等式约束的优化问题
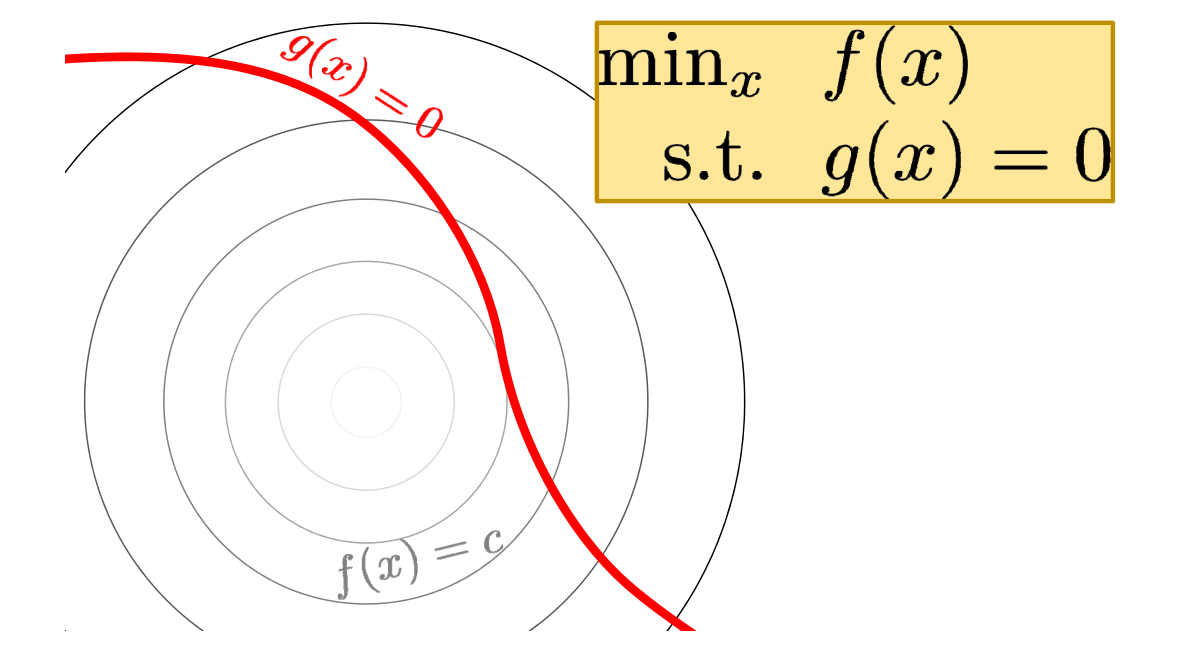 | 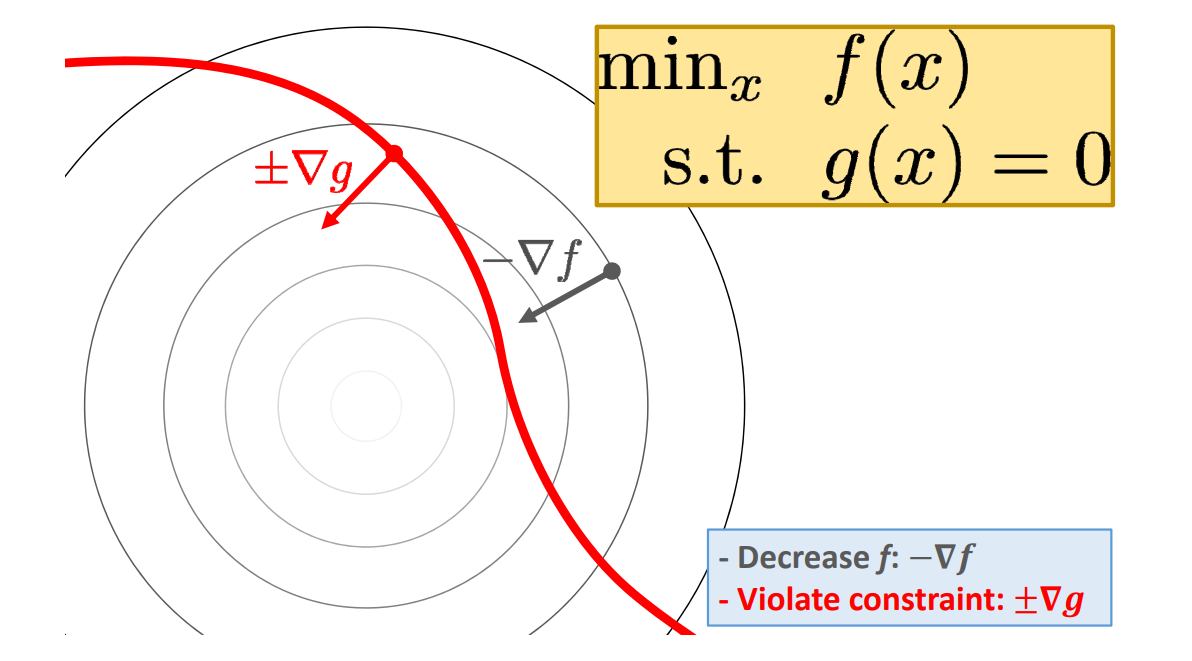 |
\(g(x)\)是红线,\(f(x)\)由等值线构成的曲面。满足约束的极小值点具有以下特点:
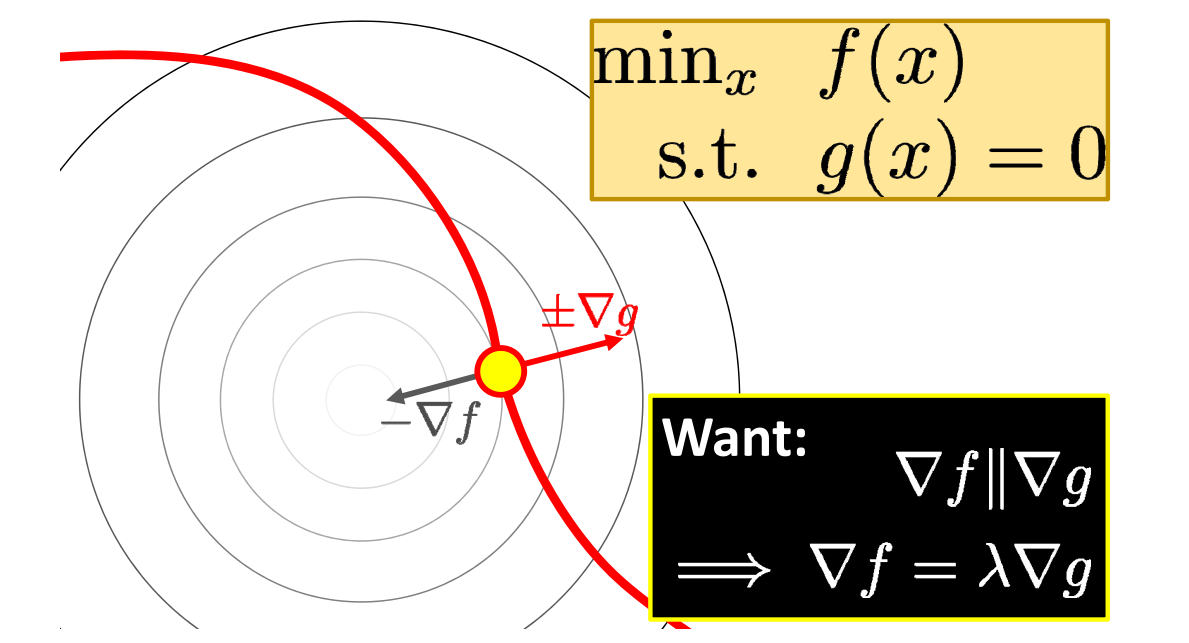
\(f(x)\)与\(g(x)\)在该点上梯度方向重合,可能同向或反向。
[1:13:26]等值约束的优化问题转化为解方程组问题
$$
\begin{array}{l}
\nabla \mathbf{f}(x) =\lambda \nabla g(x) \\
\mathbf{g}(x) = 0 \
\end{array}
$$
Many Options
• Reparameterization
Eliminate constraints to reduce to unconstrained case
• Newton’s method
Approximation: quadratic function with linear constraint
• Penalty method
Augment objective with barrier term, e.g. \(f(x)+\rho |g(x)|\)
Alternating Projection
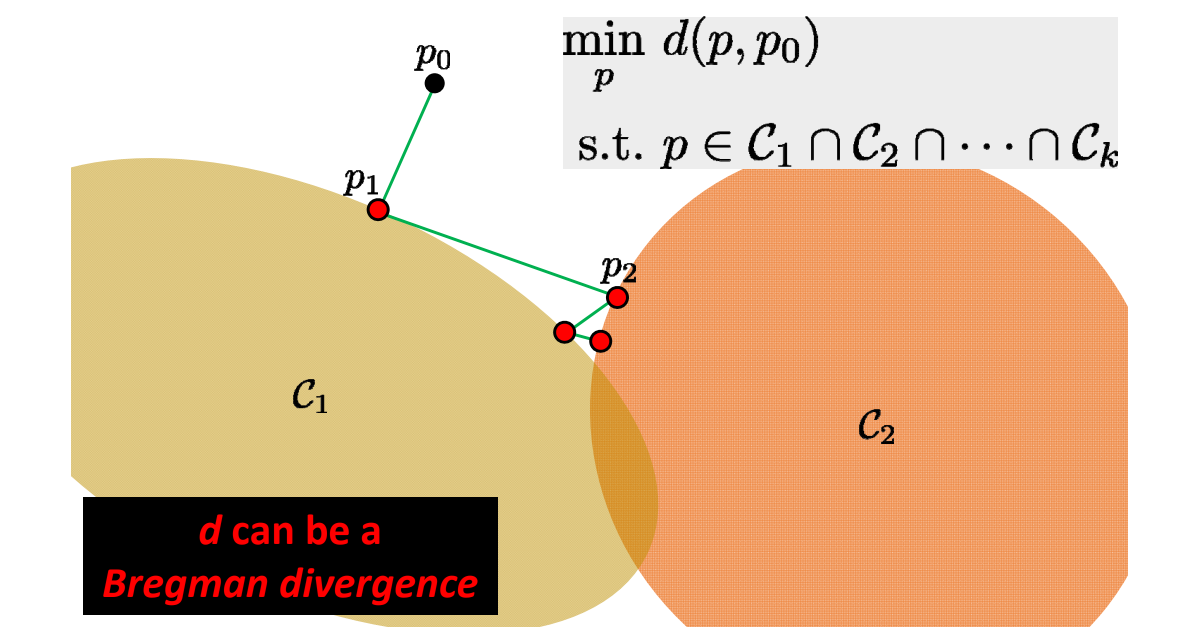
[1:14:18] \(C_1,C_2,C_3\)的代表不同的等式约束。相当于坐标法推广
Augmented Lagrangians
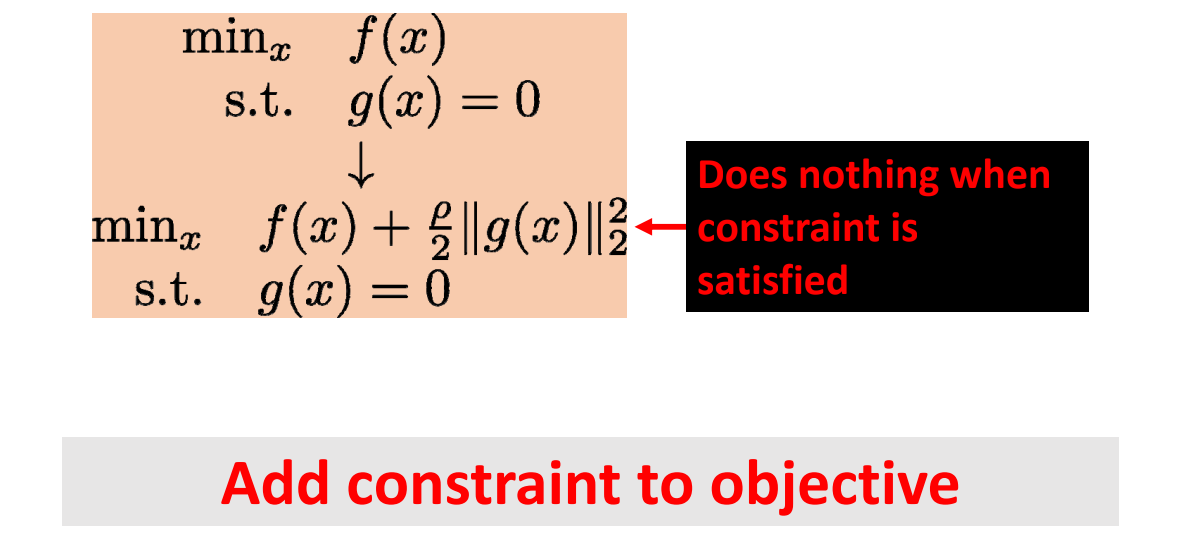
[1:15:18] 把 Constrain 作为目标函数,极小划 权\(\rho \)在优化过程中会改变
Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM)
[1:15:50] ADMM.把变量分离。把问题分成若干小问题分解为:小规模局部优化问题、闭式解全局优化问题。
$$
\begin{array}{l}
\min_{x,z}& f(x)+g(z) \\
s.t. &Ax+Bz=c \\
\end{array}
$$
$$ \wedge _\rho (x,z;\lambda )=f(x)+g(z)+\lambda ^\top (Ax+Bz-c)+\frac{\rho }{2}||Ax+Bz-c||_2^2 $$
https://web.stanford.edu/~boyd/papers/pdf/admm_slides.pdf
The Art of ADMM “Splitting”

本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/