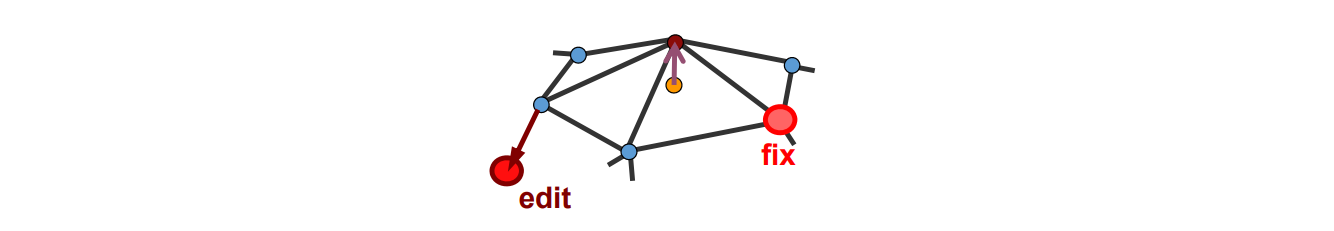
Point based editing要解决的问题
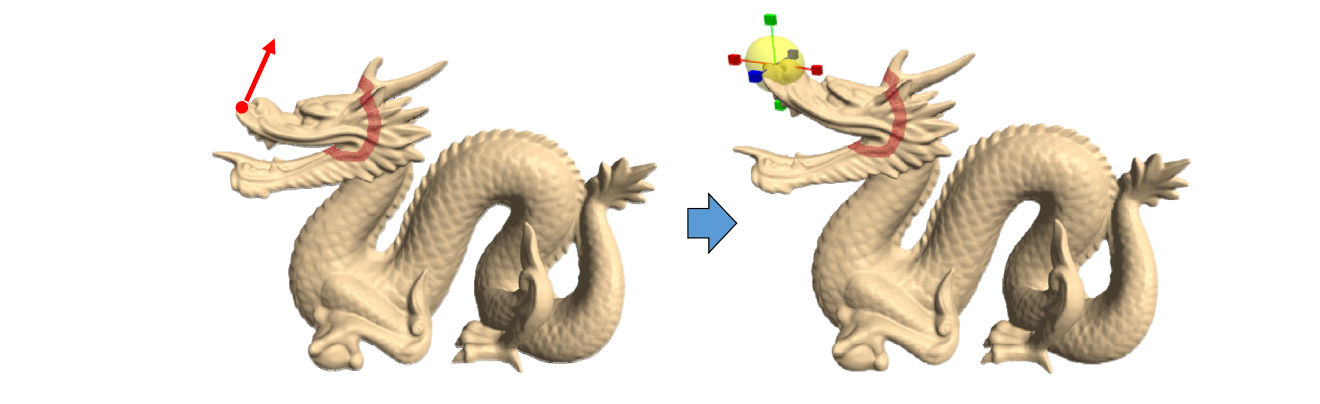
Fix 红圈上的点,Drag one or more vertices,更新红圈内的点
本质数学问题:数据插值问题,同时让f满足光滑、性质保持等约束。
$$ \begin{array}{l} \min E (f) \\ s.t. &f(x_i)=y_i,i=1,2,\dots , n \\ \end{array} $$
(1) RBF‐based Editing
(2) Moving Least Squares Method
[Siggraph 2006]
(3) Vector Field Based Deformations
[Siggraph 2006]
原理
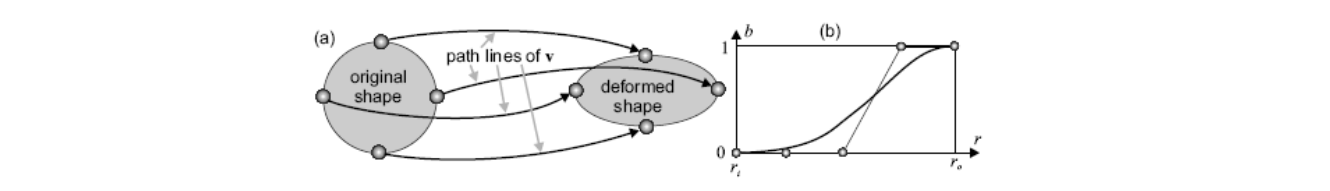
在空间定义了一个连续的场,物理在场里面流动产生新的变化
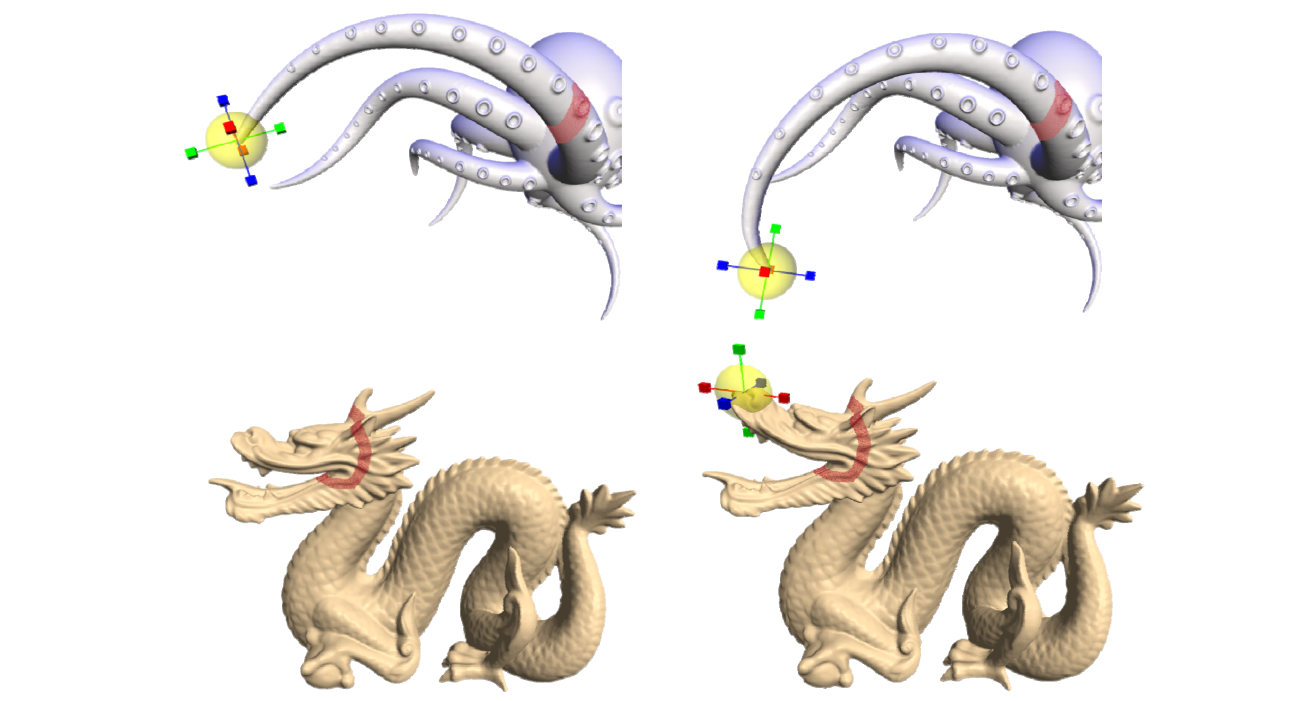
Basic model: Moving vertex along the deformation orbit – defined by the path lines of a vector field v.
Given a time‐dependent vector field V(X,t), a Path Line X(t) in space is an integral.
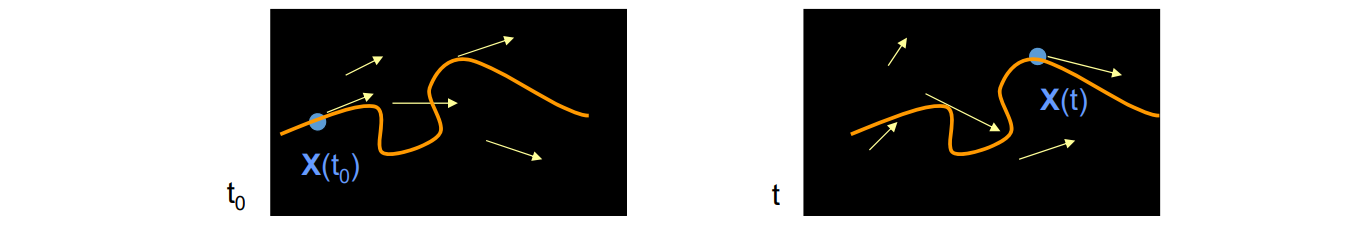
Vector Field Selection:
- Deformation Request:
• No self‐intersection
• Volume‐preserving
• Details‐preserving
• Smoothness of shape in deformation - Divergence‐free Vector Field: \(V=(V_1, V_2, V_3)\)
$$ div V=\frac{\partial V_1}{\partial x} +\frac{\partial V_2}{\partial y}+\frac{\partial V_3}{\partial z}=0 $$
[38:39]优点:物体不会产生自交
(4) Laplacian Editing [Sorkine et al. SGP 2004]
优点:
• Laplacian能体现局部细节,因此Laplacian 尽量不变可保证局部细节
• Representation with sparse matrices
• Efficient linear surface reconstruction
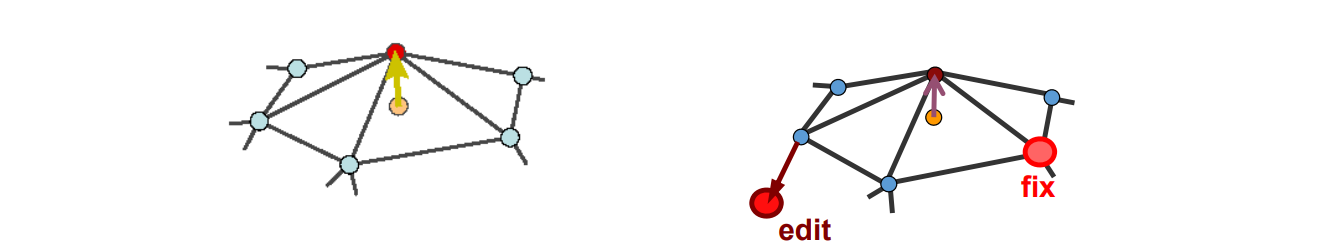
$$ \nu _i=\sum _{j\in N(i)}w_j\nu _j+\delta _i $$
优化目标
- Laplacian Approximation
$$ \tilde{X} =\underset{X}{argmin} \left ( ||LX-\delta ^{(x)}||^2+\sum _{j\in C}\omega ^2||x_j-c_j||^2 \right ) $$
第一项:局部细节不变,第二项:满足用户要求
- Gradient Approximation
$$ \min_\phi \iint _\Omega ||\nabla \phi -W||^2dA, $$
求解线性方程组
$$ LX=\delta\\ x_j=c_j, \quad j\in\left \{ j_1,j_2,\dots,j_k \right \} $$
Results
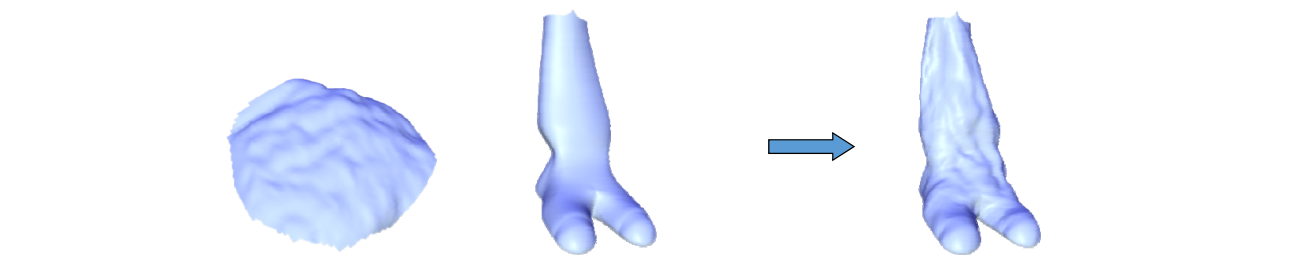
Detail transfer and mixing
这是基于Laplace的point based的一个应用
[40:45] 把一个 mesh 的 Laplacian 细节迁移到另一个 mesh上
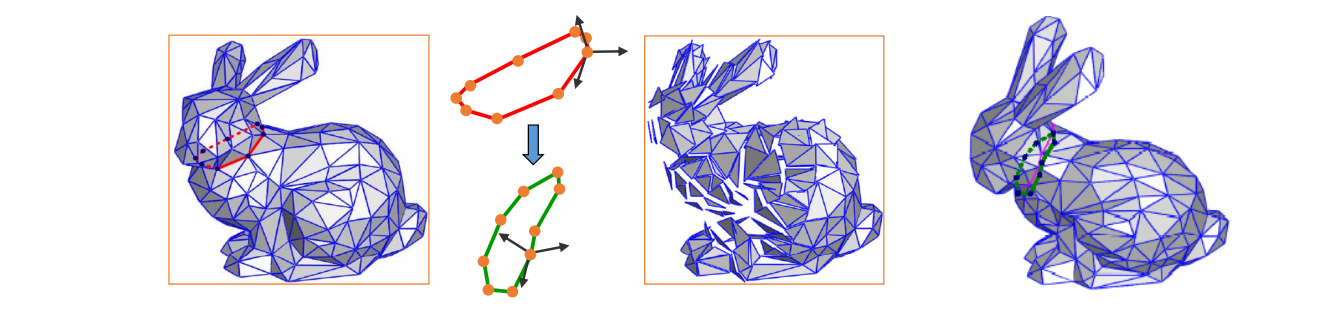
要求网格一一对应
方法:Mixing Laplacians,即Taking weighted average of \(\delta _i\) and \(\delta '_i\)
Mesh transplanting
这是基于Laplace的point based的一个应用
[41:29] 把一个模型拼接到另一个模型上

可能用[0,1]控制Laplace的混合比例,造成渐变效果。
Invariance – solutions
- Explicit transformation of the differential coordinates prior to surface reconstruction
- Lipman, Sorkine, Cohen‐Or, Levin, Rössl and Seidel [SMI 04], “Differential Coordinates for Interactive Mesh Editing”,
- Estimation of rotations from naive reconstruction
- Lipman, Sorkine, Cohen‐Or, Levin, Rössl and Seidel [SMI 04], “Differential Coordinates for Interactive Mesh Editing”,
- Yu, Zhou, Xu, Shi, Bao, Guo and Shum [SIGGRAPH 04], “Mesh Editing With Poisson‐Based Gradient Field Manipulation”,
- Propagation of handle transformation to the rest of the ROI using geodesic distances
- Zayer, Rössl, Karni and Seidel [EG 05], “Harmonic Guidance for Surface Deformation”,
- Propagation of handle transformation to the rest of the ROI using harmonic functions
(5) Poisson Mesh Editing
Yu et al. Mesh Editing With Poisson-Based Gradient Field Manipulation. Siggraph 2004.
这个方法起源于一种图片算法,把图像一部分融合到另外一个图像.让边界无缝融合,用目标的颜色结合源的梯度。
把这个方法用到3D图形上,源的梯度就演变为源的Laplace。
• The representation: the gradients of the functions X, Y, Z on each triangle of the mesh
• Deformation: propagate the transformation of the handle onto the ROI using geodesic distances
• Inspiration: Poisson Image Editing [Pérez et al. 03]

• Reconstruct a function from its gradients via the Poisson equation:
$$ \underset{f}{\arg \min } \underset{\Omega}{\int}||\nabla f-\mathbf{w}||^{2}, \quad s.t. \quad f\left |_{\partial \Omega }= f^* \right | _{\partial \Omega} $$
$$ \Downarrow $$
$$ \Delta f=\operatorname{div} \mathbf{w} \quad with \left.\quad f \right|_{\partial \Omega}=\left.f^{*}\right| _{\partial \Omega} $$
(6)(7) As‐rigid‐as‐possible Deformation
方法起源于一种2D图形算法:
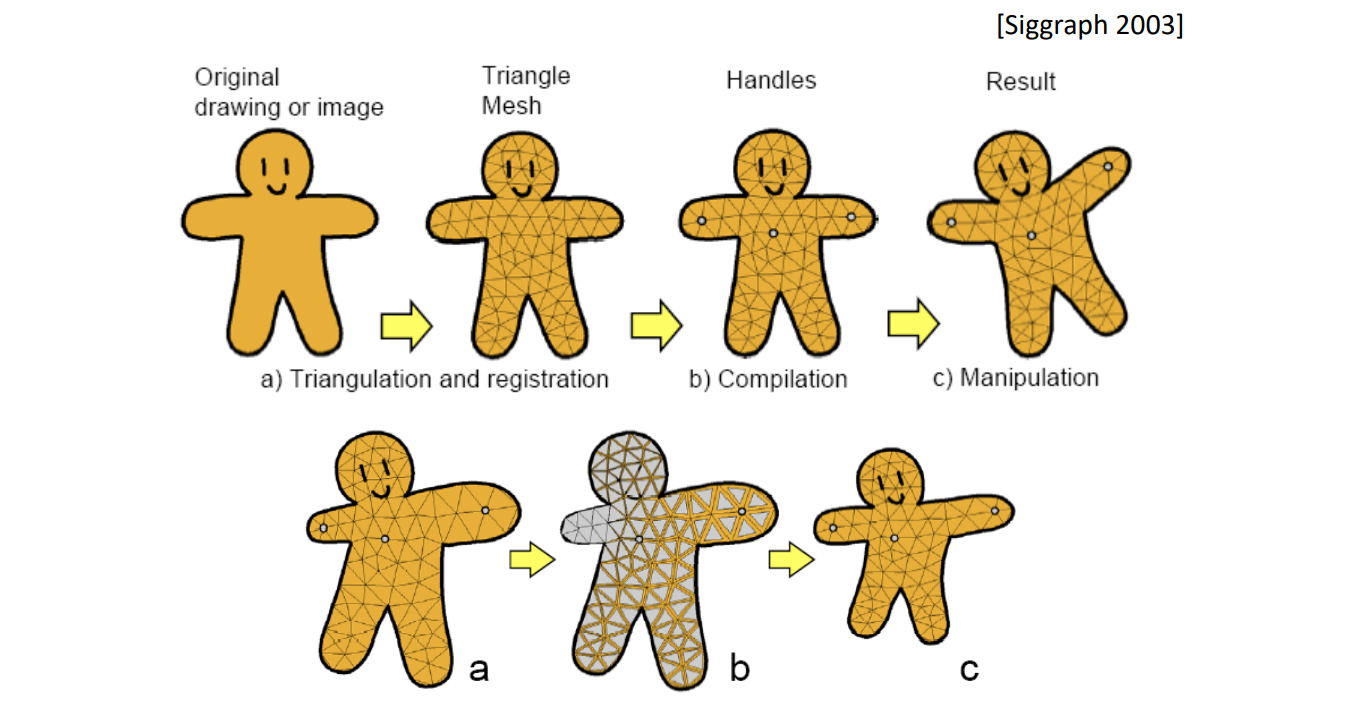
把三角形当作刚体来形变。然后再缝合。
后引申到3D:
[Sorkine and Alexa, As‐Rigid‐As‐Possible Surface Modeling. SGP 2007]
Ask all star edges to transform rigidly by some rotation R, then the shape of the cell is preserved
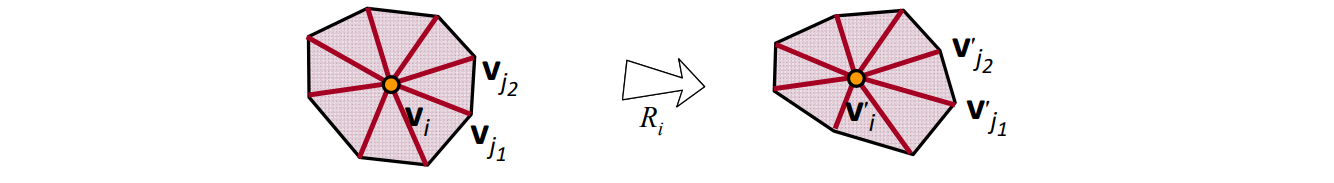
$$ \min_{\mathbf{v}^{\prime}}\sum_{i=1}^{n} \sum _{j\in N(i)}||({\mathbf{v}}^{\prime}_i-{\mathbf{v}}^{\prime}_j)-R_i({\mathbf{v}}_i-{\mathbf{v}}_j)||^2 $$
$$ s.t.\mathbf{v}^{\prime}_j=\mathbf{c} _j,j\in C $$
效果:
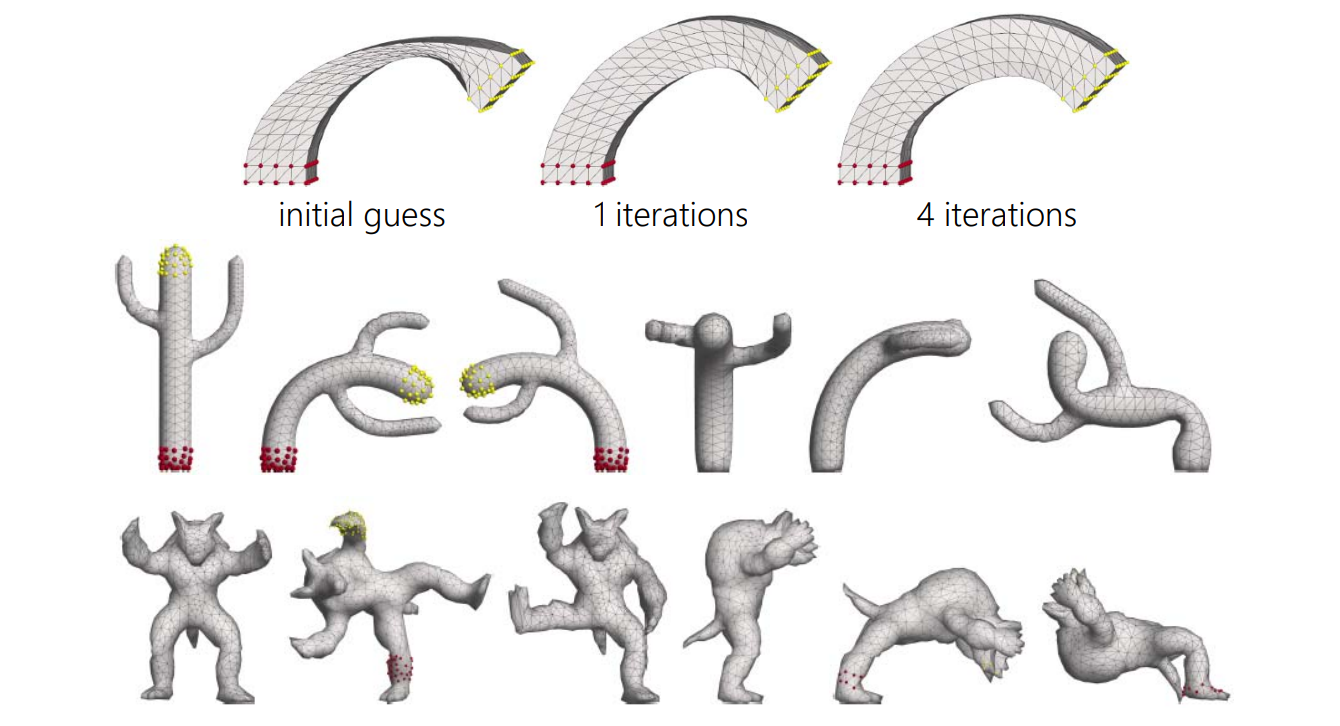
deformation 时保持 Laplacian 旋转
优点:中间会膨胀
(8) Linear Rotation‐invariant Coordinates
[Lipman et al. Siggraph 05]
保持曲面的第一形和第二形. 没听懂
• Keep a local frame at each vertex
• Prescribe changes to some selected frames
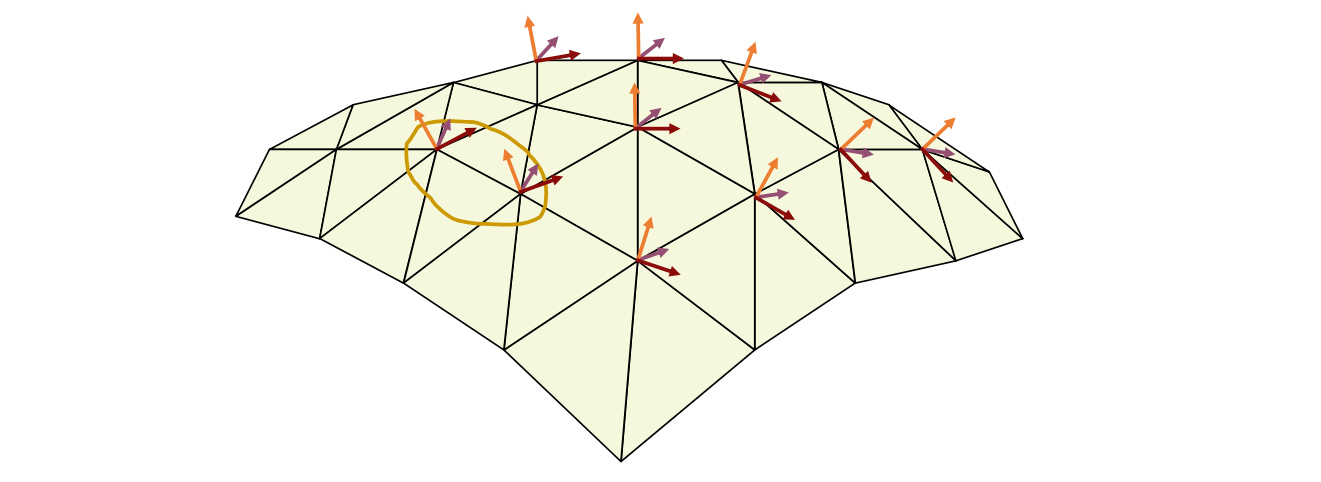
Local frame:
{\(\mathbf{a}_i, \mathbf{b}_i, \mathbf{n}_i\)}
• Encode the differences between adjacent frames
• Solve for the new frames in least‐squares sense
$$ \begin{array}{l} {\mathbf{a}_i}-{\mathbf{a}_j}=\alpha_1 {\mathbf{a}_i}+\alpha_2 {\mathbf{b}_i}+\alpha_3 {\mathbf{n}_i}\\ {\mathbf{b}_i}-{\mathbf{b}_j}=\beta _1 {\mathbf{a}_i}+\beta _2 {\mathbf{b}_i}+\beta _3 {\mathbf{n}_i} \\ {\mathbf{n}_i}-{\mathbf{n}_j}=\gamma _1 {\mathbf{a}_i}+\gamma _2 {\mathbf{b}_i}+\gamma _3 {\mathbf{n}_i} \end{array}\\ \cdots \cdots \\ constraints $$

- Reconstruction:
• After having the frames, solve for positions Frame‐based deformations
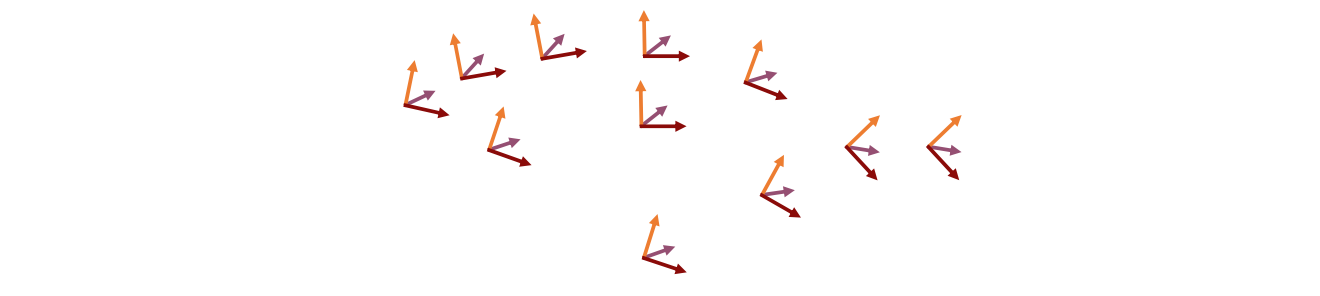
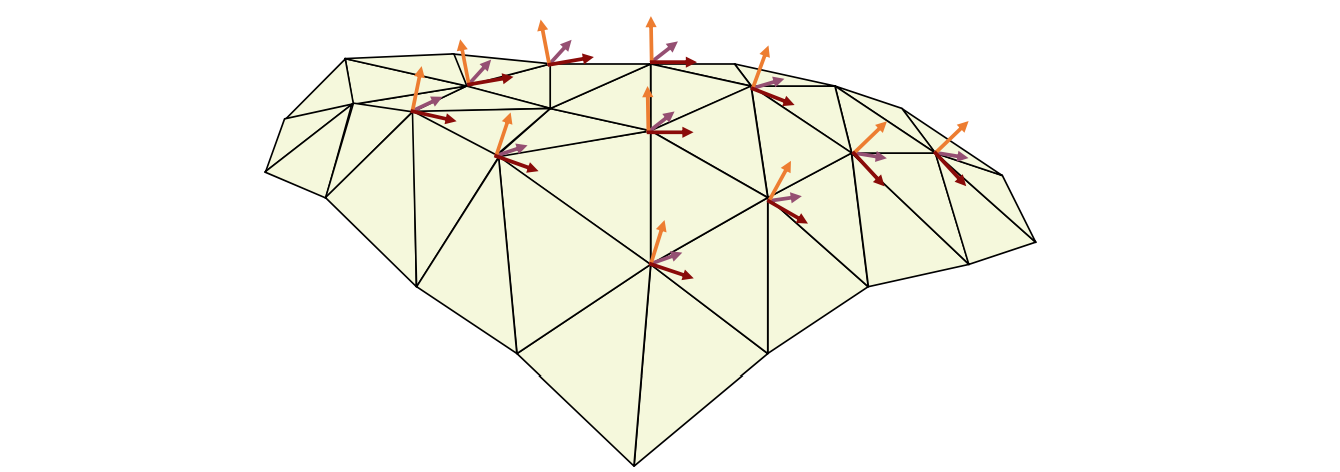
Results
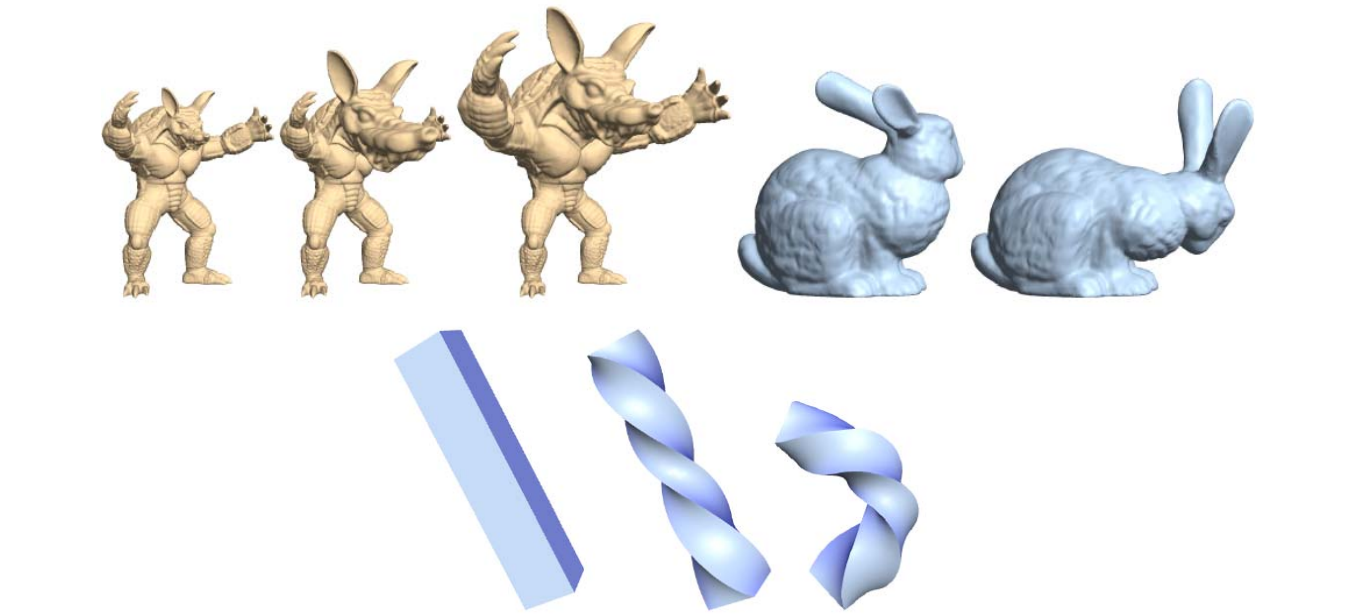
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/