Recap:
3D Content Creation的常用方法:
• Surface reconstruction
• Geometric modeling
• Geometry processing
• Creative generation
• …
Analyzing and Understanding 3D Contents
对于已有的模型,如何去分析/理解它?
• Organize Geometric Data
• Understand Structure and Relationships
• Understand Semantics and Functionality
• Synthesizing New Shapes
• …
三维几何处理:从局部到全局
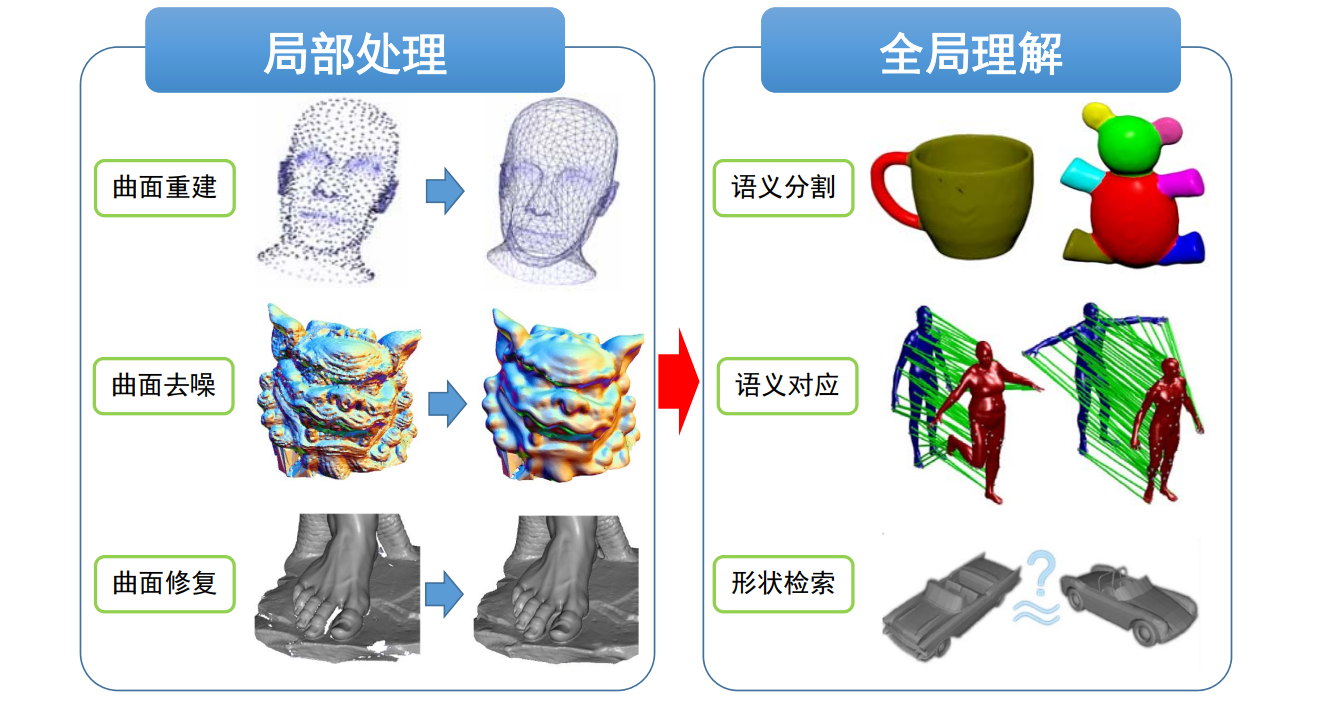
102主要是讲处理局部信息,但3D内容理解是要处理全局信息
- Local level analysis
• purely geometry/content‐driven
• mathematical formulation of objectives
• Examples: curvature and normal estimation, mesh smoothing, simplification, remeshing, parameterization… - High level analysis
• non‐local analysis
• not easy to formulate objectives mathematically
• Semantics is hard!
Problems of Shape Analysis
Understanding Shapes
Shape features
• Feature points
• Feature lines
• Saliency
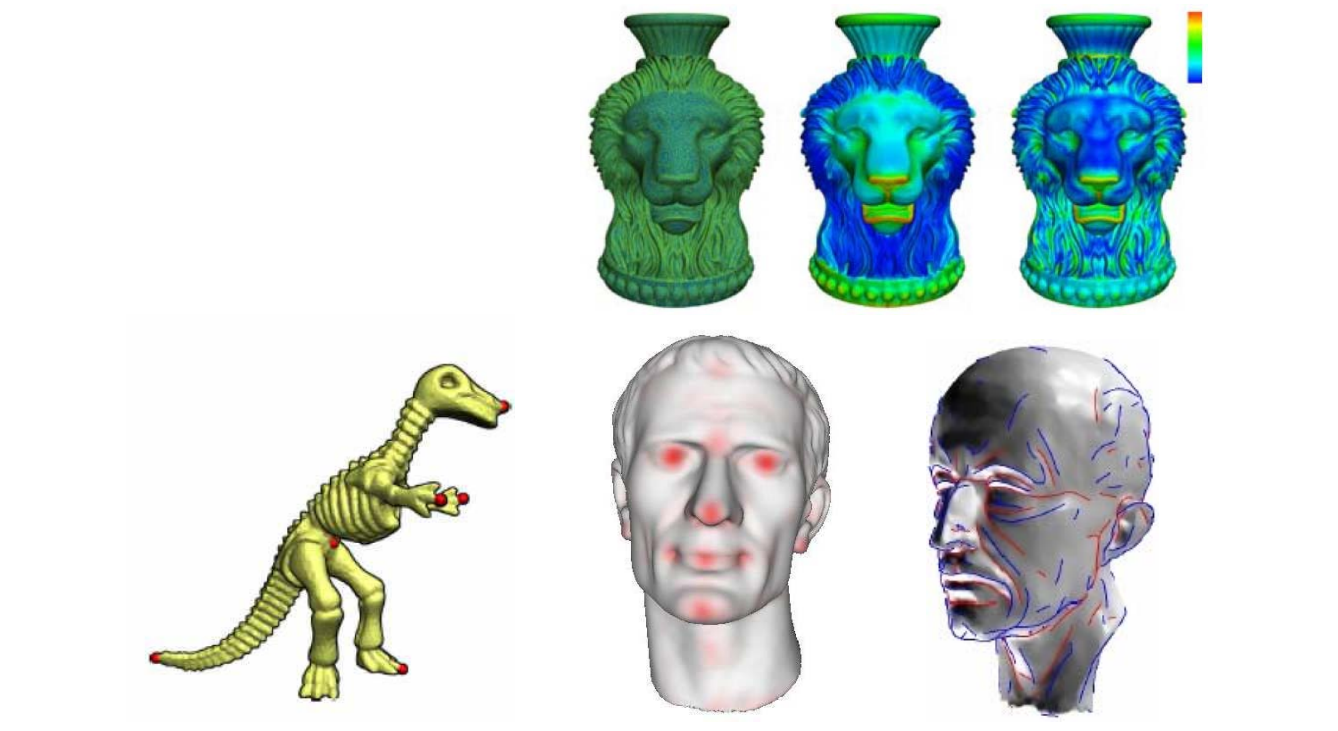

Alignment (upright)
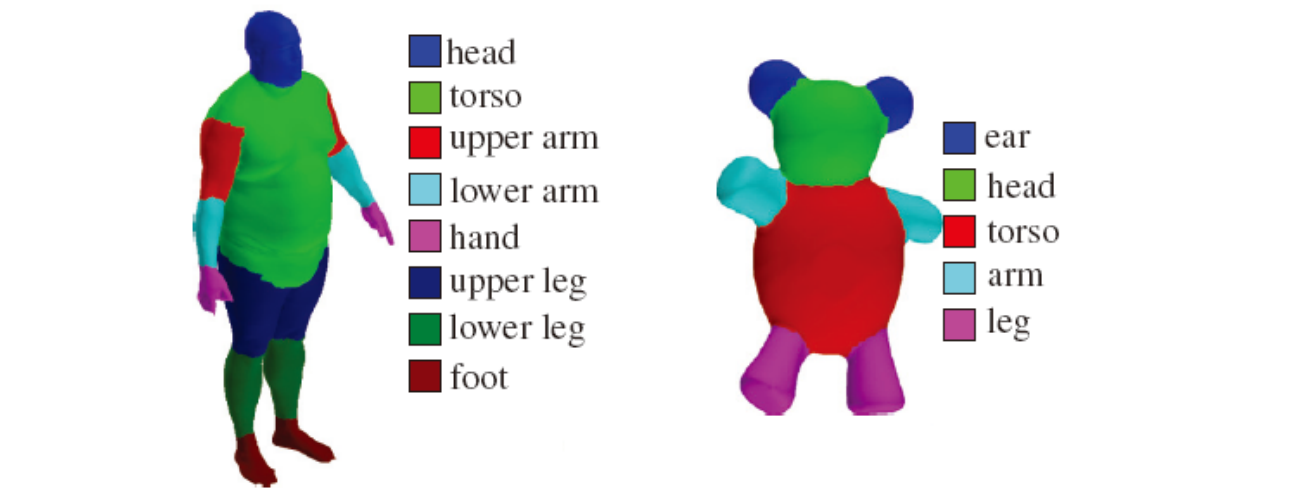
Shape segmentation (components)
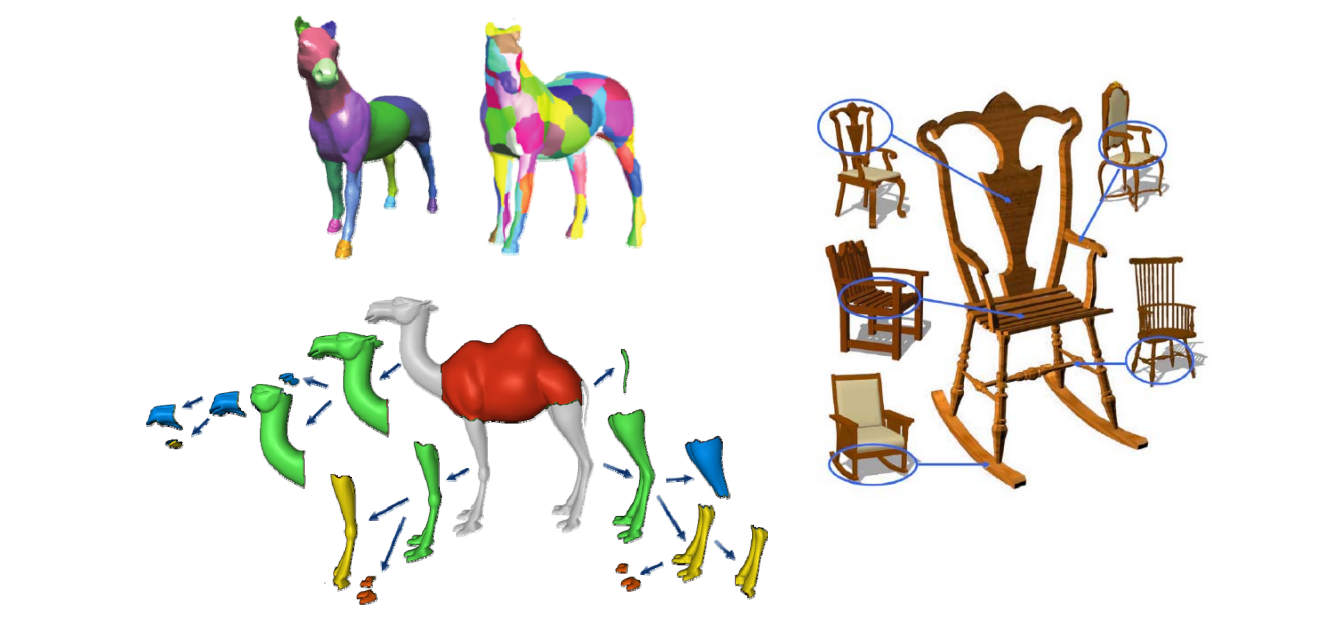

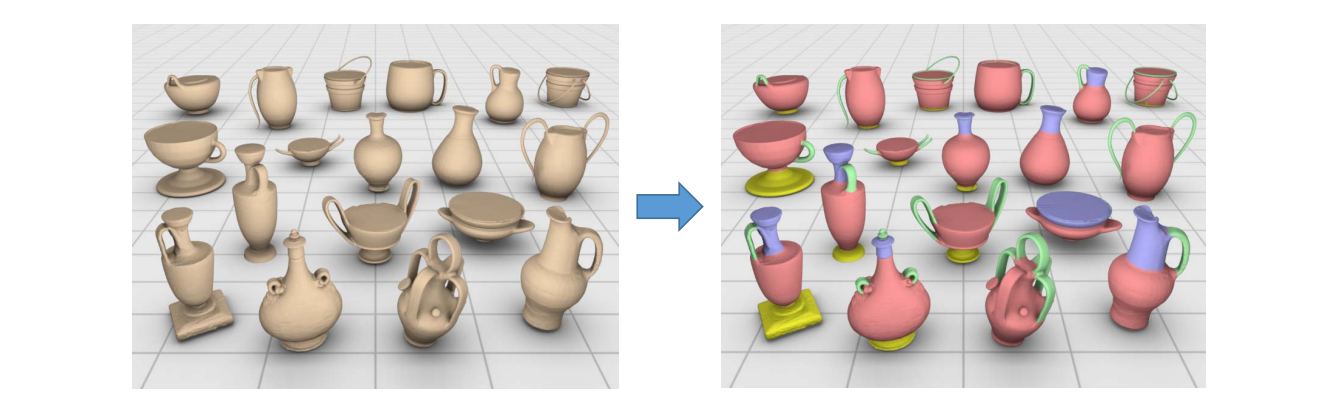
Co‐segmentation of a set of shapes
• More knowledge can be inferred from multiple shapes rather than an individual shape
Labeling
Symmetries
Skeleton
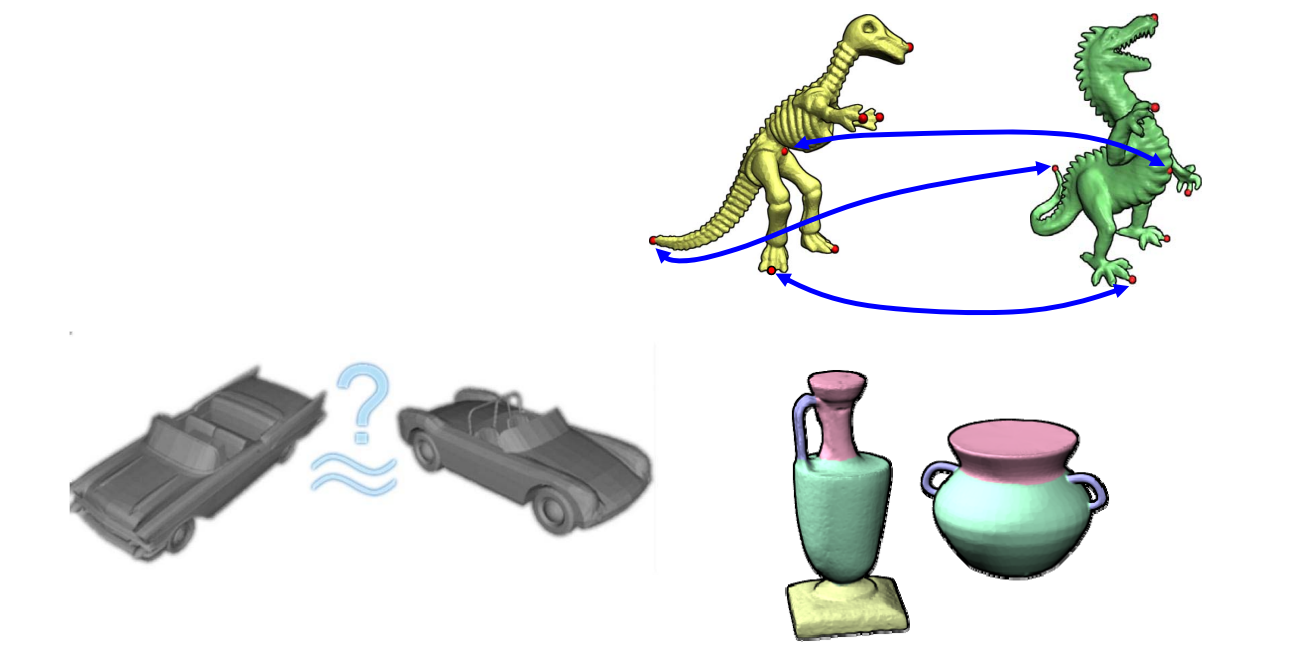
Shape matching
• Similarity
• Correspondences
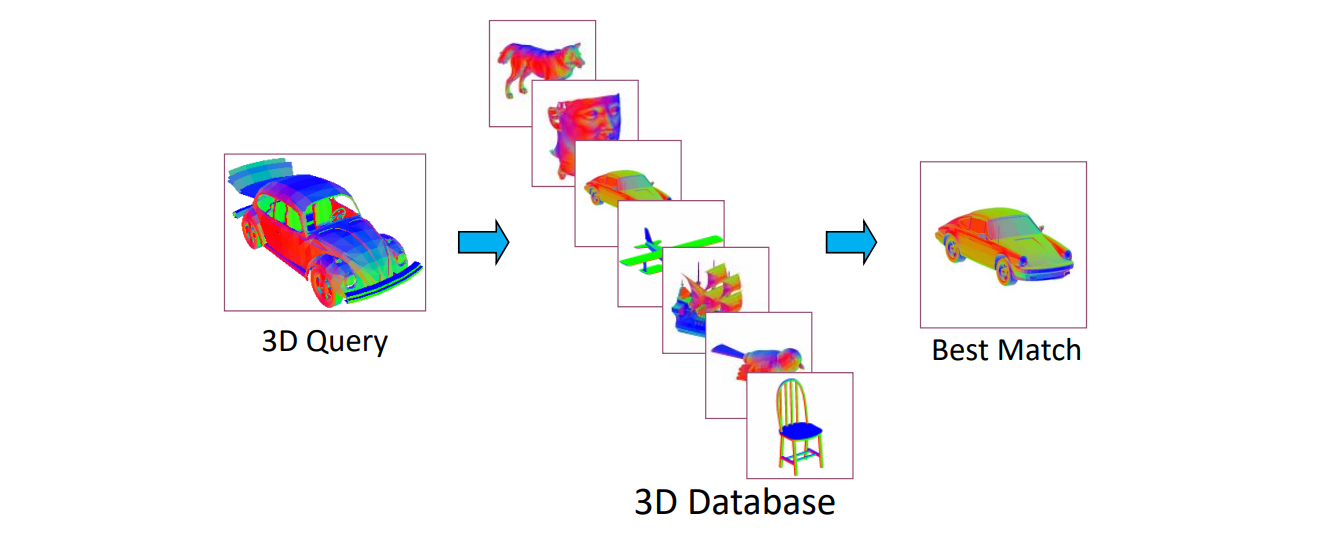
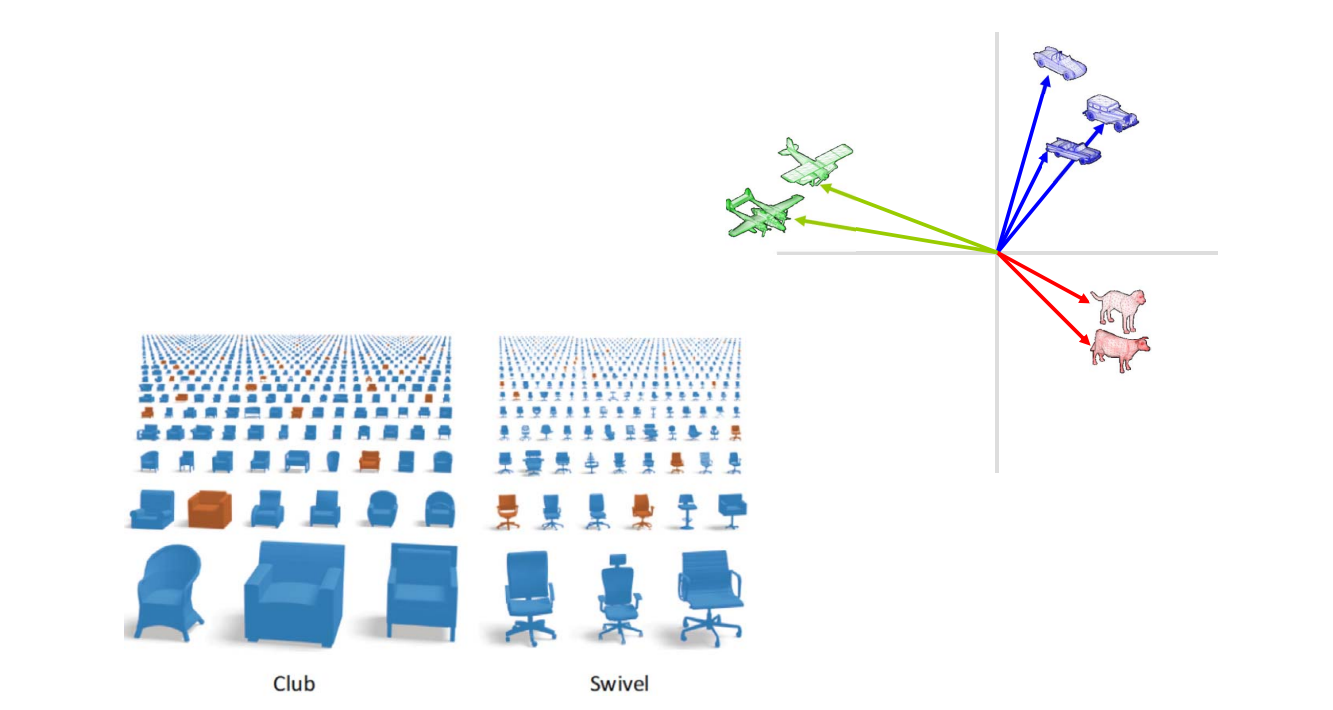
Shape retrieval 检索
Classification
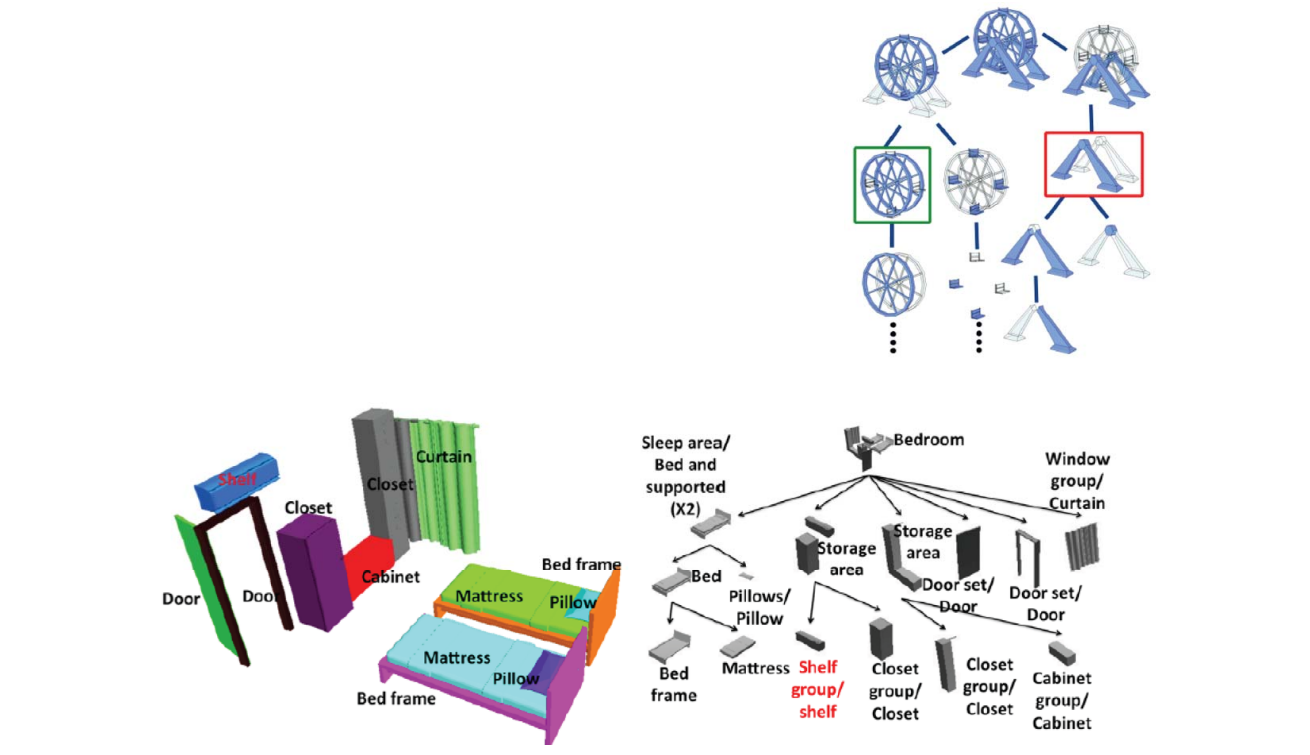
Structures
• Hierarchical structures
Functionality
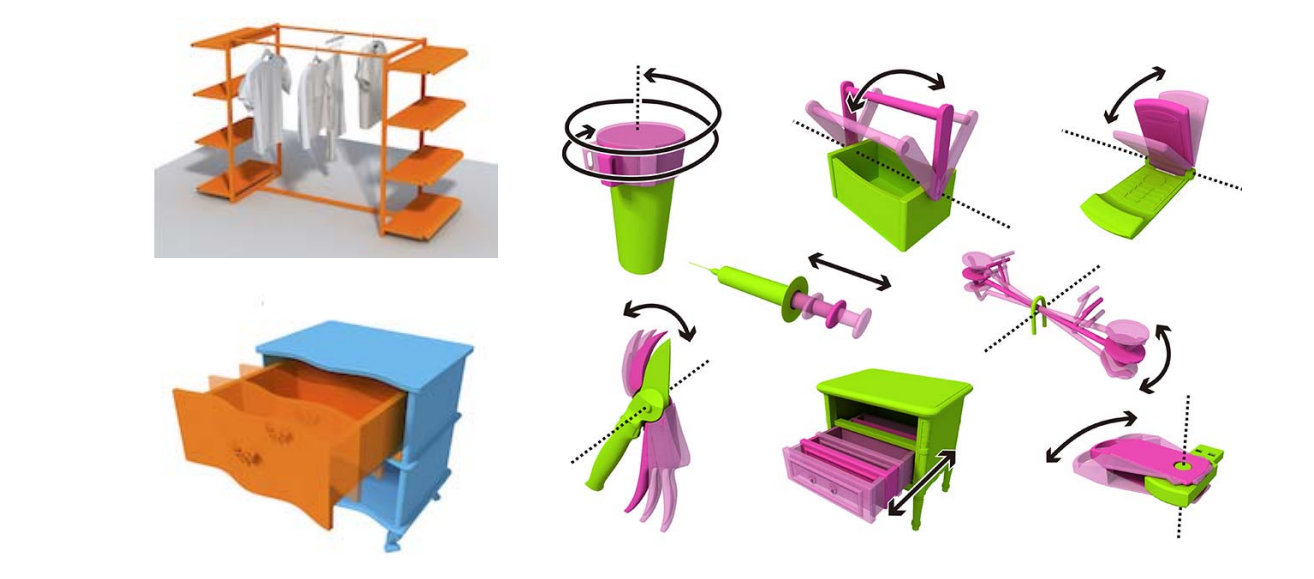
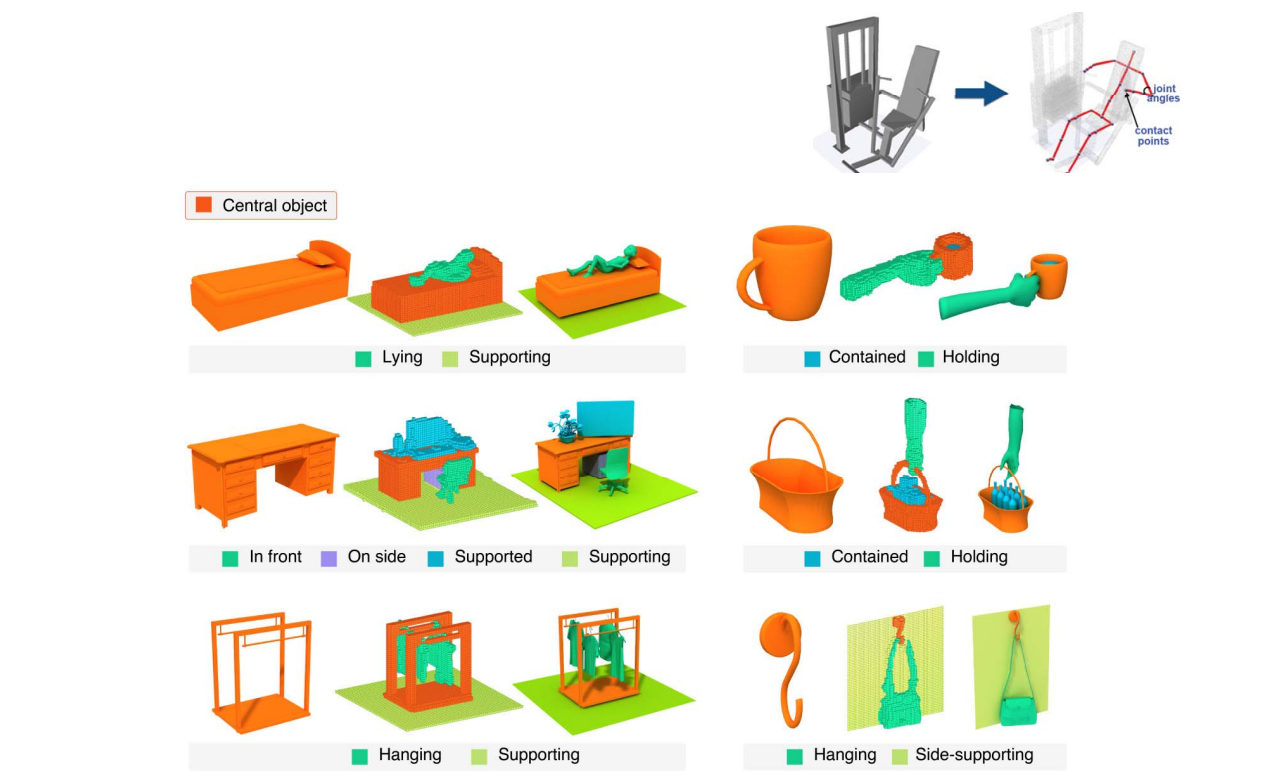
Object affordance 交互
Abstraction of shapes
• [Mehra et al. SIGAsia 2009]
Understanding assemblies
– [Mitra et al. SIG 2010]

Shape Descriptors
核心问题:形状表征(描述子、特征)
(Shape representation/descriptor/feature)
如何度量两个三维元素的相似性?
- 整体形状
- 全局描述子
- 局部形状
- 局部描述
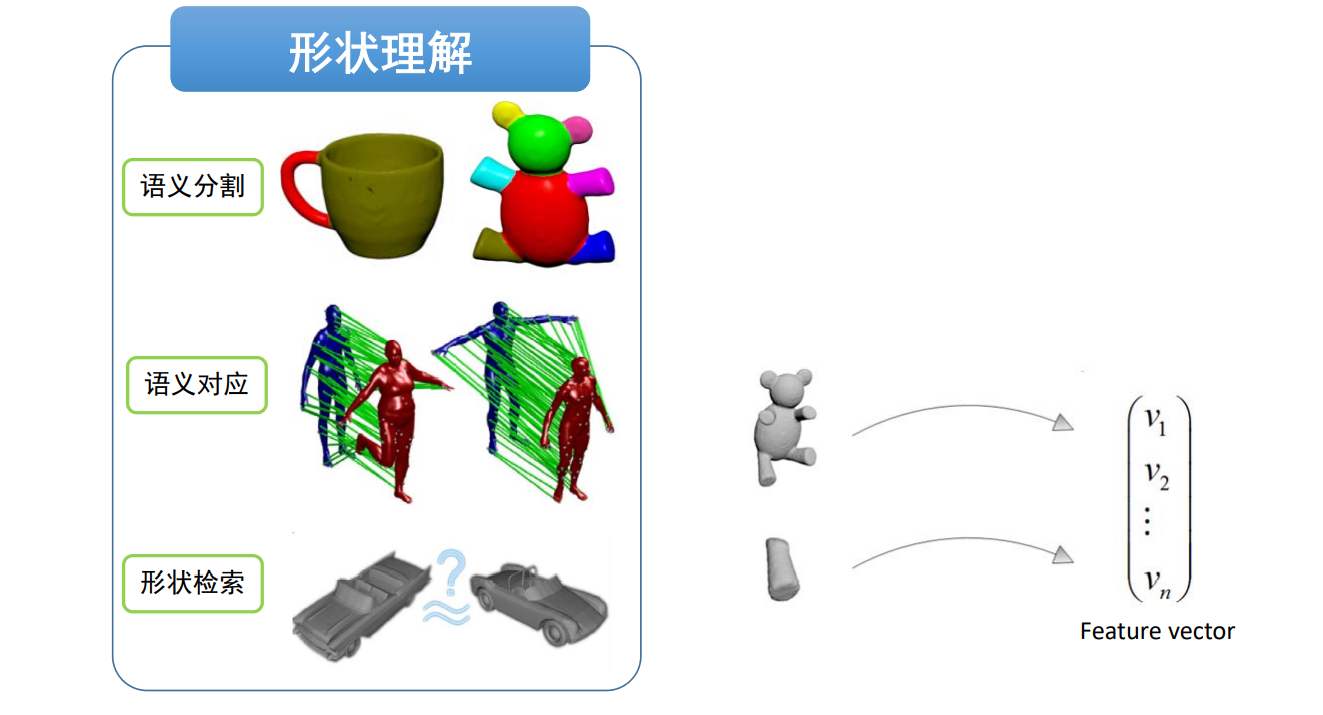
如何描述三维数据?
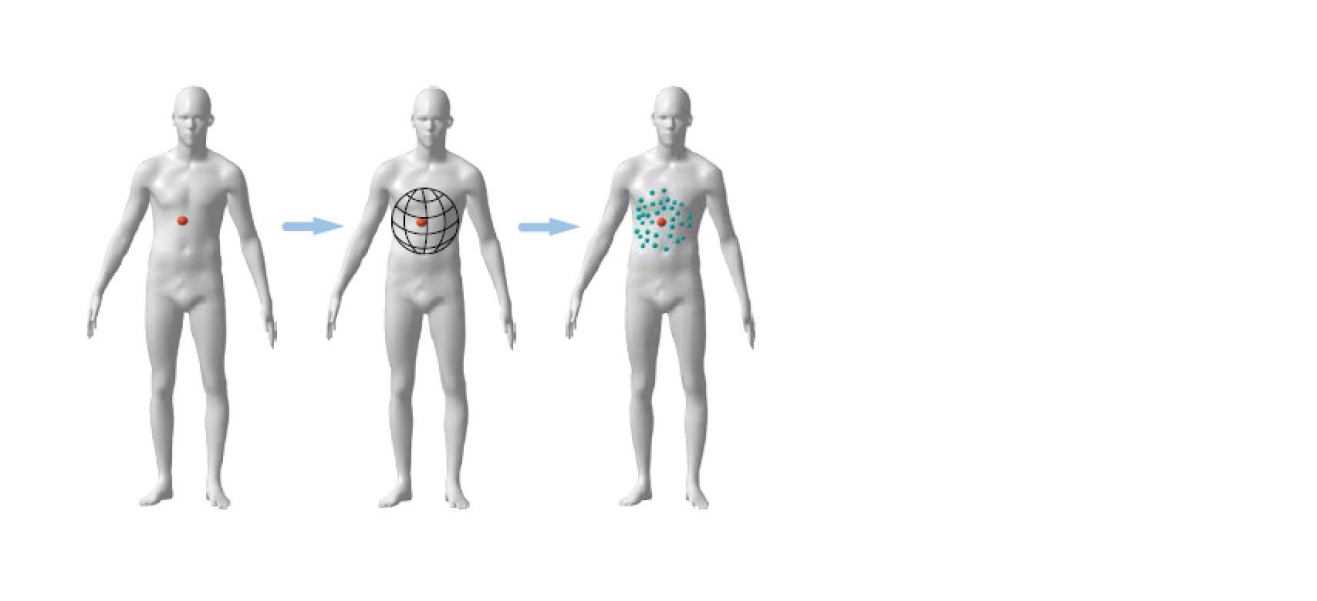
- 点坐标(x,y,z)
- 几何量:长度、角度、面积、 体积
- 微分量:法向量、曲率
- 拓扑量:连接关系、Laplace谱
- 映射度量:雅可比(变形量)、共形比
- …
模型分割‐根据特征的聚类 (Clustering/Labeling)
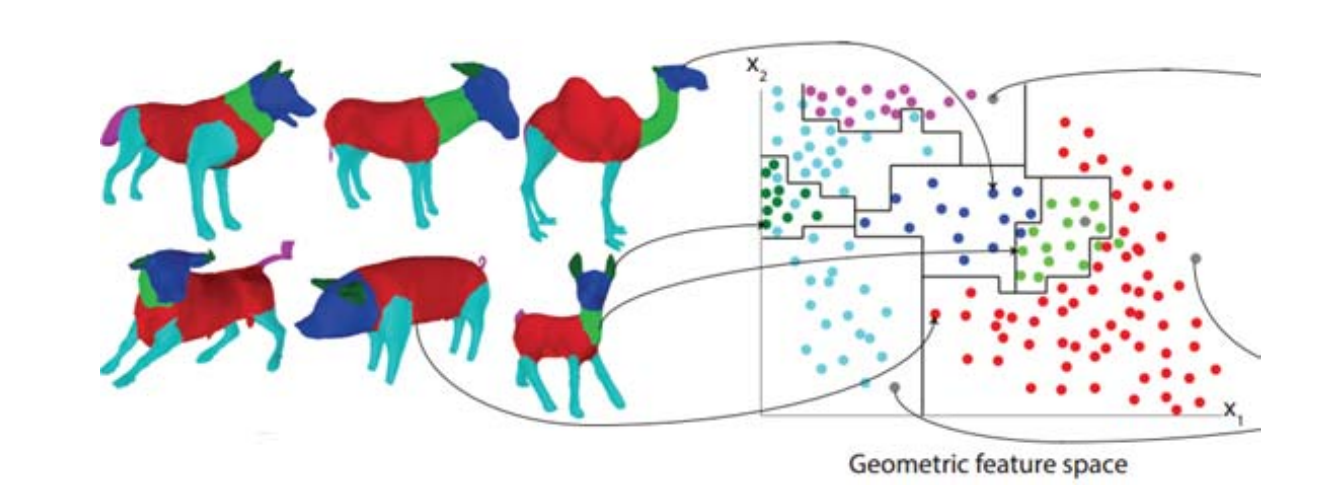
各种人工定义的3D形状特征
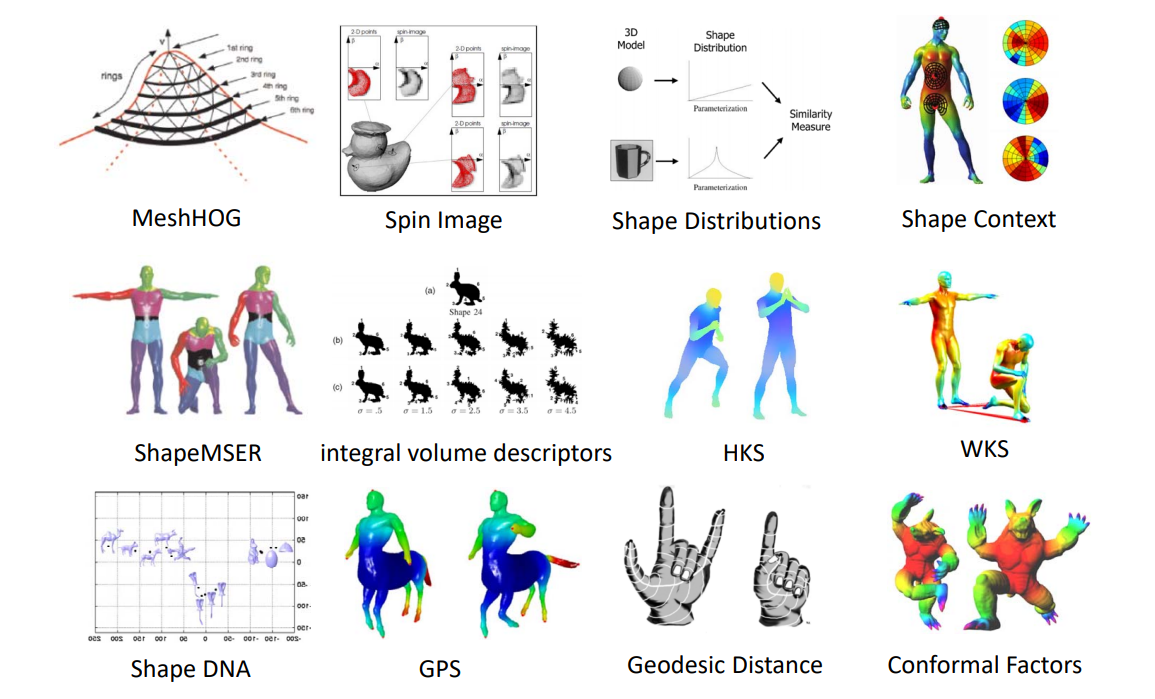
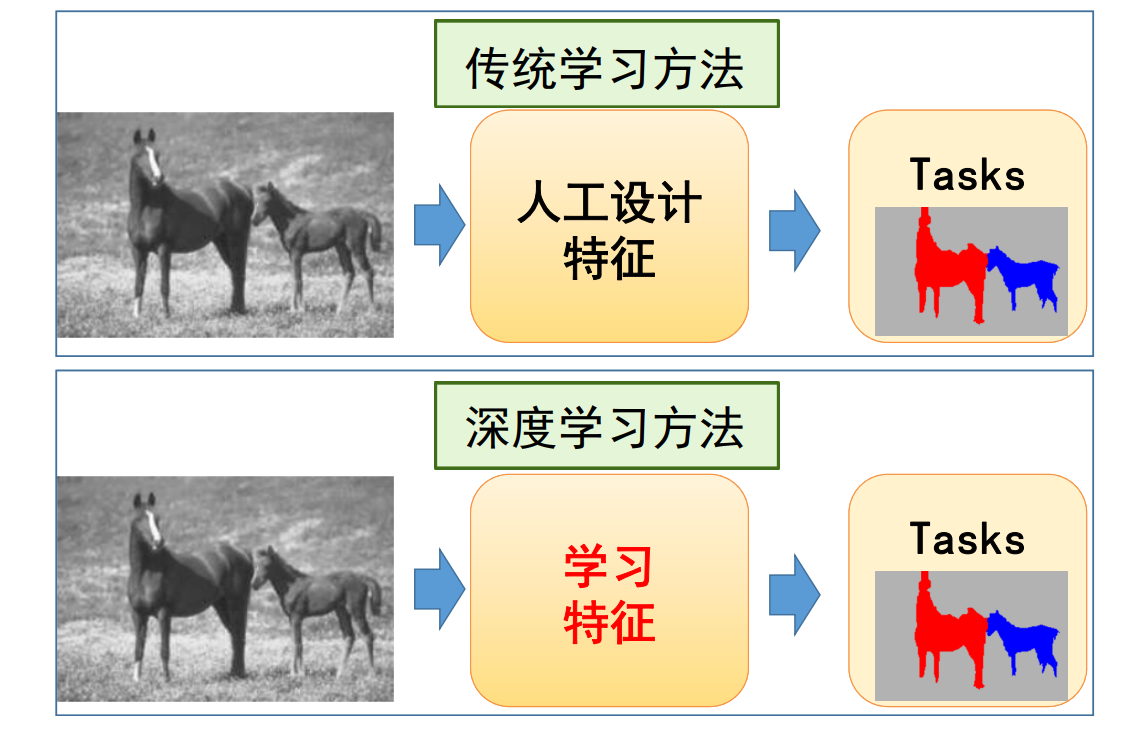
Methodology
Traditional Methods:特征工程
特征工程的两个主要问题

如何选择合适的特征?
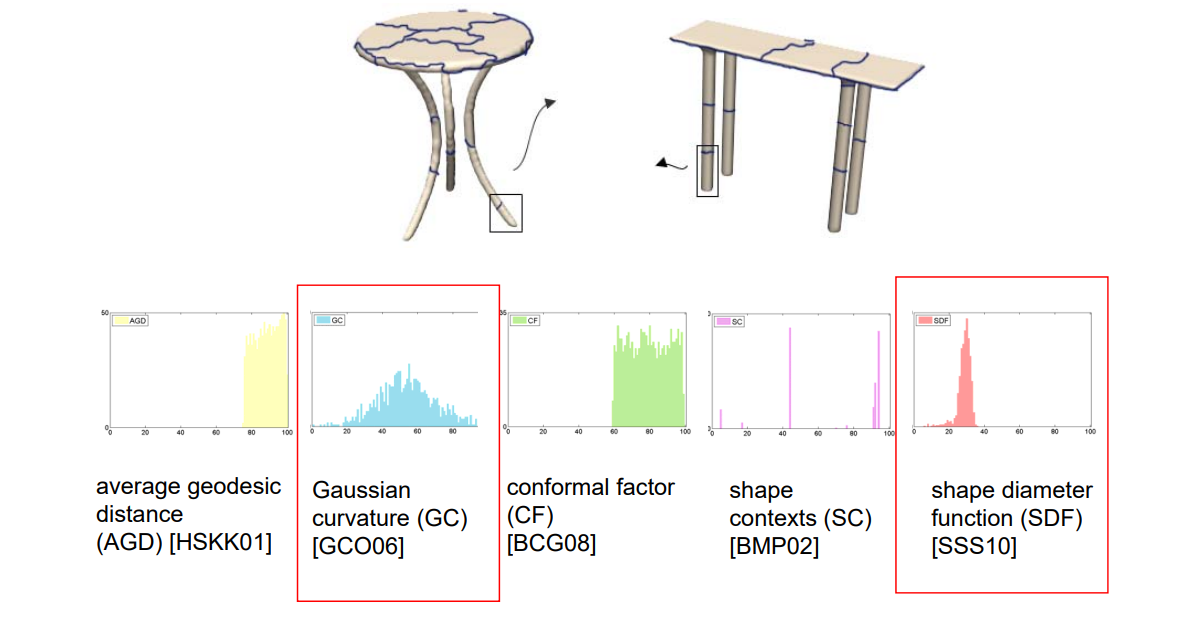
Hand‐crafted Features are not Enough
• “Hand‐crafted” feature descriptor need domain knowledge
• Too many feature descriptor, which is the best?
• Concatenation of the features may result in over‐fitting in feature space
想法:稀疏学习选择合适的特征
[Hu et al. SGP 2012]
• 稀疏学习的本质:聚类
• 子空间聚类(Subspace clustering)
Deep Learning based Methods
深度学习方法:端到端 to extract good feature descriptors!
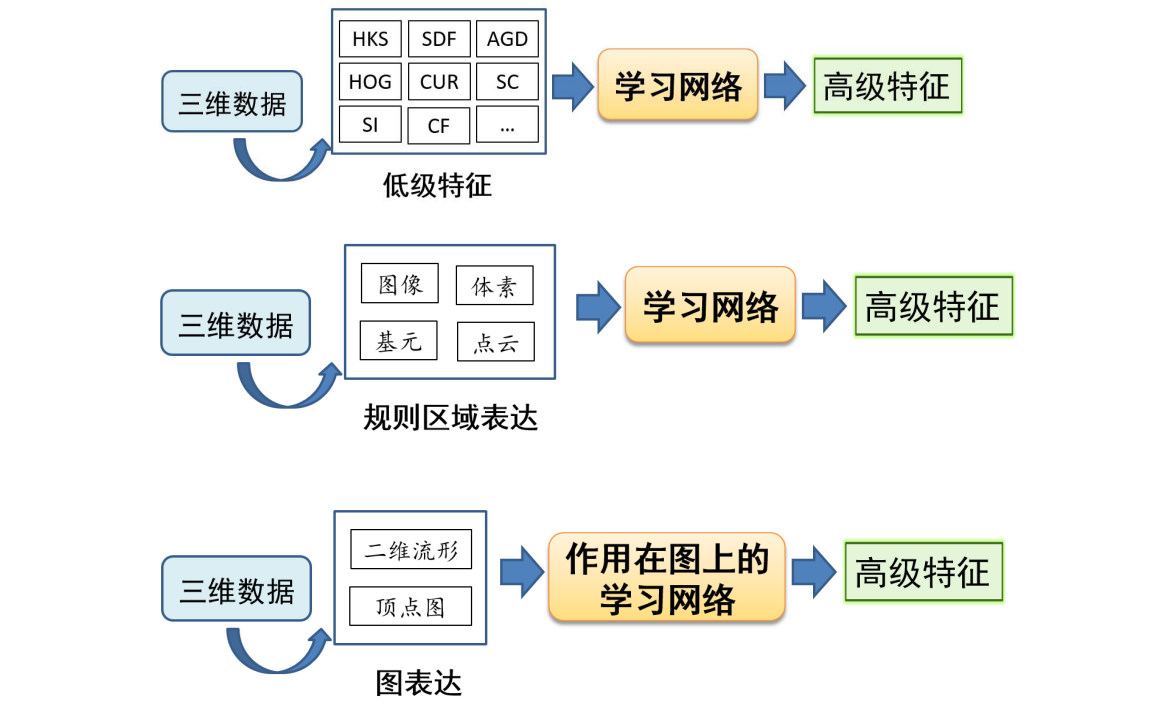
三维数据的深度学习的三种方法
关于深度学习

- 通用拟合器(较大的逼近函数空间)
- 应用三部曲
- 在哪找(网络构造)、哪个好(损失函数)、怎么找(优化)
- 仅拟合了大量样本:可能只是“虚假关系”
- 并没有“理解”或“认知”真正的规律
- 不可解释性
- 应用三部曲
- 性能依赖训练样本(数据集)
- 当数据集足够密:近似“最近邻”算法
- 训练数据集不够完备:缺乏泛化能力
- 大部分是过拟合
- 基于深度神经网络的深度学习并不是真正的AI,离 真正的“智能”仍很遥远
稀疏学习与深度学习:殊途同归
- 不同性
• 压缩感知:基于模型的,有很好的结构和数学模型;来自于数学理论的突破
• 深度学习:基于实证的,模型灵活,须通过数据进行监督学习;来自于求解速度的突破 - 一致性
• 目标:高维数据的信息(特征)提取
• 结果:从局部信息来处理全局信息
• 类似的网络结构:求解L1优化的IST (Iterative Soft‐Thresholding)算法实质上是多层网络优化
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/