4. Reconstruction
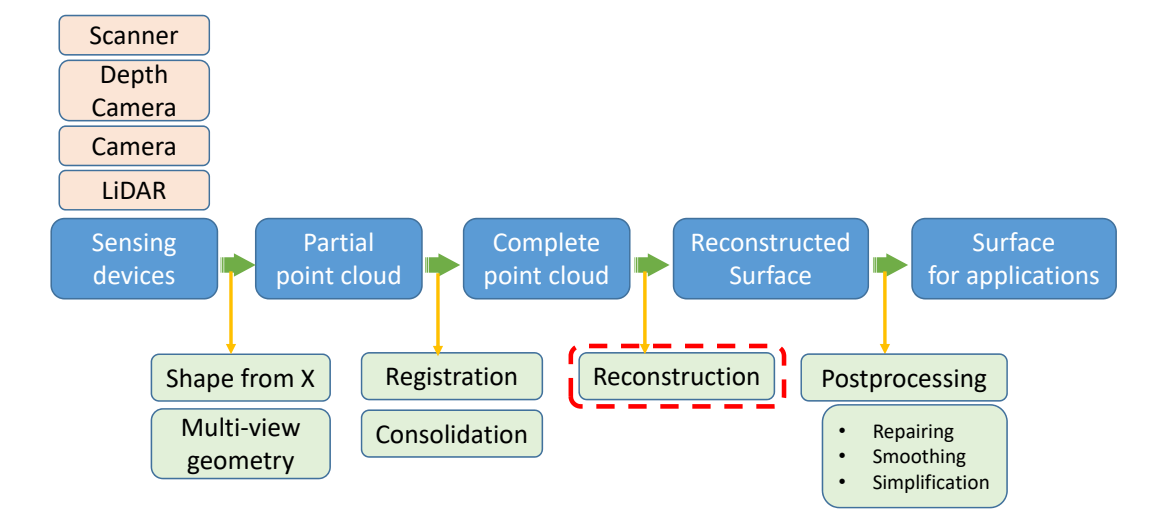
Surface Reconstruction
把3D点重建成连续的或非连续的曲面
- Input: A set of points in 3D that sampled from a model surface
- Output: A 2D manifold mesh surface that closely approximates the surface of the original model
难点:Desirable Properties
- No restriction on topological type
- Representation of range uncertainty
- Utilization of all range data
- Incremental and order independent updating
- Time and space efficiency
- Robustness
- Ability to fill holes in the reconstruction
Solutions
- Approximation methods: Constructing continuous functions (Scattered data interpolation schemes)
- NURBS surfaces
- Signed distances [Hoppe et al. 1992]
- Radial basis function reconstruction [Carr et al. 2001]
- Poisson reconstruction [Kazhdan et al. 2006]
- Discrete methods: Constructing triangle meshes directly
- [Amenta & Bern 1998]
- Power‐crust [Amenda et al. 2001]
- Cocone [Dey & Giesen 2001]
- [Cazals & Giesen 2006]
- …
Approximation methods
NURBS surfaces
[59:30] NURBS 逼近法:用一个函数逼近点云
Implicit Approximation Methods (similar to GAMES 102‐9)
第一步: Convert point cloud into a signed distance field
For every point, add two off‐surface points, one inside and one outside the surface in the direction of the normal
Add a point only if it is closest to its source
N≈3n points
[1:01:26] \(n\)个点产生了\(3n\)个点,分别是(-1,0,1)
第二步:Construct an implicit function whose iso‐surface with iso‐value 0 to approximate the field
构造高维(4D)曲面,使得函数的0整面经过这些点
第三步: Extract the mesh surfaces from the implicit function
Marching cube methods
Complexity
- Storage O(\(N^2\))
- Solving the \(W_i O(N^3)\)
- Evaluating f(x) O(N)
Carr et al. Reconstruction and representation of 3D objects with Radial Basis Functions, SIGGRAPH 2001.
(2) MPU Implicits
根据距离场自适应地剖分,一种自适应版本的Marching Cube
MPU = Multi‐level partition of unity implicits:
- Given: data points with normal
- Computes: hierarchical approximation of the signed distance function
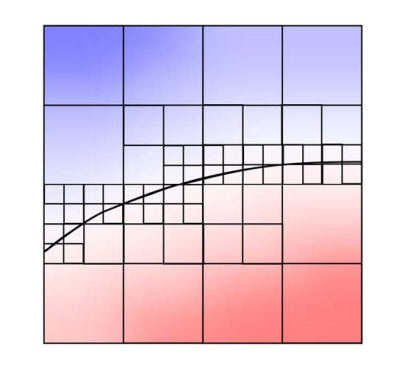
Ohtake et al. Multi‐level Partition of Unity Implicits, SIGGRAPH 2003
(3) Possion reconstruction
Idea: fitting an indicator function
$$ \chi M(x)=\begin{cases} 1 & \text{ } x\in M \\ 0 & \text{ } x\notin M \end{cases} $$
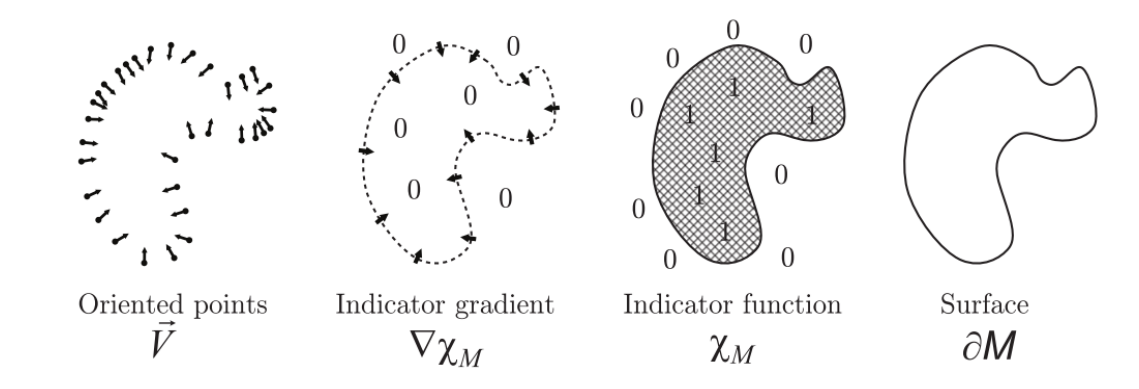
Kazhdan et al. Poisson surface reconstruction. SGP 2006.
隐函数方法对法向非常敏感
不仅逼近函数,还逼近梯度本身
把重建问题变成方程求解隐函数的问题
[1:08:39]隐函数求解后要找到上面的点,用 Marching Cube
(4) Marching Cube
method for approximating surface defined by isovalue \(\alpha\), given by grid data
- Input:
- Grid data (set of 2D images)
- Threshold value (isovalue) \(\alpha\)
- Output:
- Triangulated surface that matches isovalue surface of \(\alpha\)
具体步骤:
- First pass
- Identify voxels which intersect isovalue
- Second pass
- Examine those voxels,For each voxel produce set of triangles,approximate surface inside voxel
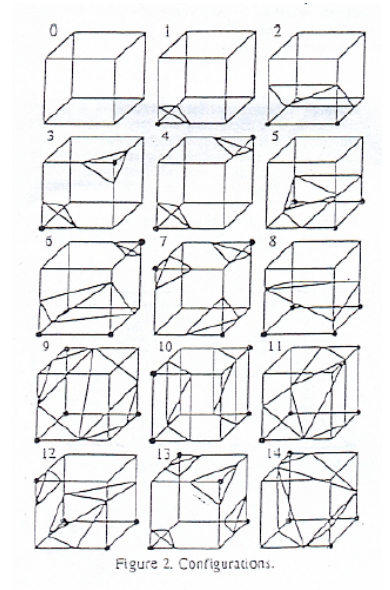
Discrete methods
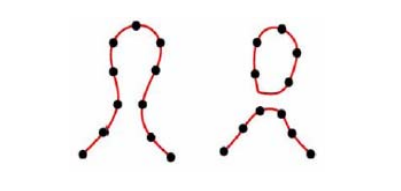
Curve from Points
第一步:Connect the Dots
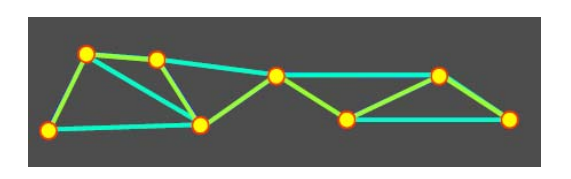
Can be ambiguous
- Use Voronoi Diagram
- Construct Delaunay triangulation
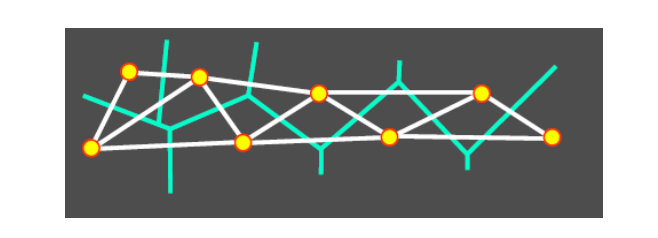
第二步:基于字典学习的曲面重建
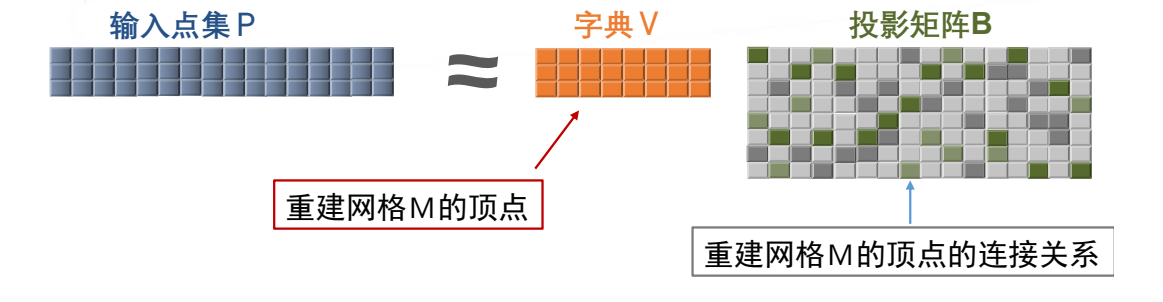
Xiong et al. Robust Surface Reconstruction via Dictionary Learning. Siggraph Asia 2014.
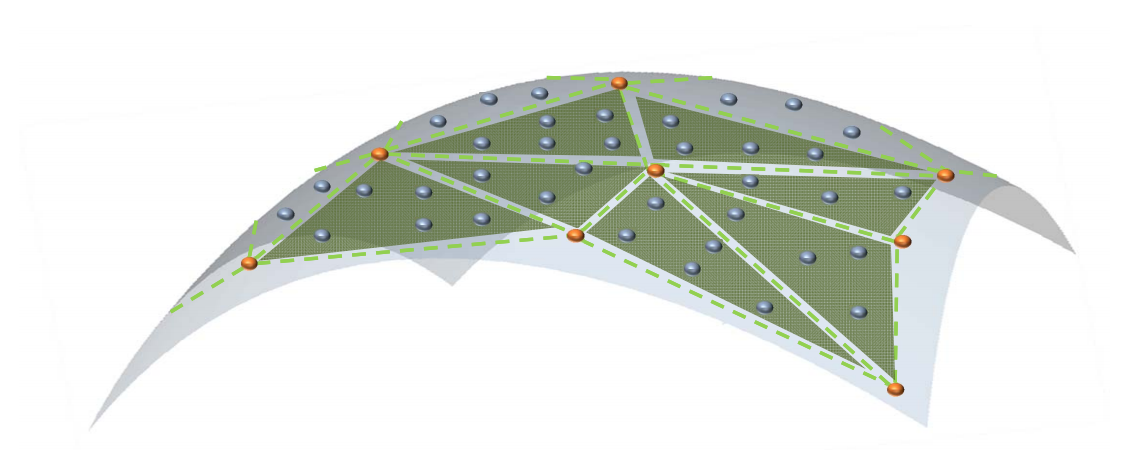
- 输入:三维点集(蓝色点)P
- 输出
- 采样点集(红色点)V
- V构成的三角网格M,使得M逼近P
问题
- 误差度量:如何度量点集P与网格M之间的误差?
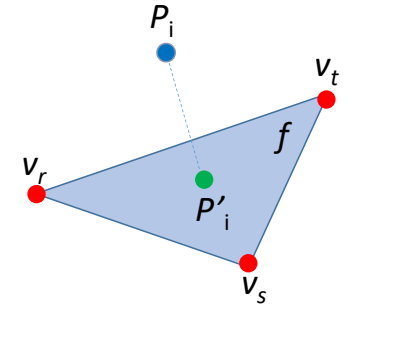
答:某个点到三角形的距离
难点:红点的位置和连接关系未知
度量:蓝点到三角形面片的距离最小
用交替法求解V和B,稀疏优化中的字典学习问题
$$ d(\mathbf{p}_i,f) =|| \mathbf{p}_i-\mathbf{p}_i^{\prime} || $$
$$ \begin{aligned} =\min _{\substack{\alpha+\beta+\gamma=1 \\ \alpha, \beta, \gamma \geq 0}}||\mathbf{p}_i-(\alpha \mathbf{v}_r+\beta \mathbf{v}_s+\gamma \mathbf{v}_t)|| \end{aligned} $$
\({P}' _i=\alpha ^{\ast}V_r+\beta ^{\ast}V_s+\gamma ^{\ast}V_t\)
\((\alpha ^{\ast},\beta ^{\ast},\gamma ^{\ast})\):\({P}' _i\)相对与\(f\)的重心坐标
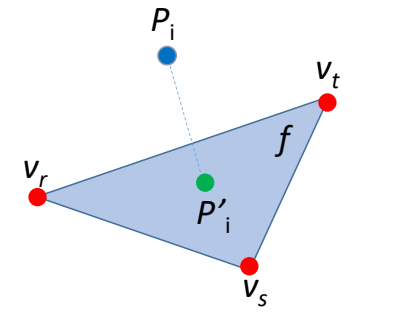
某个点到三角形的距离
$$ d(\mathbf{p}_i,f) =|| \mathbf{p}_i-\mathbf{p}_i^{\prime} || $$
$$ \begin{aligned} =\min _{\substack{\alpha+\beta+\gamma=1 \\ \alpha, \beta, \gamma \geq 0}}||\mathbf{p}_i-(\alpha \mathbf{v}_r+\beta \mathbf{v}_s+\gamma \mathbf{v}_t)|| \end{aligned} $$
\(\mathbf{V}=[\mathbf{V}_1,\mathbf{V}_2,\cdots ,\mathbf{V}_m] \in \mathbb{R }^{3\times m}\)
Vertex matrix of M
特点
- Iterative Refinement
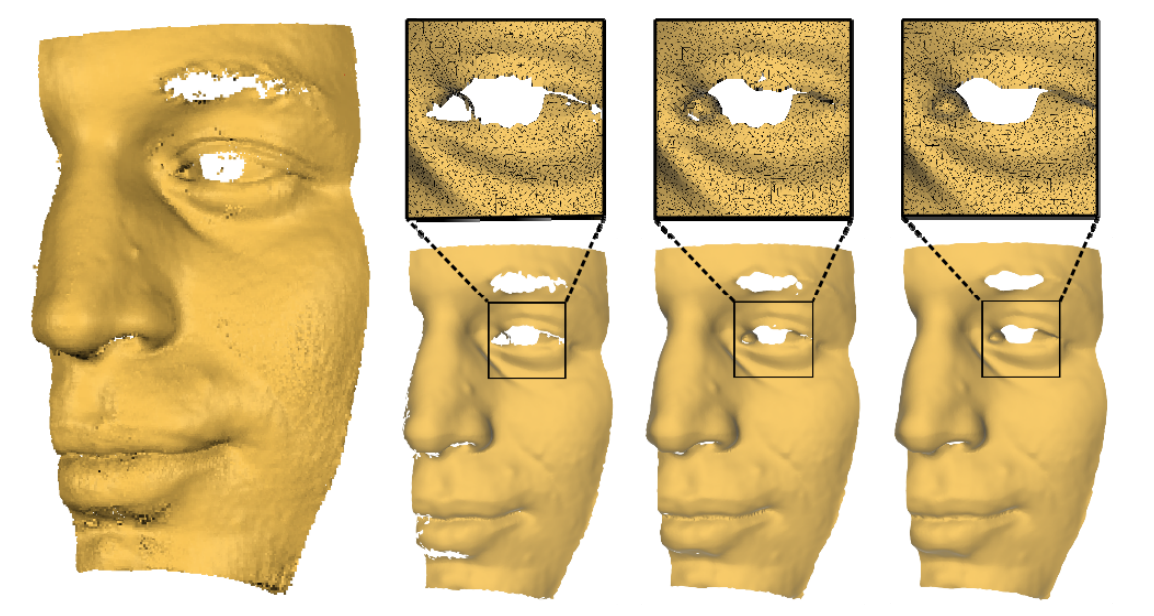
- Resistant to Noise
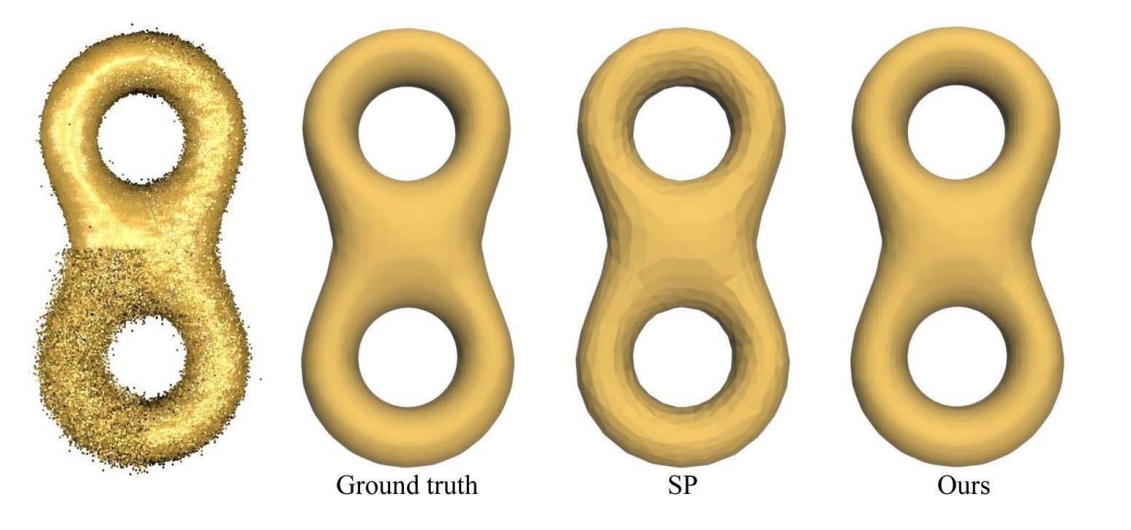
- Feature Preserving
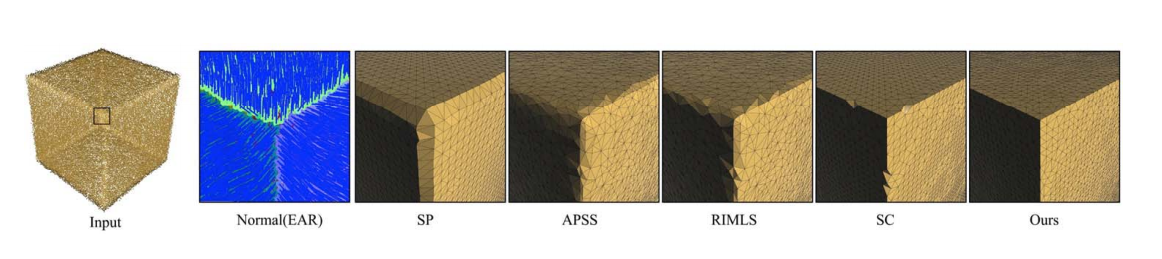
Implicit methods need normal information, while normal estimation is another challenging problem.
Conclusion
Model the surface reconstruction problem via dictionary learning
- VS Implicit method
- Straightforward
- Approximation error is considered
- VS Existing Explicit method
- Denoising the input point cloud
- Global approximation error
dictionary learning是一种半显式的方法。
Hybrid Methods
(1) Competing Fronts
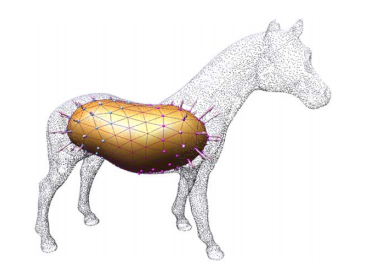
[1:21:10] 假设物体是封闭曲面。
物体内的距离场不断膨胀,形成 mesh
Sharf et al. Competing Fronts for Coarse–to–Fine Surface Reconstruction. Eurographics 2006.
(2) Cooperative Evolutions
- Two deformable models
- One from interior
- The other from exterior
- Alternative evolutions
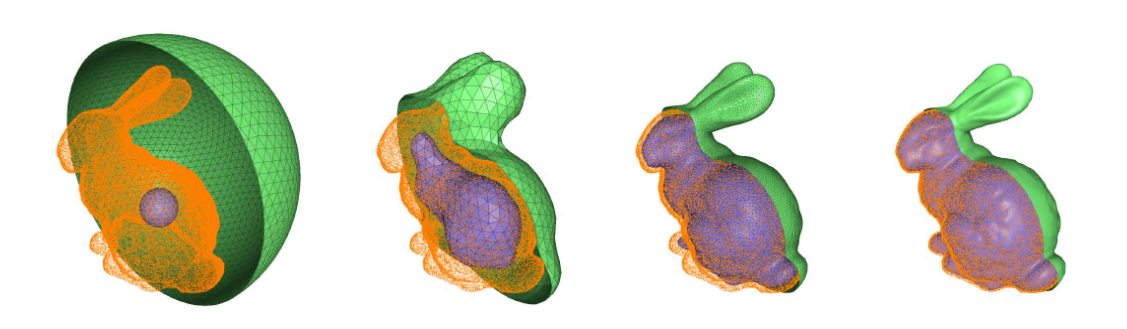
[1:23:02] 改进版:里面的球不断膨胀。外面的球不断收缩,直到两个曲面靠近,适用于有大的空洞的物体。
Lu and Liu. Surface Reconstruction via Cooperative Evolutions. CAGD 2020.
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/