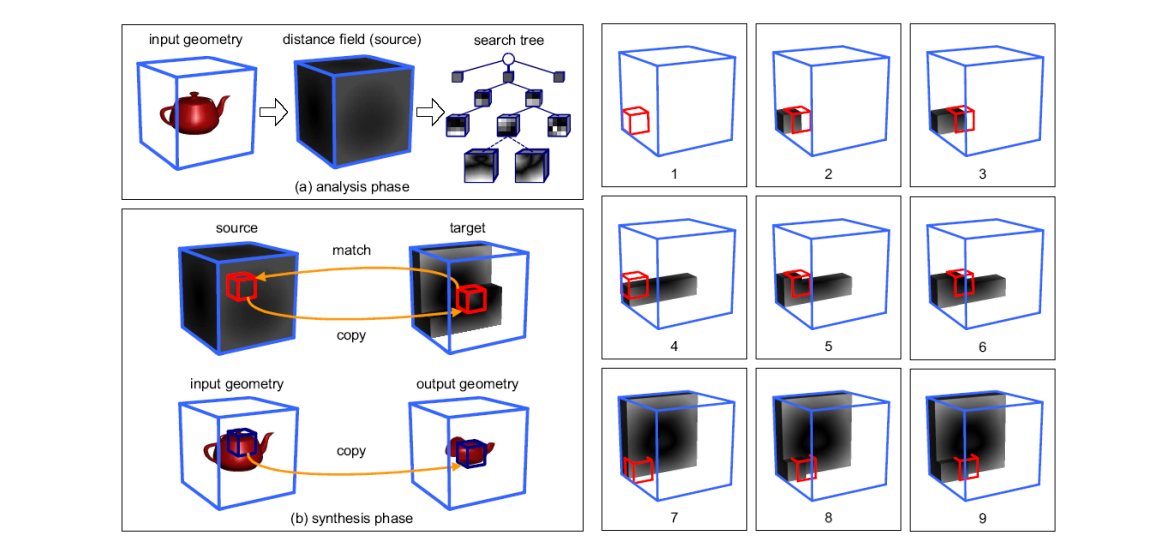 [Lagae et al., TR 2004] | Laplace | 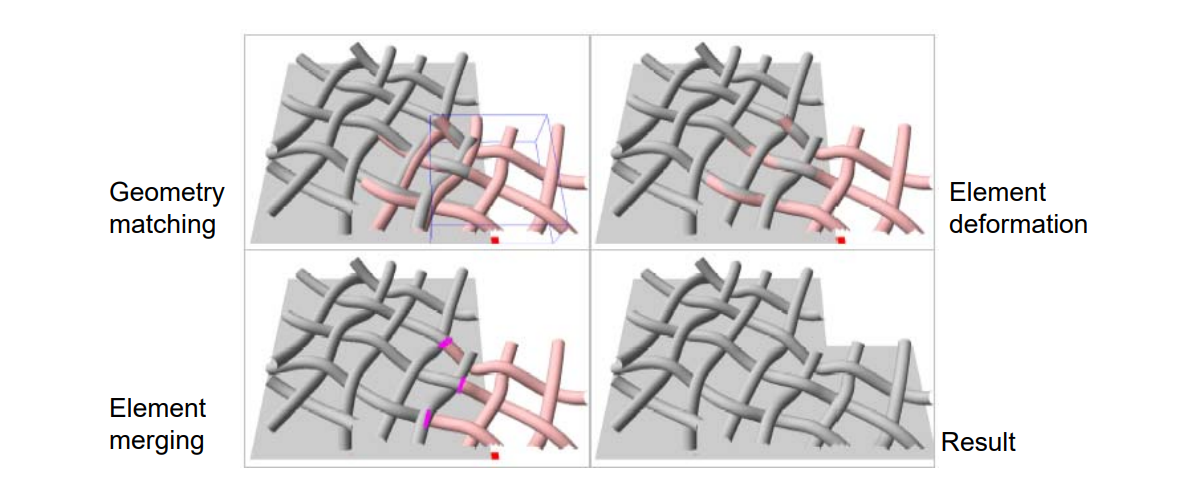 [Zhou et al., Siggraph 2006] |
方法:
• 3D distance field based method
• Image analogies extended to volumes
• Mesh‐based geometric texture synthesis technique
Summary: Texture Synthesis
• An important topic on content generation (2D/3D) textures or repeated geometries
• A well‐studied topic
• Many applications
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/