2. 2D Texture Synthesis
挑战
简单重复的效果不好:
Desirable Properties
• Result looks like the input
• Efficient
• General
• Easy to use
• Extensible
Challenges
• how to capture the essence of texture?
• from repeated to stochastic texture
方法论
- Parametric Techniques
• Compute global statistics in feature space and sample images from texture ensemble directly - Non‐parametric Techniques
• Estimate local conditional probability density function and synthesize pixels incrementally
Parametric Techniques
• Hypothesize a mathematical model for texture representation
• Match model parameters of input and output texture
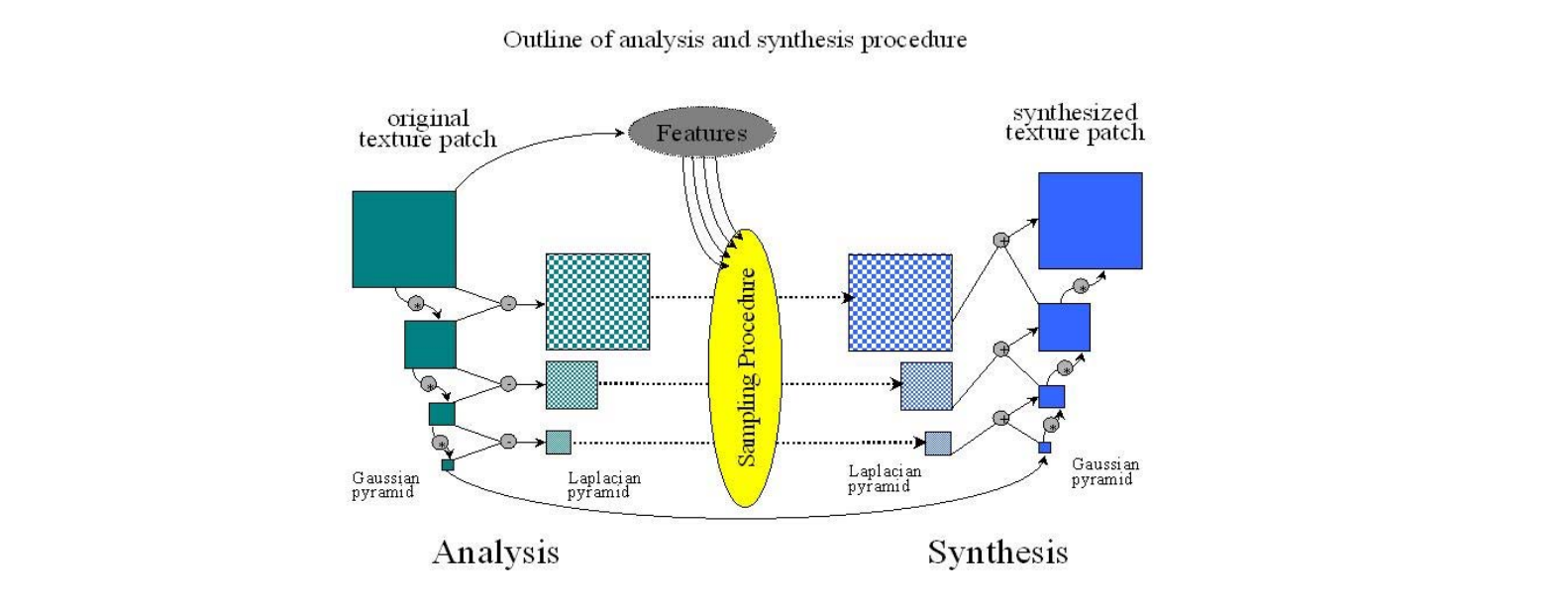
对每个分辨率,用一个函数提取它的feature,再还原出原始纹理
有点像VAE
Pyramid‐Based Texture Analysis/Synthesis
[Heeger & Bergen, Siggraph 1995]
• Initialize J to noise
• Create multiresolution pyramids for I and J
• Match the histograms of J’s pyramid levels with I’s pyramid levels
• Loop until convergence
• Can be generalized to 3D
| Good Case | Bad Case |
|---|---|
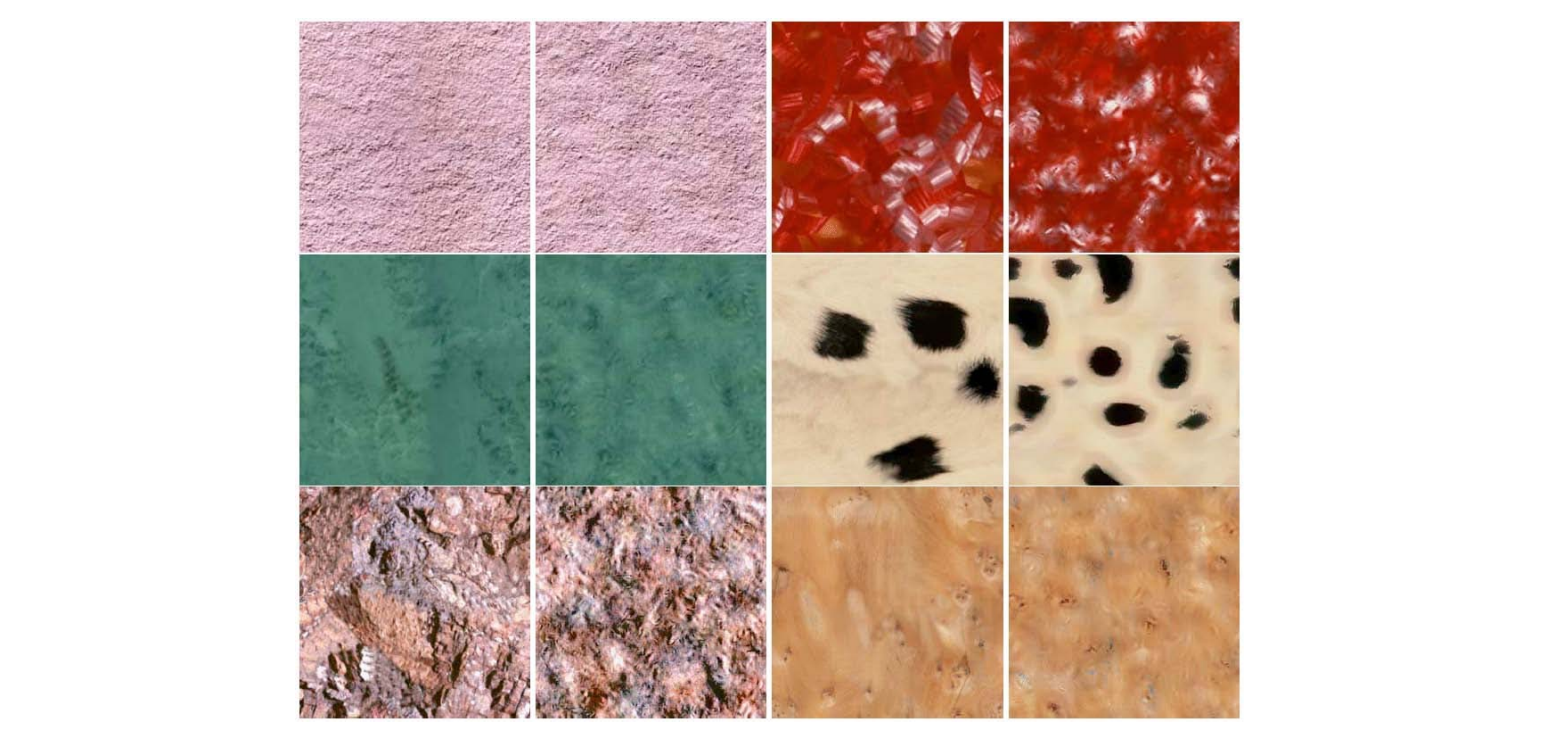 | 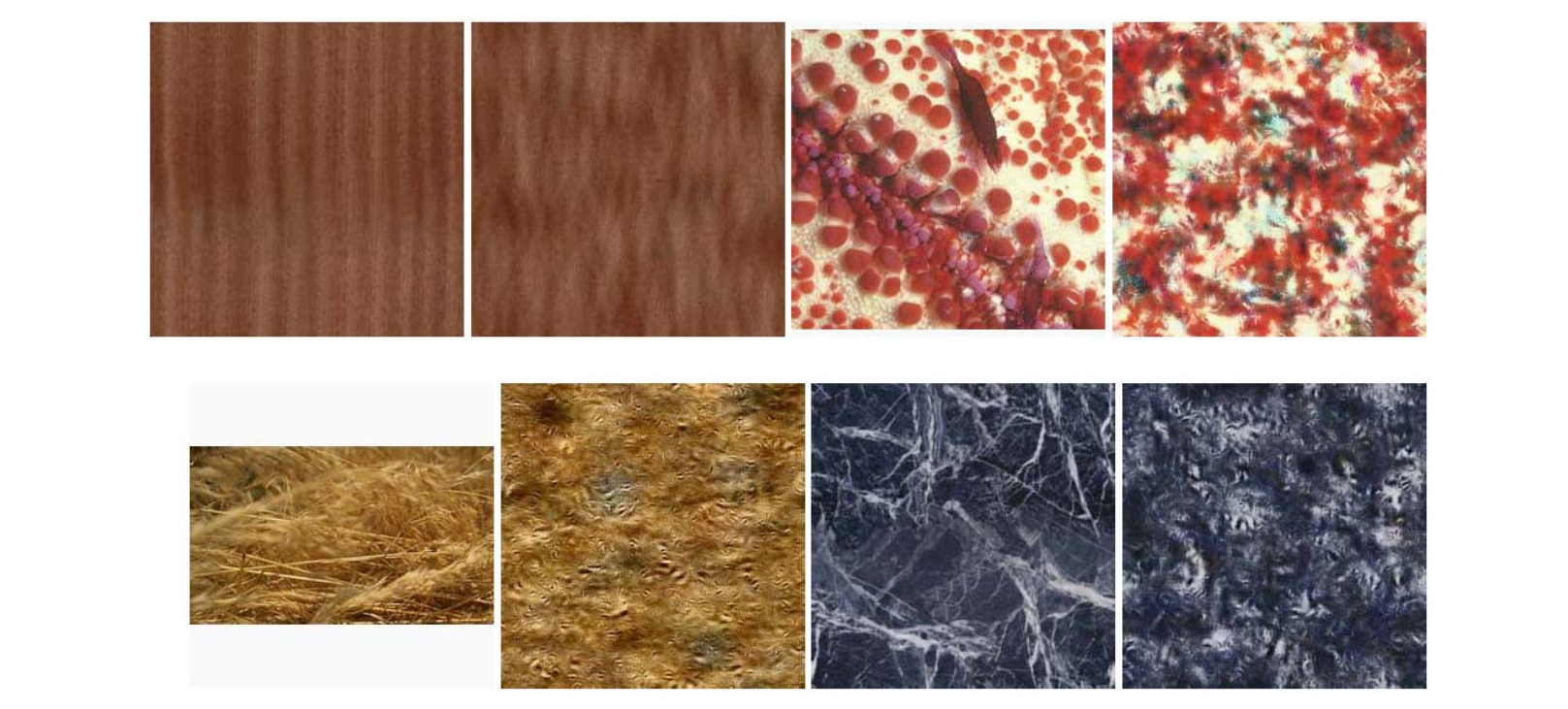 |
只体现了分布,没有体现特征
Non‐Parametric Techniques
- Synthesis by copying from the input
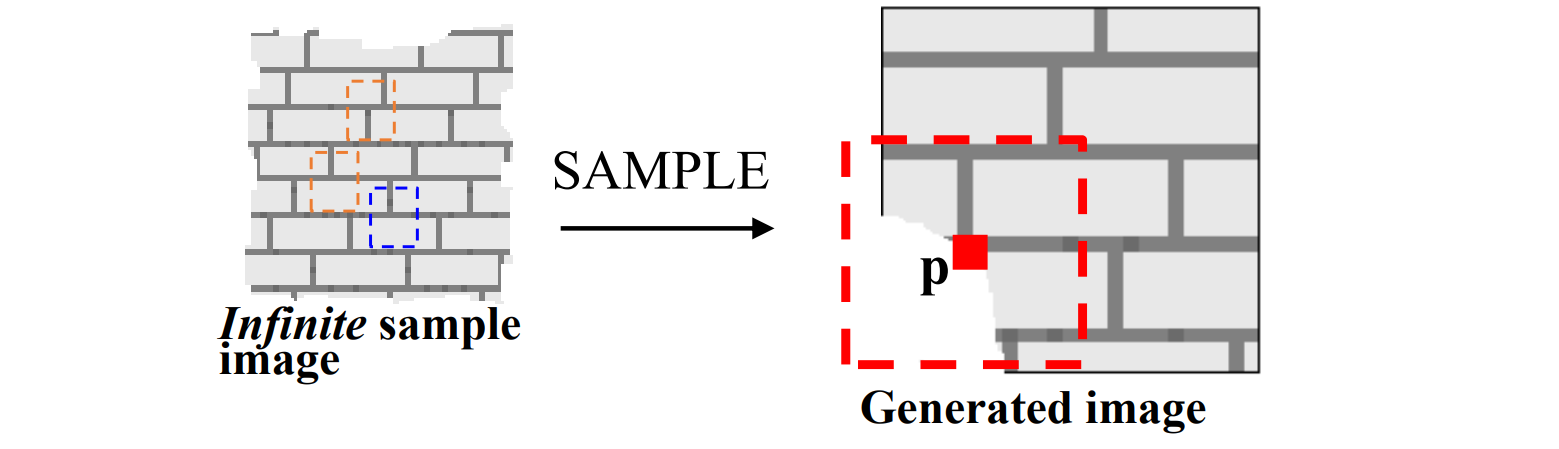
- Markov‐Random Field Model
• Pixel appearance depends only on neighborhood
🔎 Markov Random Field
Synthesizing One Pixel
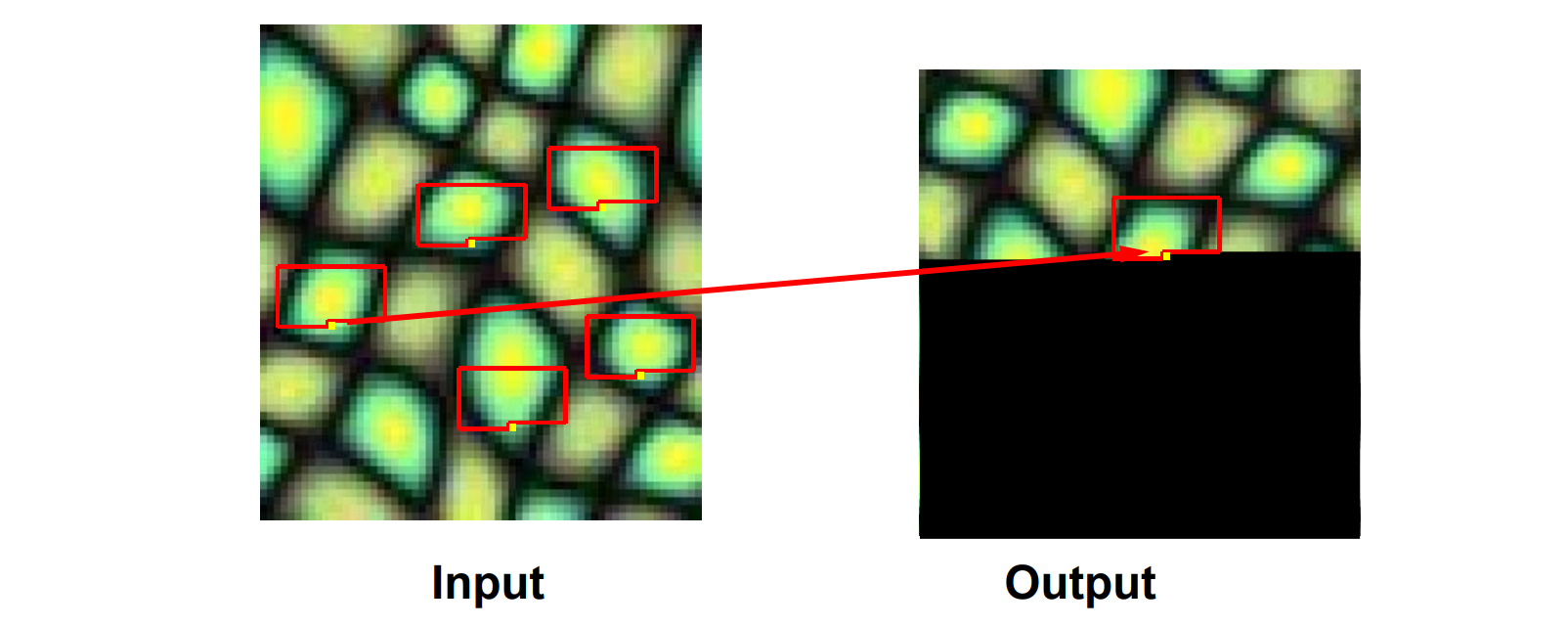
• Assuming Markov property, what is conditional probability distribution of p, given the neighbourhood window?
• Instead of constructing a model, let’s directly search the input image for all such neighbourhoods to produce a histogram for p
• To synthesize p, just pick one match at random
例子:
👆 Select Best Neighborhood from all Candidates
Randomness Parameter
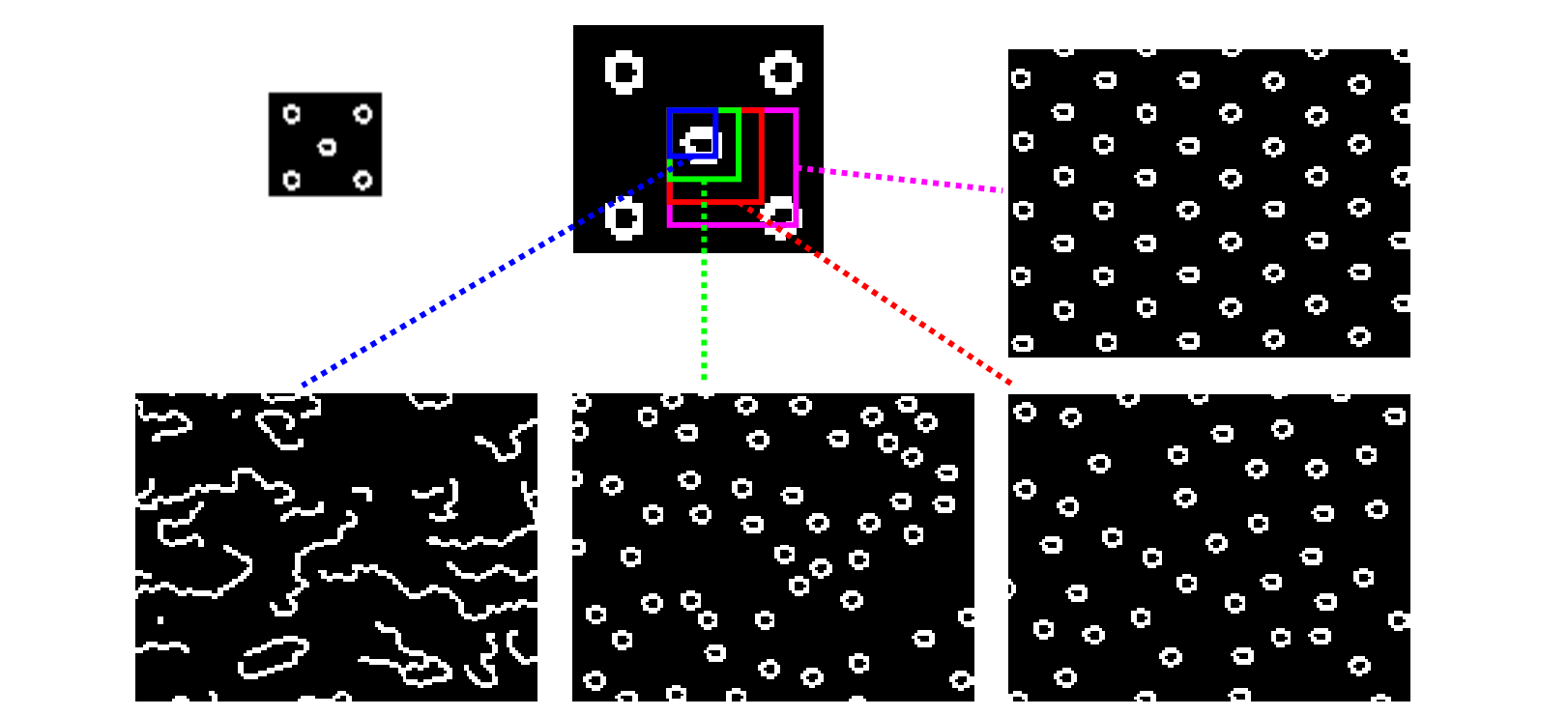
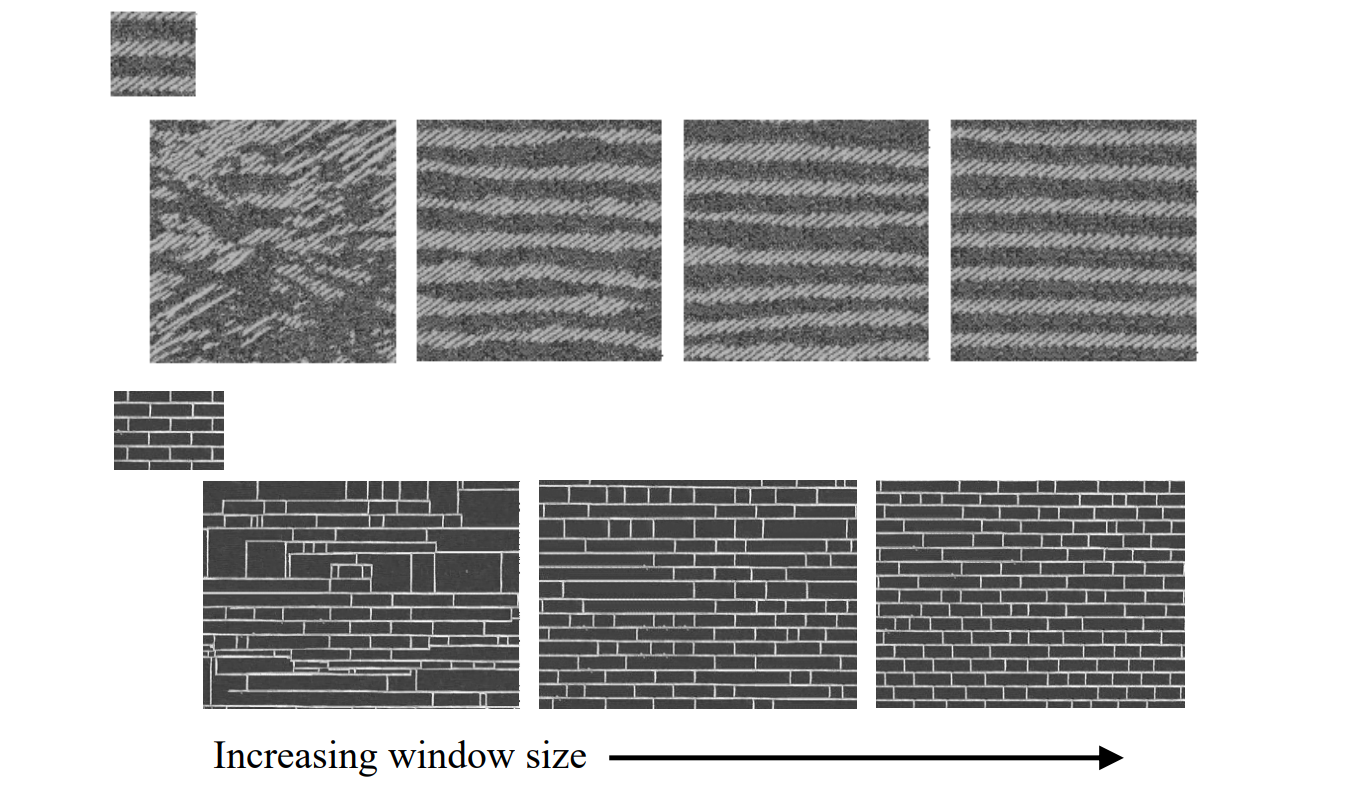
选择不同大小的框,会得到不同的效果
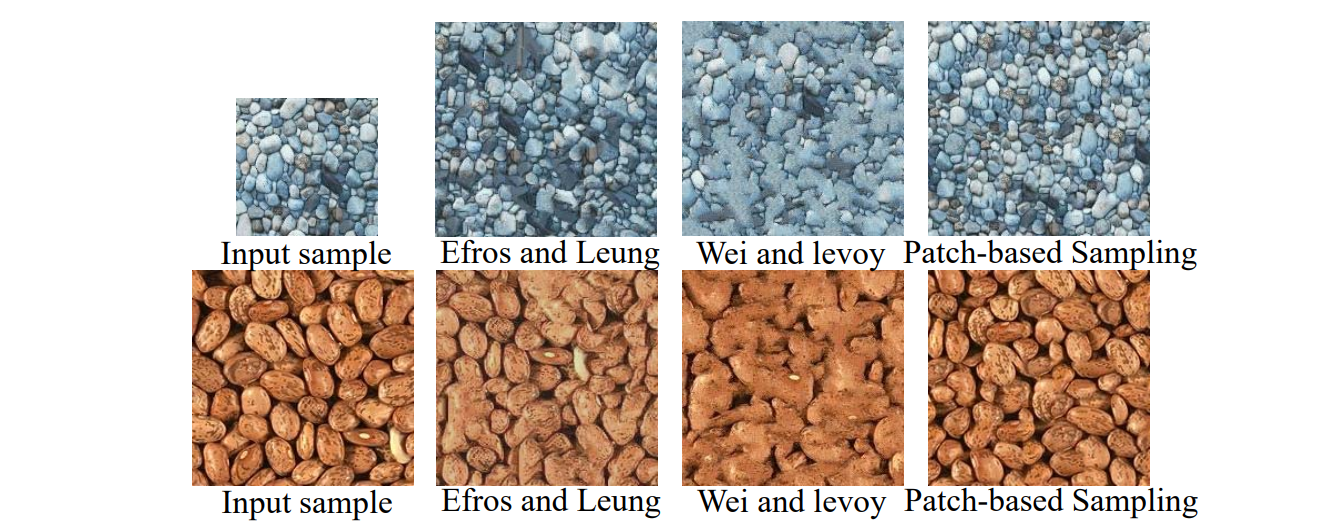
Patch‐based Synthesis
[Liang et al. TOG 2002]
Copy patches instead of single pixels
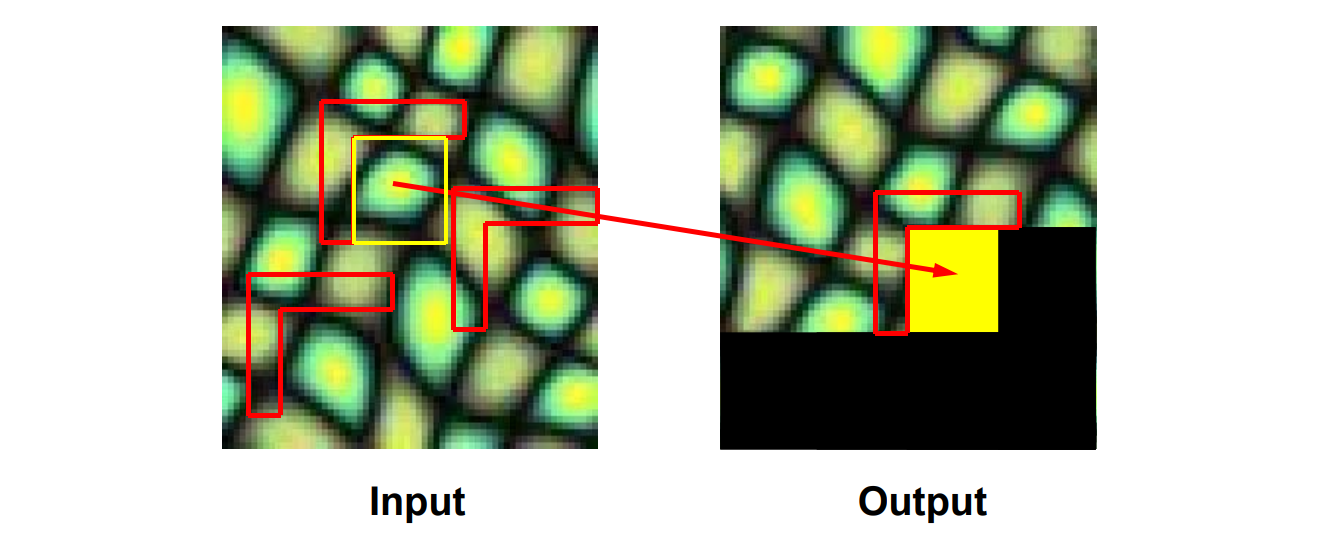
Select Best Neighborhood from all Candidates
Synthesis Result

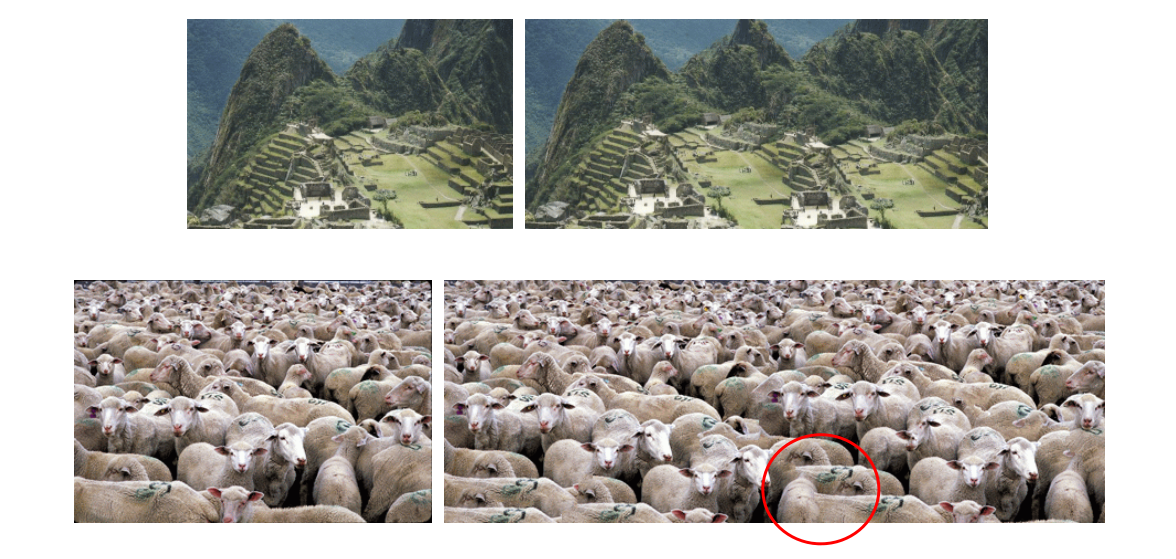
• Efros’ algorithm has a tendency to grow garbage and Wei’s TSVQ acceleration further aggravates this problem. In Contrast, patch‐based sampling avoids growing garbage
优点:
- Speed
• Orders of magnitude faster than existing texture synthesis algorithm
• Real‐time synthesis - Quality
• Synthesize high‐quality textures ranging from regular to stochastic
• Avoid growing garbage
• Synthesize subjectively better natural textures
Mincut: Graph-cut based
[Efros&Freeman, Siggraph 2002]
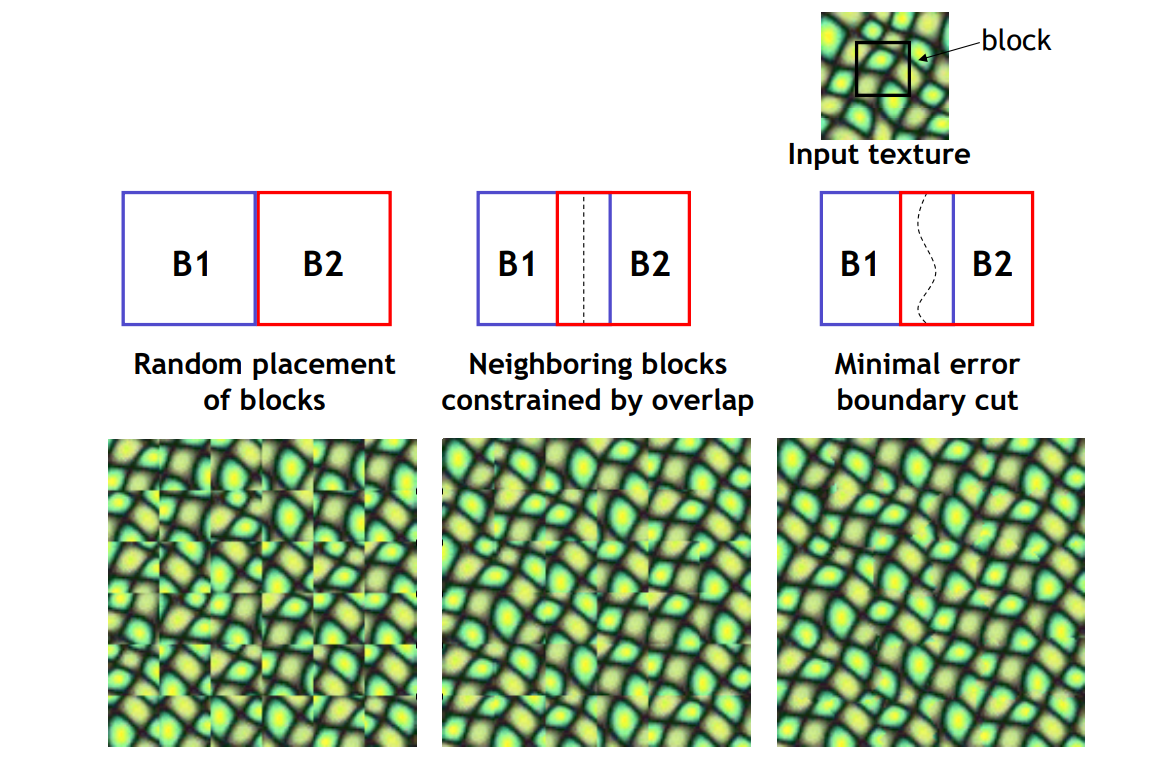
用动态规划减少割缝处的突变
Minimal error boundary
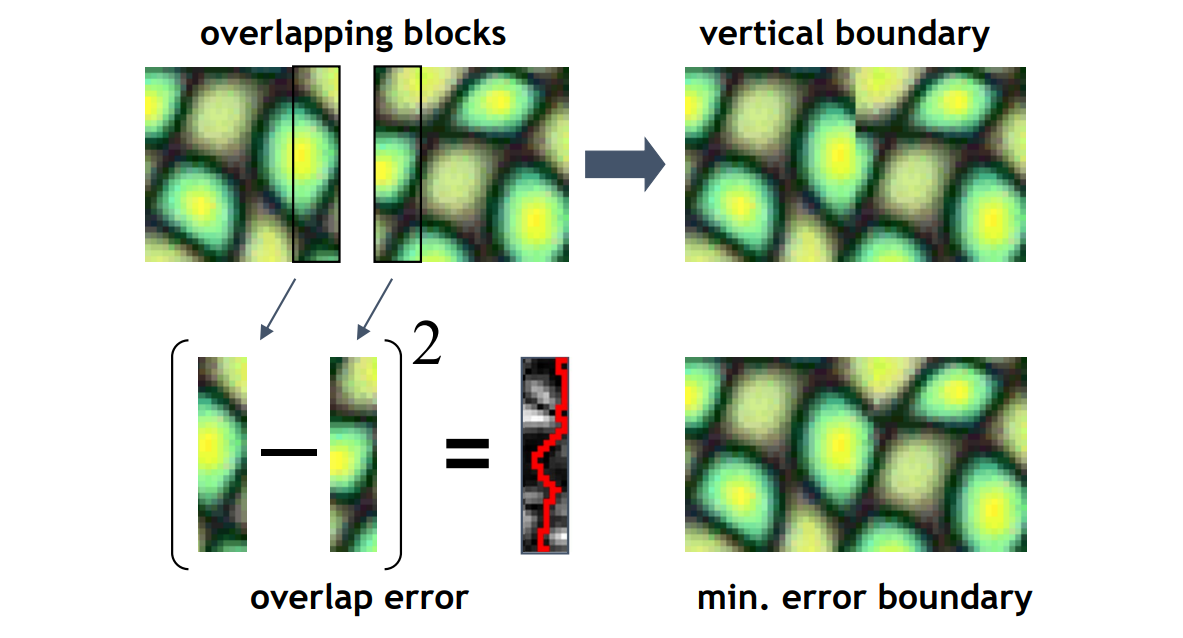
Seam Optimization
最大流最小割问题

Construct graph such that:
Graph Mincut \(\Leftrightarrow\) Best Seam
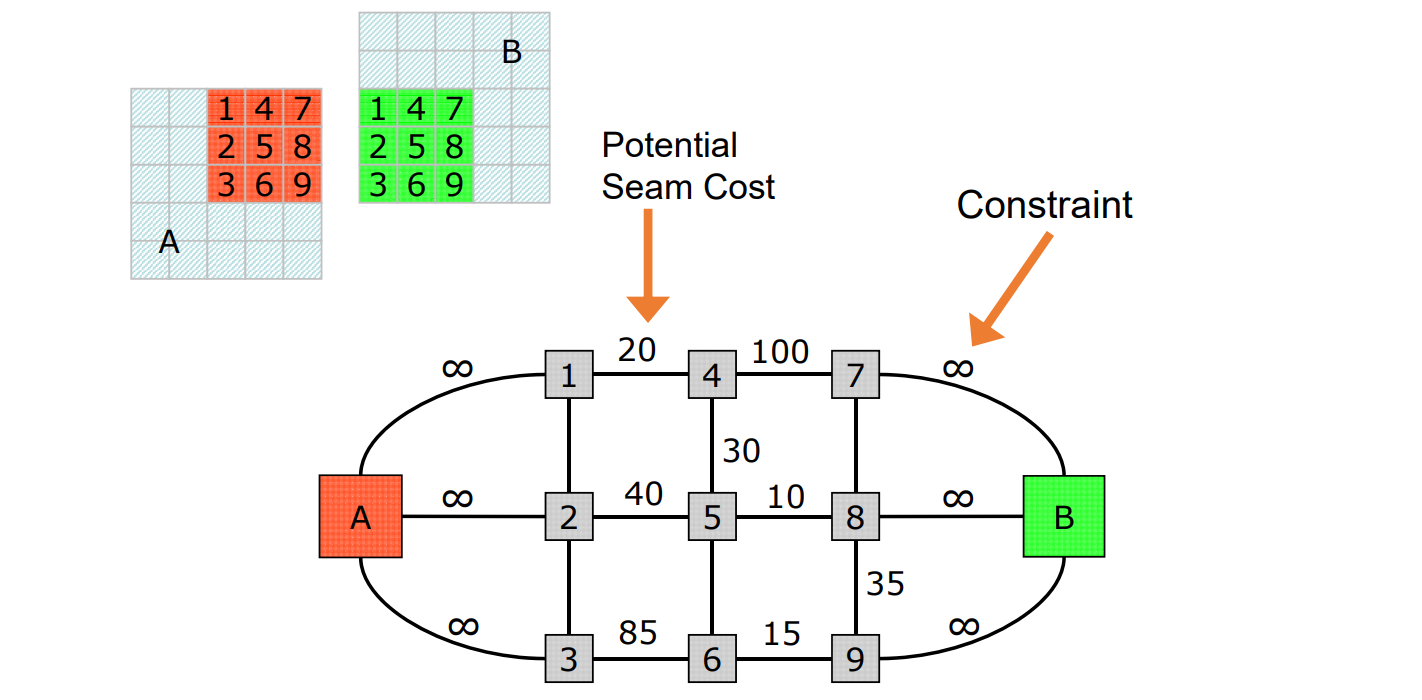
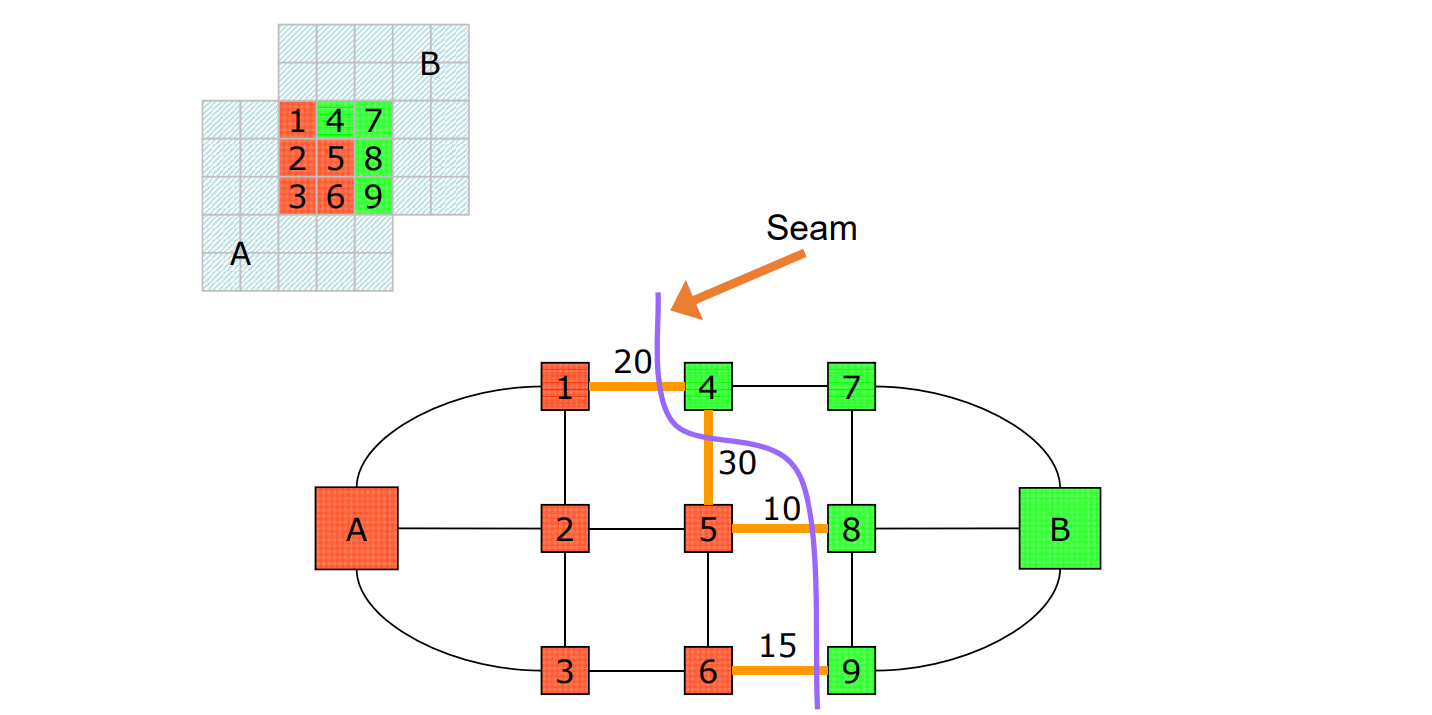
Results: Natural Images

Texton‐based Synthesis
[Zhang et al., Siggraph 2003]
• Texton: texture element / texture pattern
• Texture elements don’t break apart using texton synthesis
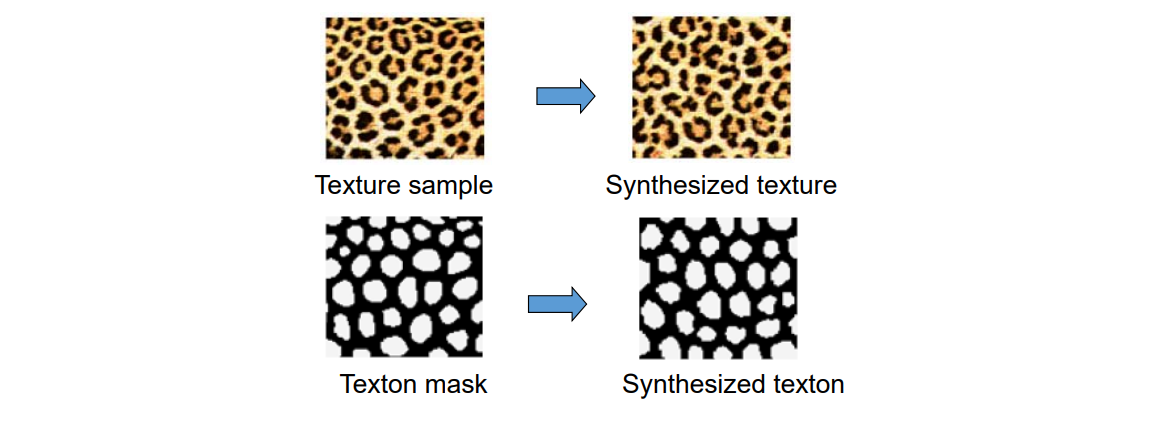
Feature Map + Texture Map
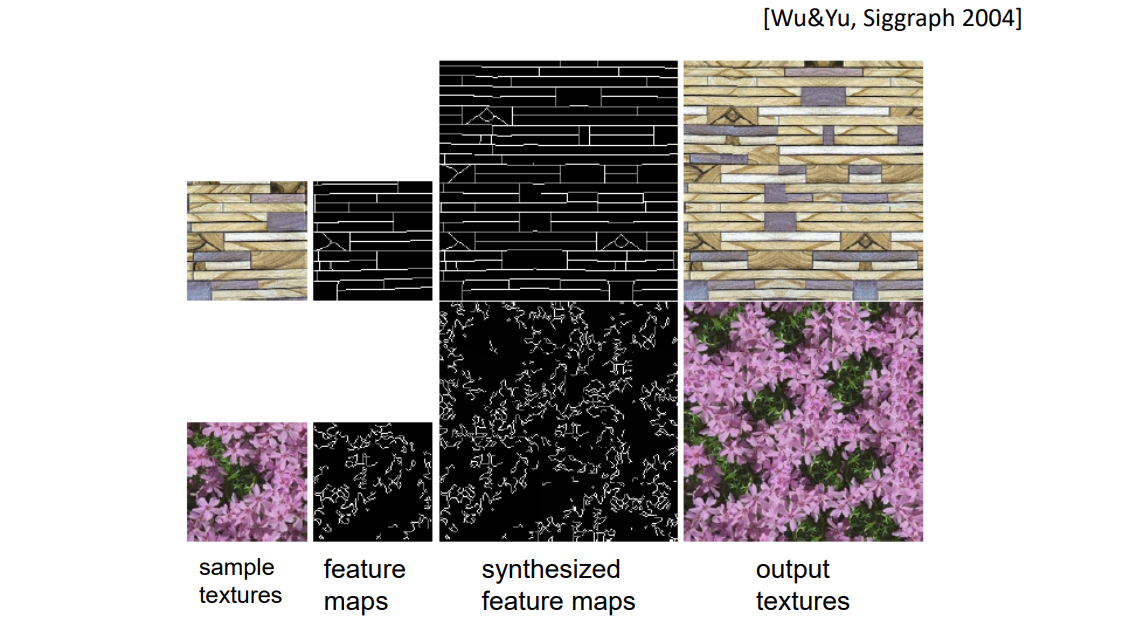
寻求保持纹理的特征
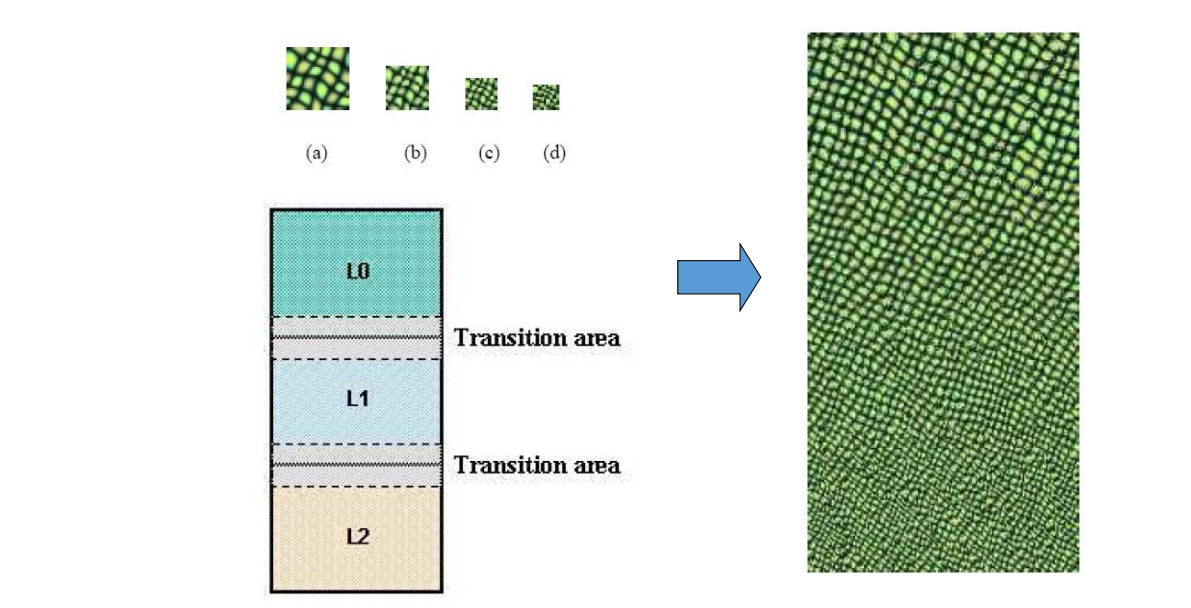
Synthesis with Local Size Control
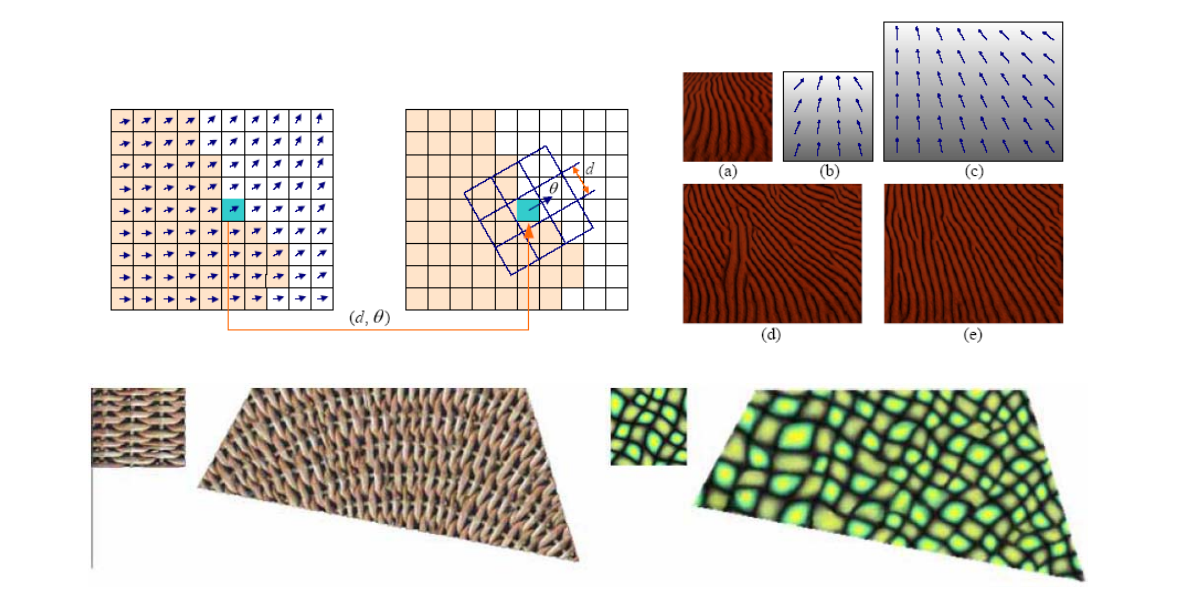
Synthesis with Vector Field Control
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/