关于简化
简化原因
- 冗余数据:信息熵
- 由于计算能力不足,需要简化模型
- 有些场景中,不需要足够精细的模型(LOD)
Simplification Applications
- Level‐of‐detail modeling
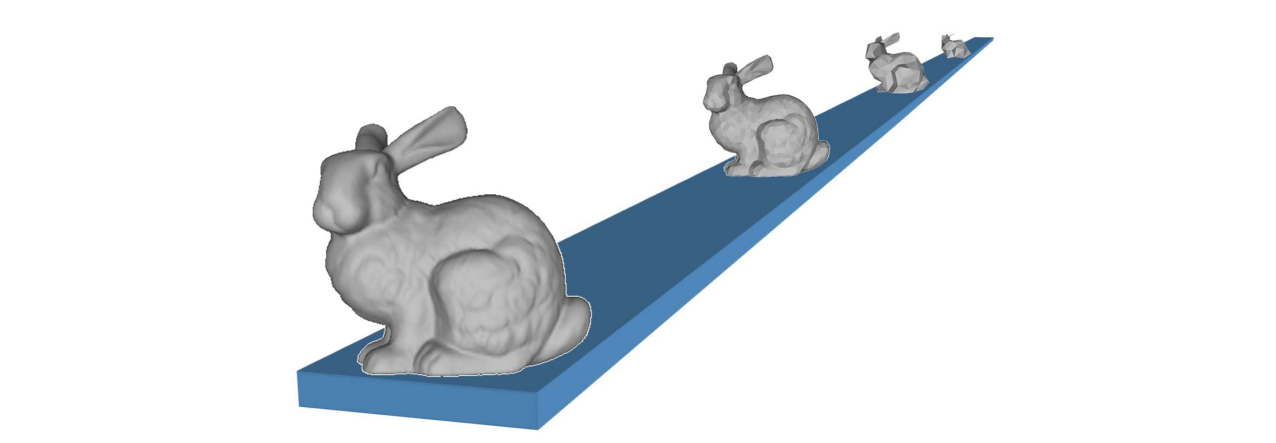 • Generate a family of models for the same object with
different polygon counts
• Generate a family of models for the same object with
different polygon counts
• Select the appropriate model based on estimates of the object's projected size - Simulation proxies
• Run the simulation on a simplified model
• Interpolate results across a more complicated model to be used for rendering
Tradeoff
• Size
• Error
• Quality
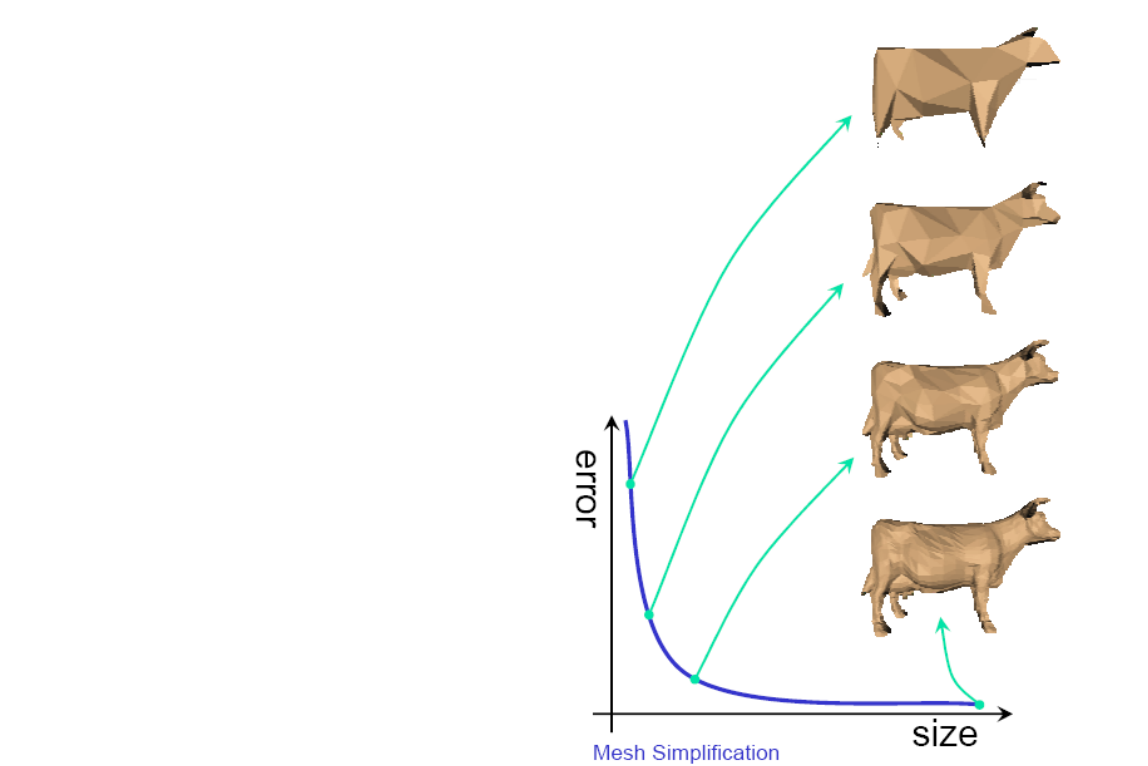
Performance Requirements
- Offline
• Generate model at given level(s) of detail
• Focus on quality - Real‐time
• Generate model at given level(s) of detail
• Focus on speed
• Requires preprocessing
• Time/space/quality tradeoff
简化算法
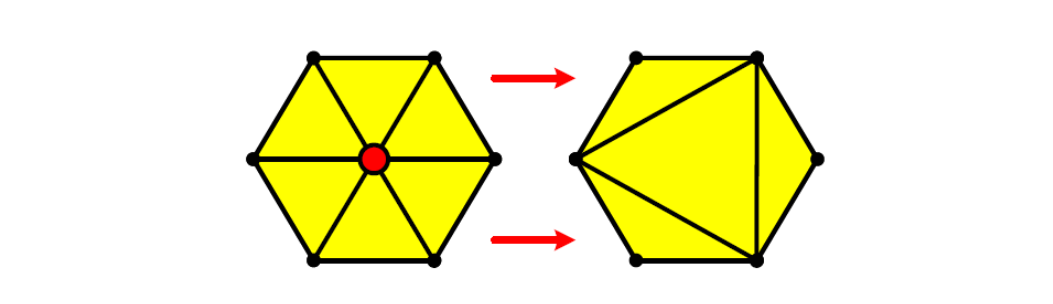
顶点删除 [图54:51]
方法一
v ← v‐1,f ← f‐2
Remaining vertices是subset of original vertex set
方法二
Pair contraction (cluster of two vertices)
Vertices may move
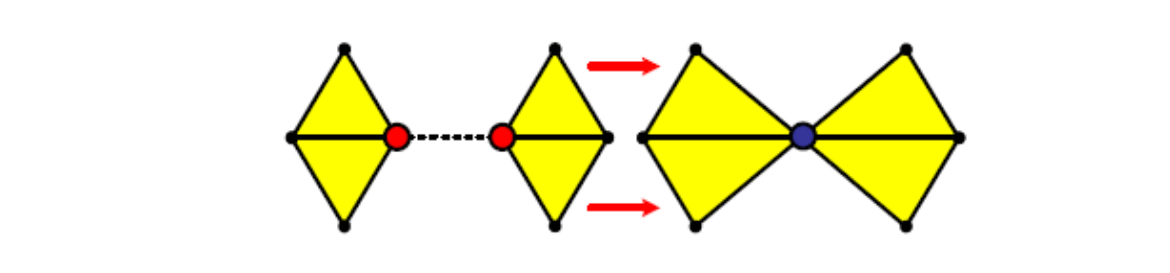
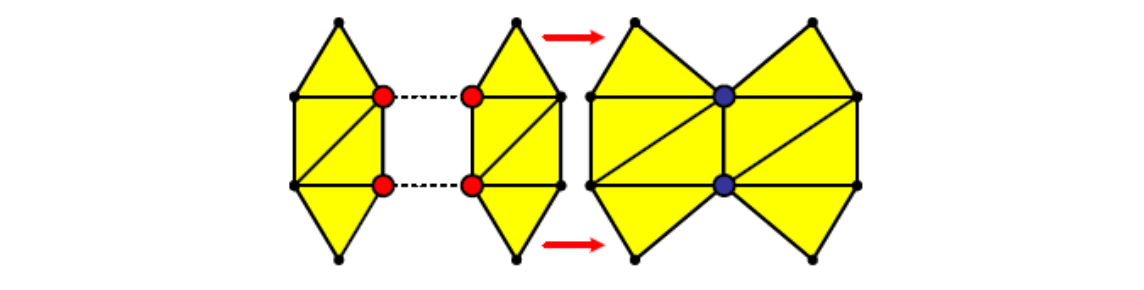
边收缩 [图56:46] Edge collapse
方法一
v ← v‐1,f ← f‐2
Vertices may move
- 原理:
- 选择一条边,把边坍缩成点
- 建立边周围的点到新点之间的边
- 使坍缩后的形状与坍缩前尽量接近
- 要解决的问题:
- 要坍缩哪些边?
- 边坍缩成点以后,这个点应该放在什么位置?
- 怎么衡量坍缩后的形状与坍缩前的接近程度?
方法二
Cluster contraction (set of vertices)
Vertices may move
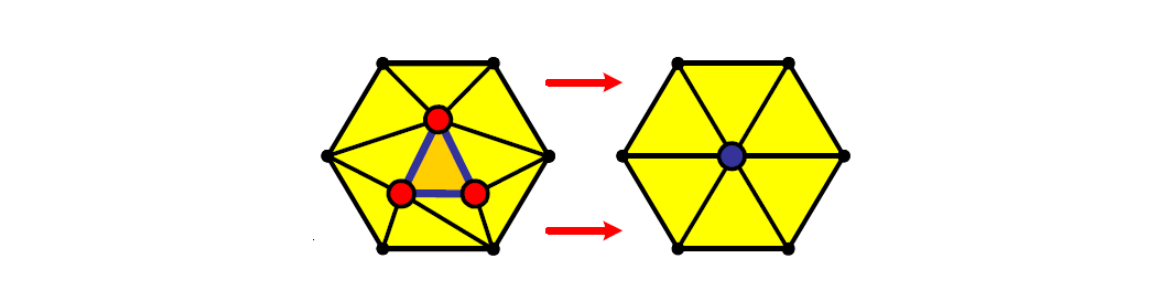
面 Triangle collapse
方法一
v ← v‐2,f ← f‐4
Vertices may move
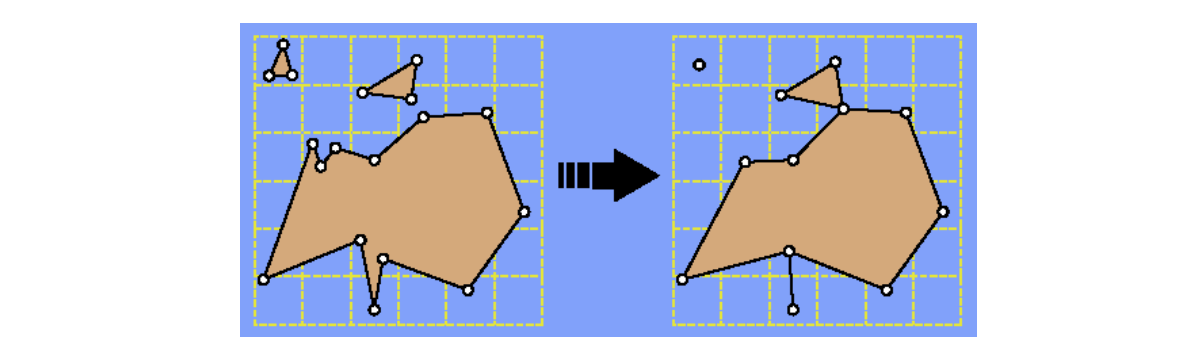
方法二
聚类法:[57:46],画格子,格子内的三角形收缩、点合并会产生非流型和悬挂边
Merge all vertices within the same cell
简化度量
衡量坍缩后的形状与坍缩前的接近程度
• 几何
• 视觉:纹理、材质、法向…
Local vs. Global Error
全局优于局部,具体见下一页
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/