回顾
\(R^3\)中的参数曲面:link
参数化(Parameterization):link
参数化的重要性:link
参数化期望保持的几何性质
• 保角映射(angle‐preserving):conformal(共形)
• 保面积映射(area‐preserving):authalic
• 等距映射(isometric):conformal + authalic
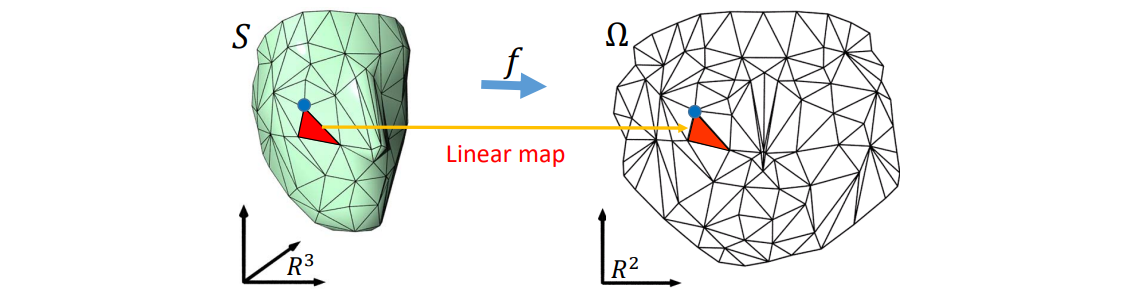
👆 \(f\) is approximated by piecewise linear maps between pairs of triangles
参数化引起的扭曲
Low distortion
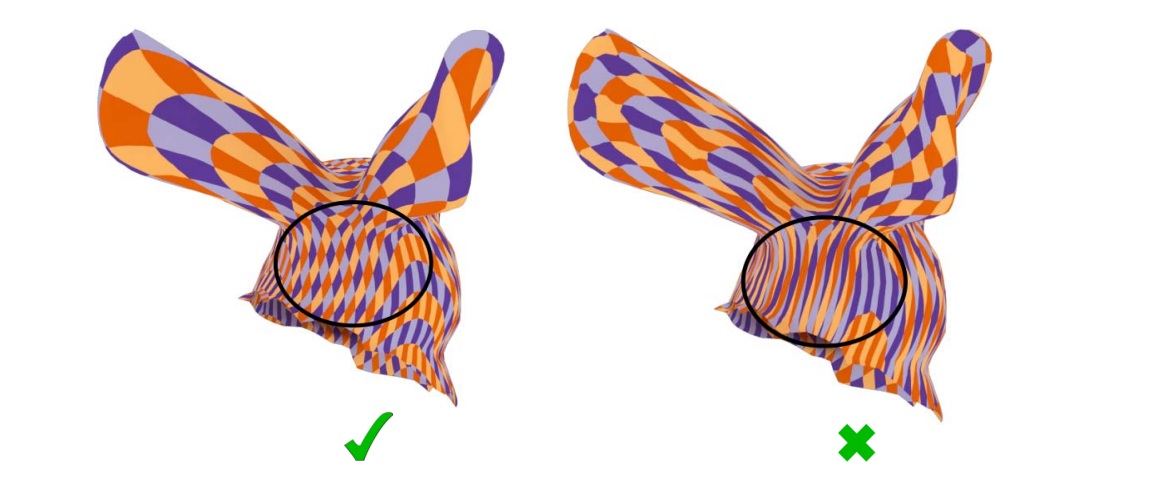

扭曲来源
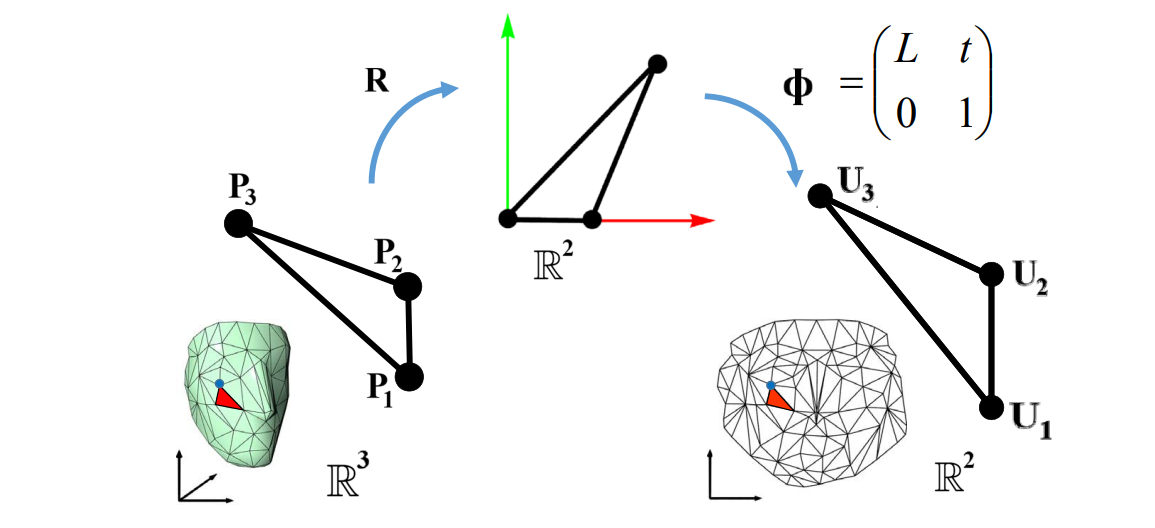
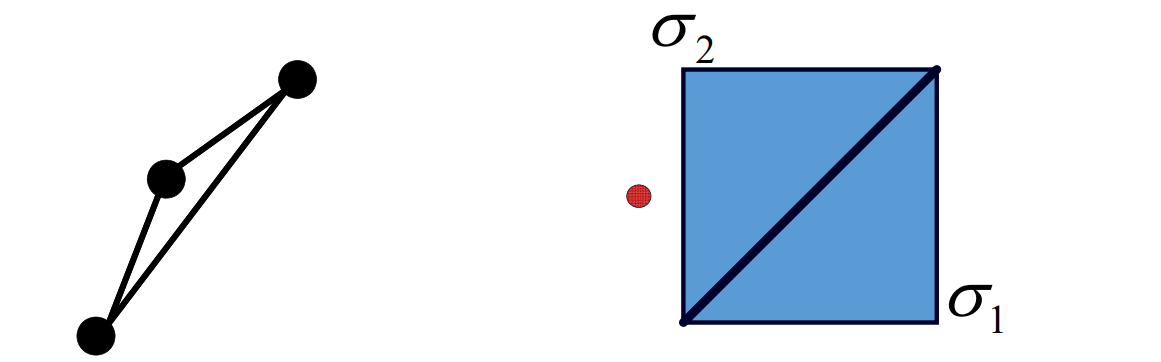
R 把3D三角形旋转为平面三角形。
\(\phi \)是两个平面三角形之间的变形。扭曲都来自\(\phi \)
\(\phi 是奇异矩阵,因此2D是3×3.扭曲都来自L(2×2)\)
线性变换都可以用transformation matrix表示,都可以通过矩阵的性质来分析变换特点
扭曲度量
$$ L=U\begin{pmatrix}\sigma_1 & 0 \\0 &\sigma _2 \end{pmatrix}V^* $$
$$ \sigma _2\ge \sigma _1 $$
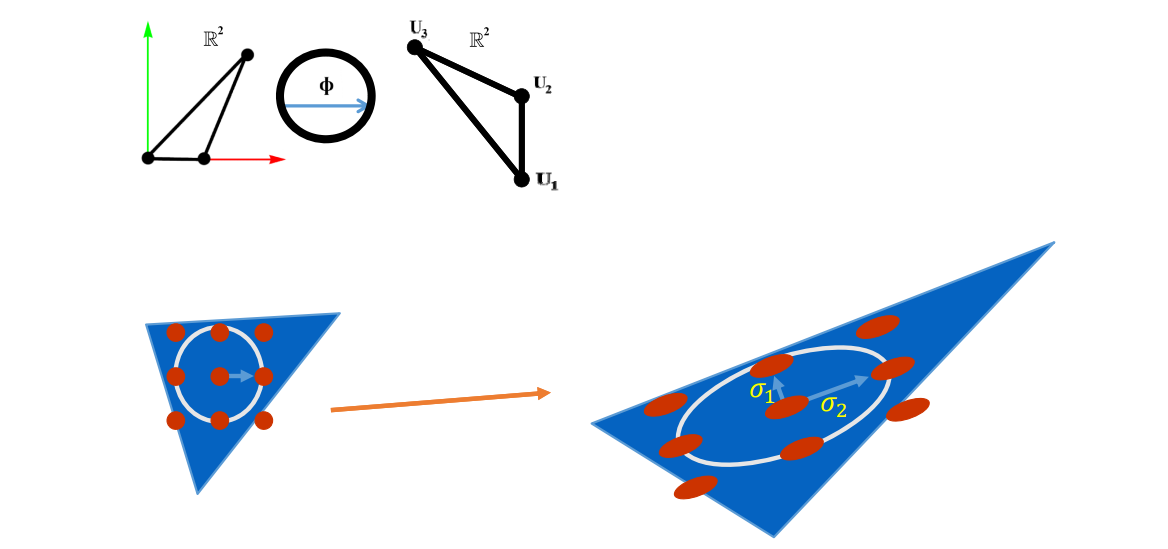
\(L 是 2×2, 做SVD, \sigma_{1}和\sigma_{2}\)是奇异值。
• angle‐preserving (conformal) \(\sigma _1=\sigma _2\)
• area‐preserving (authalic) \(\sigma _1\sigma _2\)
• length‐preserving (isometric) \(\sigma _1=\sigma _2=1\)
Local Injectivity
Flip free triangles
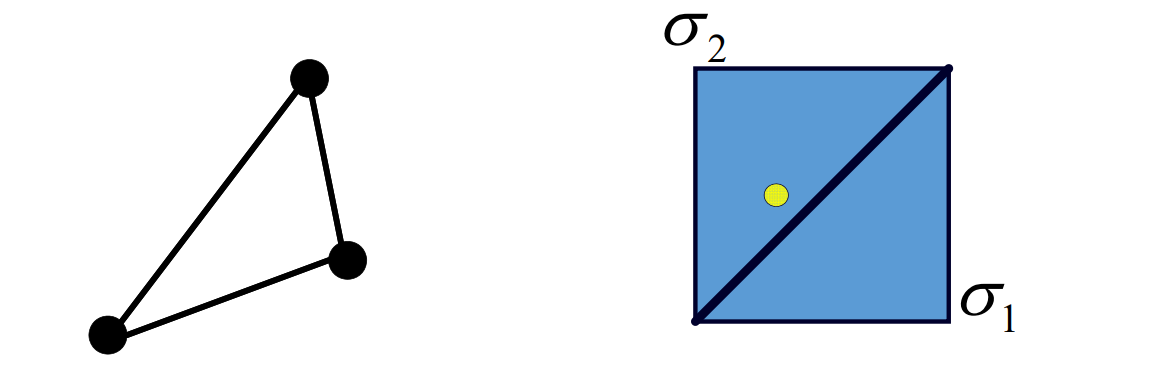
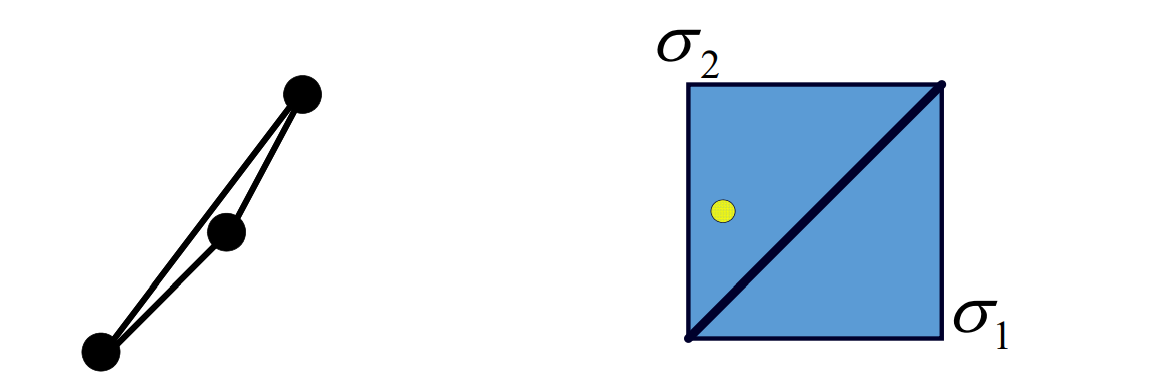
翻转度量
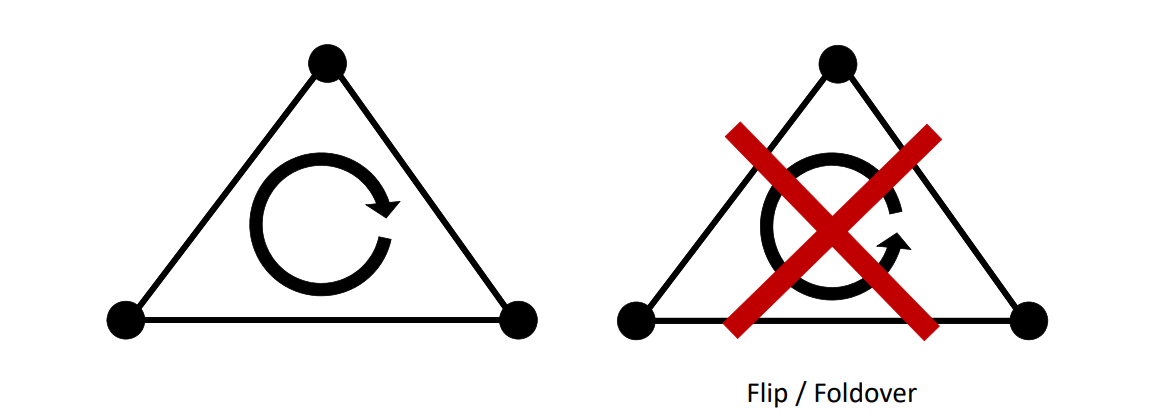
翻转\(\sigma_{1}\cdot \sigma_{2}<0 \)
Distortion (Flip/Foldover)
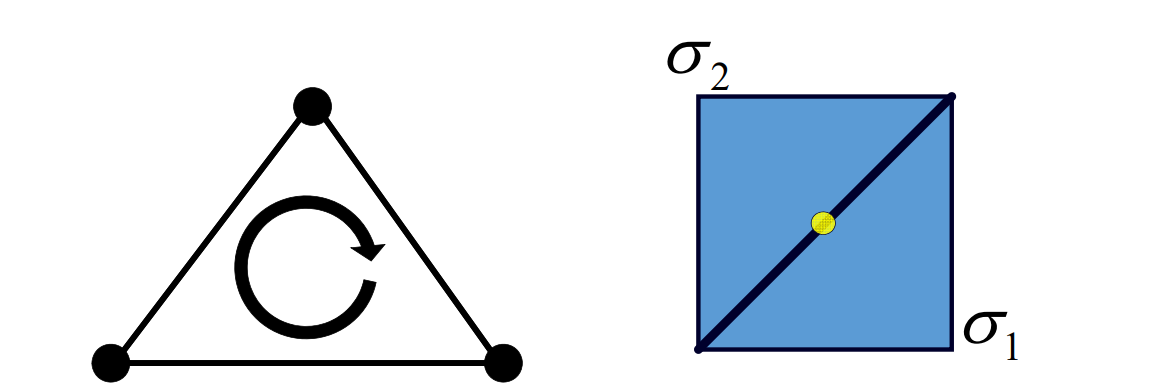 |  |
 |  |
Methods of Mesh Parameterization
Tutte’s method and its variants
Tutte’s embedding method
Tutte’s method [Tutte 1963; Floater 1997, 2003]
外部点:映射到 convex boundary 上。
内部点:1 邻域点的线性组合,权自己定义。通过求解稀疏方程组确定点的位置。
优点:简单、不翻转。
缺点:扭曲大。
Variants of Tutte’s embedding method
Geometry‐based optimization methods
• Representation based methods [Sheffer and Sturler 2001; Sheffer et al. 2005; Chien et al. 2016b; Fu and Liu 2016]
• ARAP [Sorkine and Alex 2007; Liu et al. 2008]
• Bounded distortion methods [Lipman 2012; Aigerman et al. 2014; Kovalsky et al. 015]
Angle Based Flattening (ABF) & ABF++
[Sheffer and Sturler 2001; Sheffer et al. 2005]
基于角度的展开,把角度当作变量,求解参数化的网格
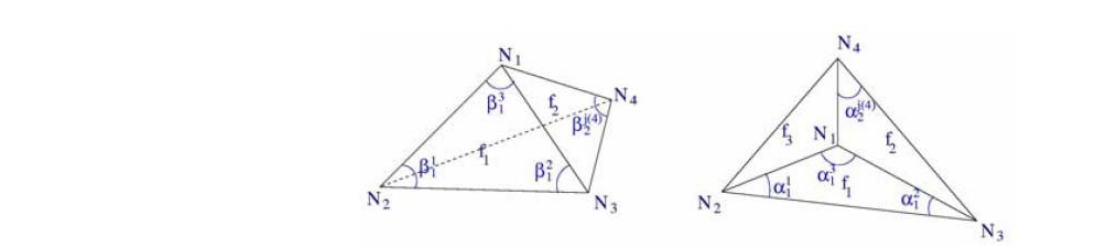
目标:minimize (relative) deviation of angles
$$ F(\alpha )=\sum_{i,j}w_i^j(\alpha _i^j-\beta _i^j)^2 $$
Initial choice for weights:
$$ w_i^j=\beta _i^{j^-2} $$
Constraints:To avoid flipped triangles
$$ g^1(\alpha )\equiv \alpha _i^j\ge \varepsilon $$
$$ g^2(\alpha )\equiv \alpha _i^1+\alpha _i^2+\alpha _i^3=\pi $$
$$ g^3(\alpha )\equiv \sum _k\alpha _i^j(k)=2\pi $$
$$ g^4(\alpha )\equiv \prod _k\sin(\alpha _i^{j(k)-1})-\prod _k\sin(\alpha _i^{j(k)+1})=0 $$
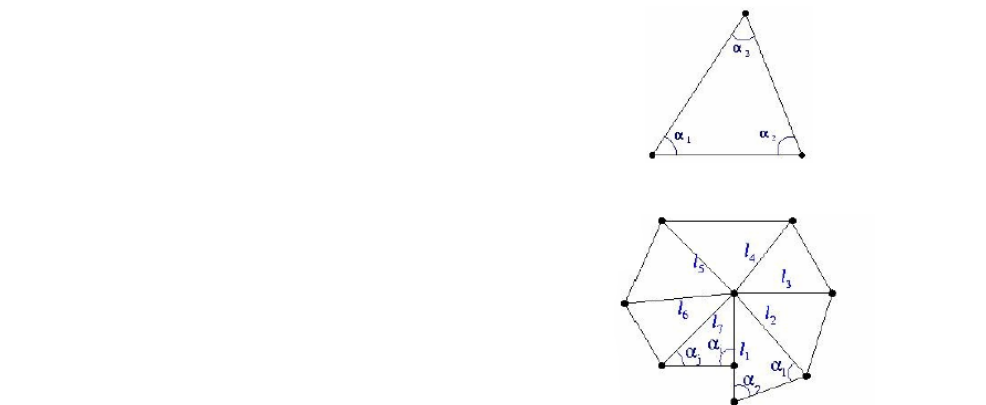
$$ \frac{l_1}{l_2} =\frac{\sin(\alpha _1) }{\sin(\alpha _2) } $$
$$
\frac{l_1}{l_2} \cdots \frac{l_2}{l_1}=\frac{\sin(\alpha _1) }{\sin(\alpha _2) }\cdots \frac{\sin(\alpha _i) }{\sin(\alpha _j) }
$$
求解:用 Lagrange 算法解带约束的优化问题
Simplex Assembly [Fu and Liu 2016]
优化三角形变换的系数
✅Instead of vertex positions, treat the affine transformation as variables
✅Use a barrier function to prevent the inversion
✅No theoretically guaranteed to avoid foldovers
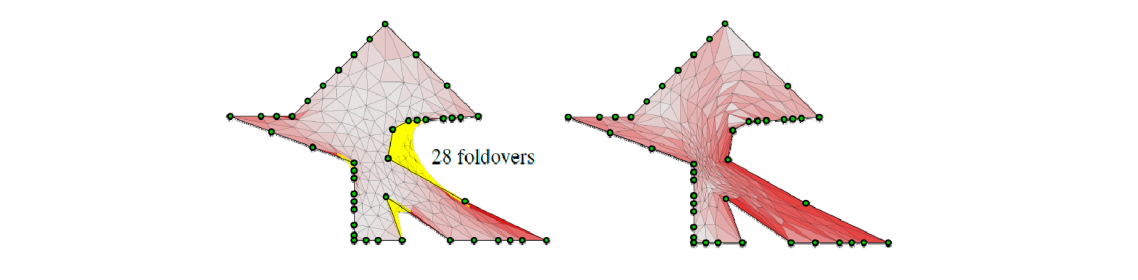
[Fu and Liu. Computing Inversion‐Free Mappings by Simplex Assembly. Siggraph Asia 2016]
Foldover free guaranteed optimization methods
[Smith and Schaefer 2015; Kovalsky et al. 2016; Jiang et al. 2017; Claici et al. 2017; Rabinovich et al. 2017; Shtengel et al. 2017; Zhu et al. 2018]
以 Tuttle 算法为基础,调整边界点位置,减少扭曲
Flip‐free parameterization methods
- Start with a flip‐free (valid) initialization
- Reducing the distortion while guaranteeing the validity
• Generally non‐convex nonlinear optimization
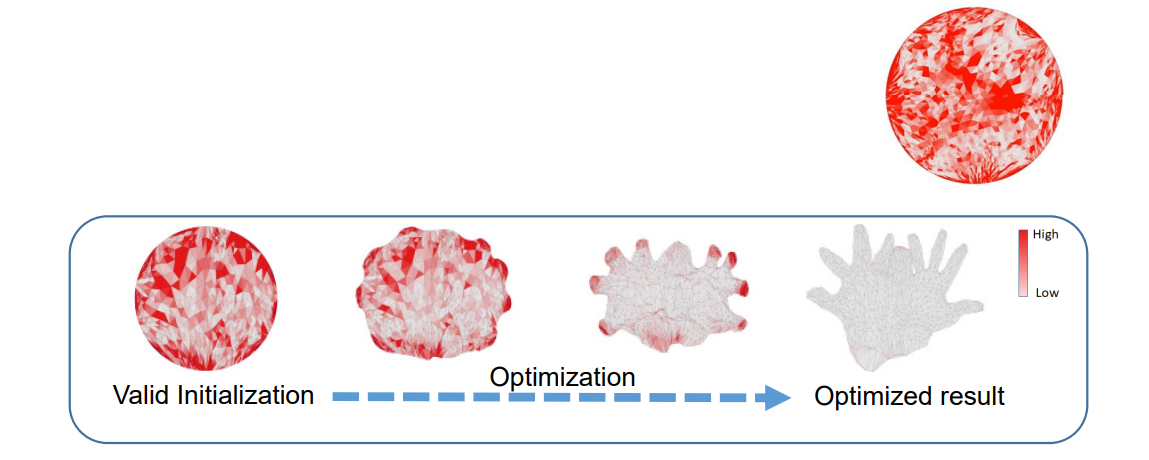

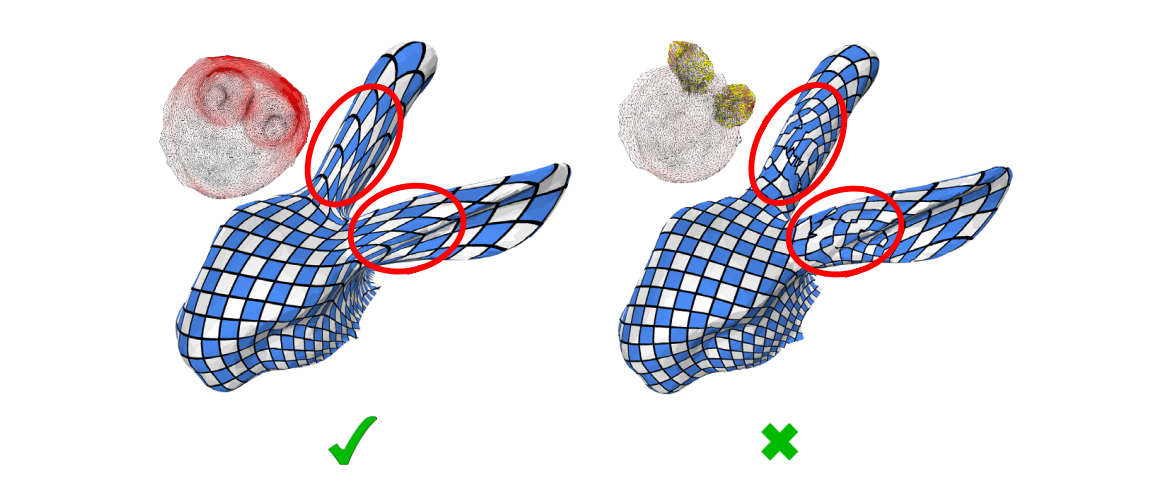
红色表示扭曲大,白色表示扭曲少
调整的同时移动顶点,减少扭曲,关键是如何度量扭曲
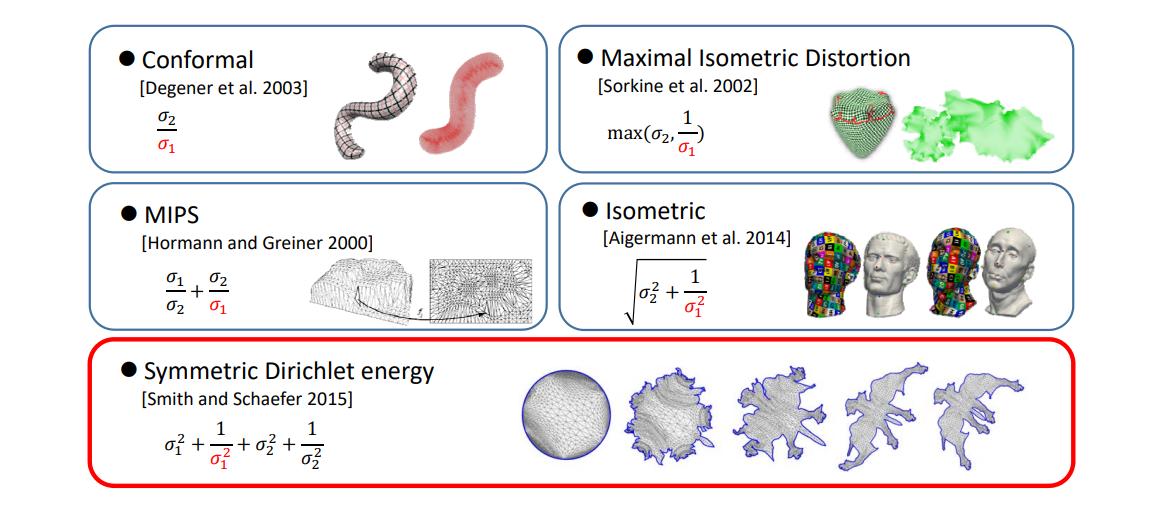
度量扭曲的方法[22:43](最后一个最常用)
目标:
$$ \min_{V} E(V)=\sum _{t\in T}(\sigma _1^2+\frac{1}{\sigma _1^2} +\sigma _2^2+\frac{1}{\sigma _2^2}) $$
s.t \(\sigma _1\sigma _2>0,\) \(\forall t\)
• The cost function is highly nonlinear and nonconvex
• The constraints are nonlinear
• The Heissian matrix is highly non‐definite
Computationally expensive for large scale meshes!
求解:
Input: a valid parameterization initialization \(𝑥_0\)
Repeat
\(p=-H^{-1}\nabla E(x)\)
How to find a good decent direction?
\(𝛼_{max}\)← injective maximal search step
\(𝛼\) ←line search by backtracking from \(𝛼_{max}\)
\(x ← 𝒙 + 𝛼p\)
Until converged
Output: a locally injective parameterization
局限性:非线性、非凸问题、且参数多
因此优化效率低
More
❗ 后面没展开讲的方法,就不记了,没讲清楚,记了也没用
AQP:利用离散 Laplacian 作为 Hessian 的近似
SLIM: \(\dots ,加权 \dots \)
AKVF:\(\dots 向量场算子\dots\)
CM:使用隐式 Laplacian 矩阵,二阶方法、速度更快
各种方法都是找更好的H近似,使得优化过程更快更稳定。
- Accelerated Quadratic Proxy (AQP)
Kovalsky et al. Accelerated Quadratic Proxy for eometric Optimization. Siggraph 2016.
- Scalable Locally Injective Mappings (SLIM)
Rabinovich et al. Scalable Locally Injective Mappings. Siggraph 2017.
- Isometry‐Aware Preconditioning (AKVF)
Claici et al. Isometry‐Aware Preconditioning for Mesh Parameterization. SGP 2017.
- Composite Majorization (CM)
Shtengel et al. Geometric Optimization via Composite Majorization. Siggraph 2017.
- Blended Cured Quasi‐Newton (BCQN)
Zhu et al. Blended Cured quasi‐Newton for Distortion Optimization. Siggraph 2018.
Progressive Paramerization
• Near‐degenerate triangles (i.e., large distortion) in the initializations by Tutte’s method
• Small iterative step and slow convergence in existing methods
• Key: even one extremely large distortion term can restrict the line search step size!

[Ligang Liu et al. Progressive Parameterizations. Siggraph 2018]
问题描述:
[图28:52]以脖子为边界。头挤在中间,中间扭曲很大⇒能量大⇒下降慢
解决方法:
[图29:29] 不优化整体,或寻找更好的H逼近,而是中间那区域
*个人感觉不 make sense *
[图30:35]
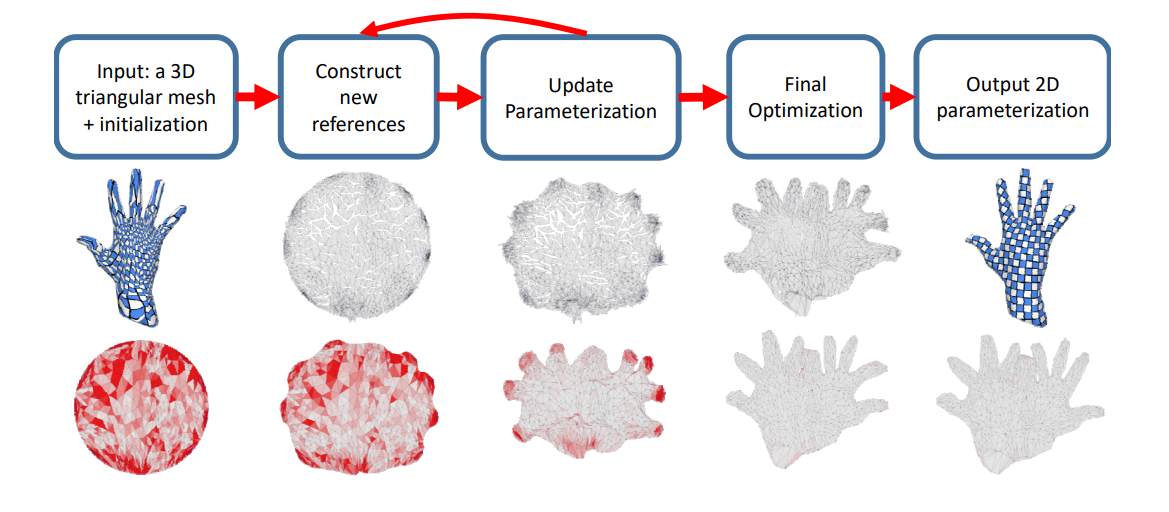
[Ligang Liu et al. Progressive Parameterizations. Siggraph 2018]
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/