Laplacian Editing
[Sorkine et al. SGP 2004]
What’s are Details?
• Detail = surface – smooth (surface)
• Smoothing = averaging
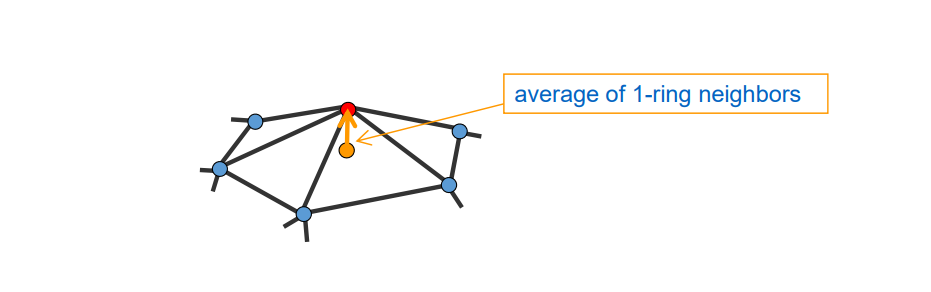
What’s the Difference?
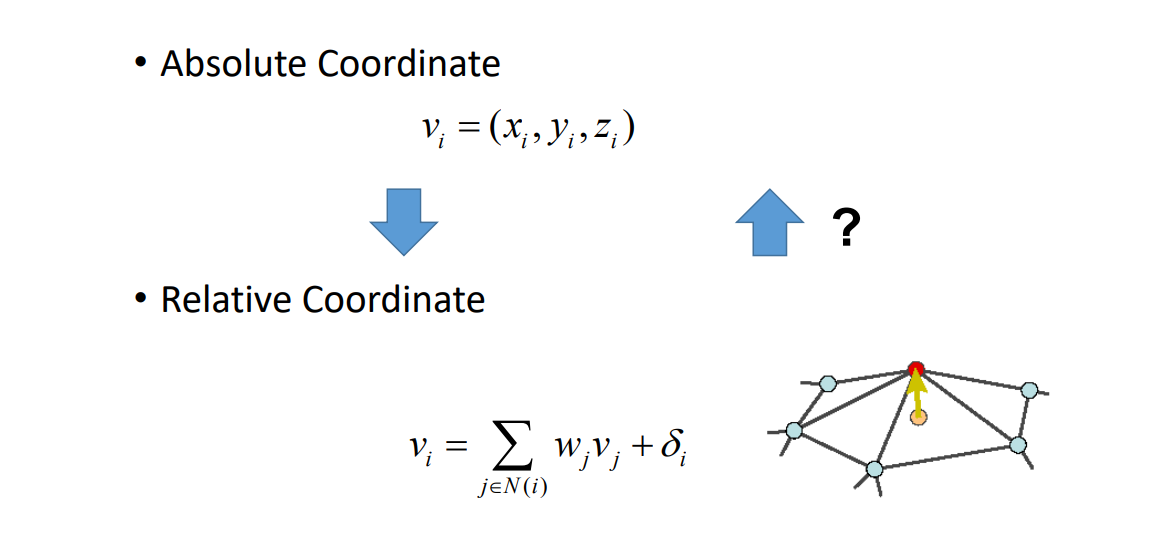
Laplacian Editing
- Local detail representation – enables detail preservation through various modeling tasks
- Representation with sparse matrices
- Efficient linear surface reconstruction
Editing framework
- The spatial constraints will serve as modeling constraints
- Reconstruct the surface every time the modeling constraints are changed
Detail constraints: \(LX=\delta \)
Modeling constraints: \(x_j=c_j,j\in\) {\(j_1,j_2,\dots j_k\)}
用户对 mesh 的一个点进行编辑,算法更新其他的点,得到合理结果。
本质:保持 mesh 的 Laplace 不变,因为 Laplace 描述了曲面的特征。
准确说是 Laplace 长度不变,方向有可能旋转。
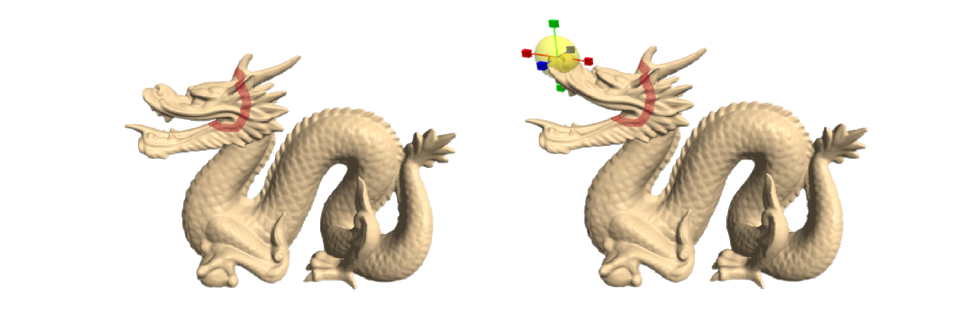
Direct Detail Preserving
Rotation Transformation
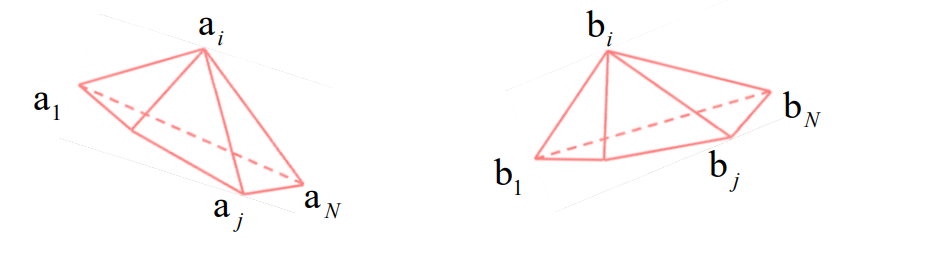
$$ \begin{pmatrix}b_1-b_i \\\vdots \\b_N-b_i \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}a_1-a_i \\\vdots \\a_N-a_i \end{pmatrix}R_i $$
Reconstruction
• Soft constraints
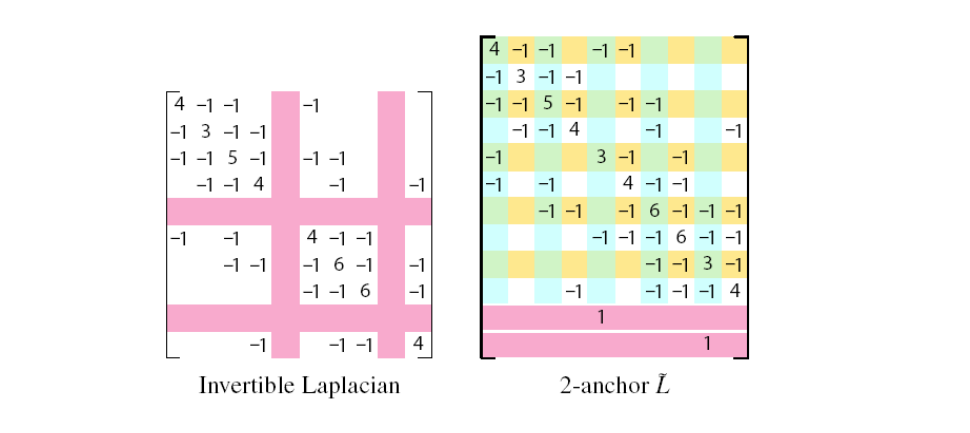
$$ L^TLv=L^T\delta $$
Variational Viewpoint
• Laplacian Approximation
$$ \tilde{X} =\underset{X}{argmin} (||LX-\delta ^{(x)}||^2+\sum _{j\in C}w^2||x_j-c_j||^2). $$
• Gradient Approximation
$$ \underset{\phi }{min} \iint _\Omega ||\nabla \phi -w||^2dA, $$
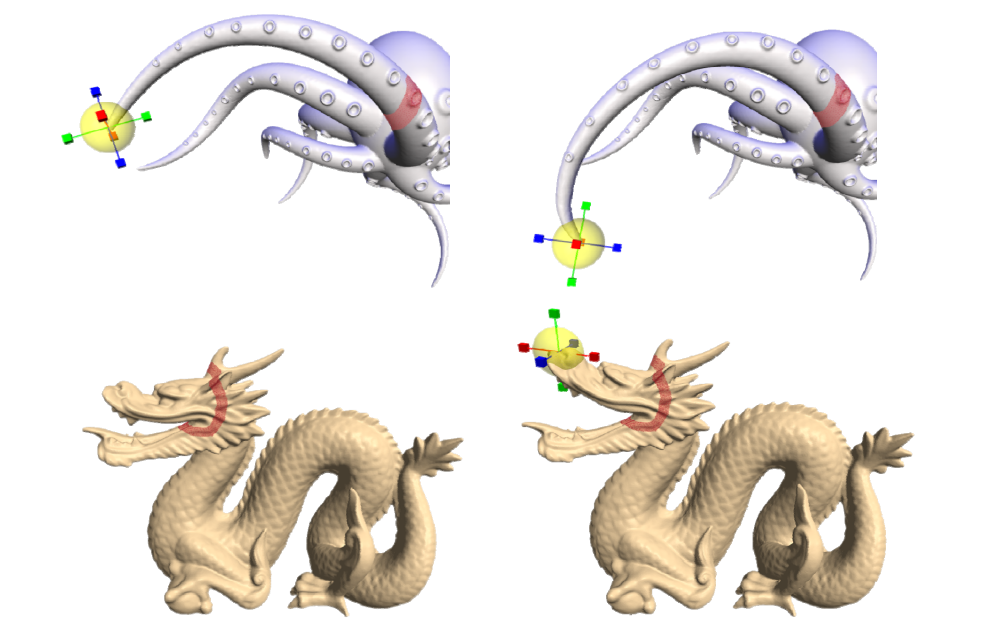
User Interfaces
• ROI is bounded by a belt (static anchors)
• Manipulation through handle(s)
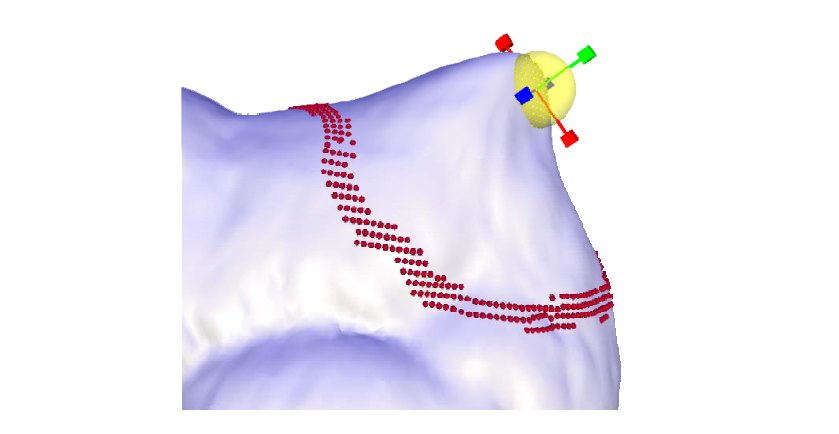
Results
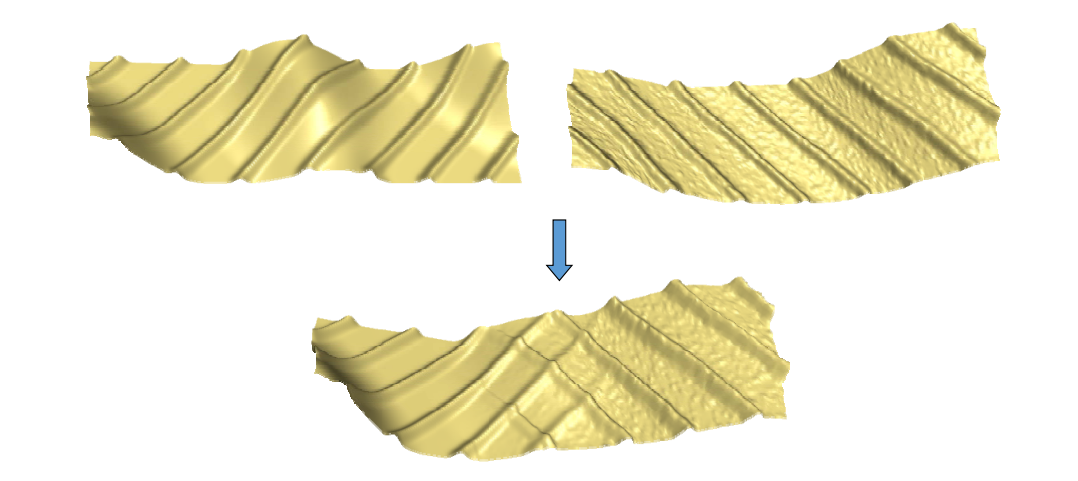
Detail transfer and mixing
• “Peel“ the coating of one surface and transfer to another
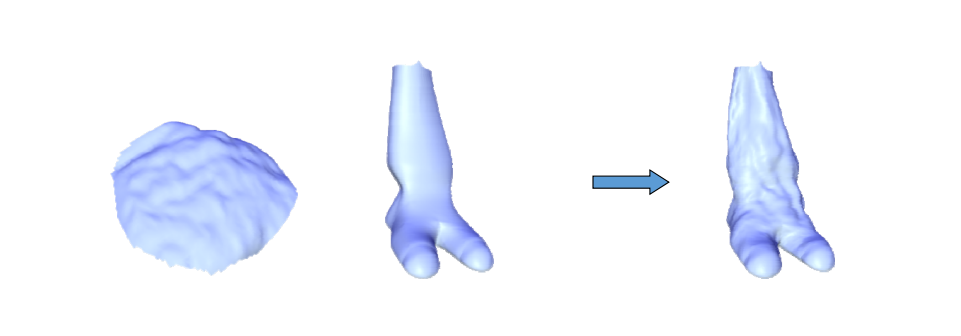
第一步:Parameterization onto a common domain and elastic warp to align the features, if needed
第二步:Detail peeling:
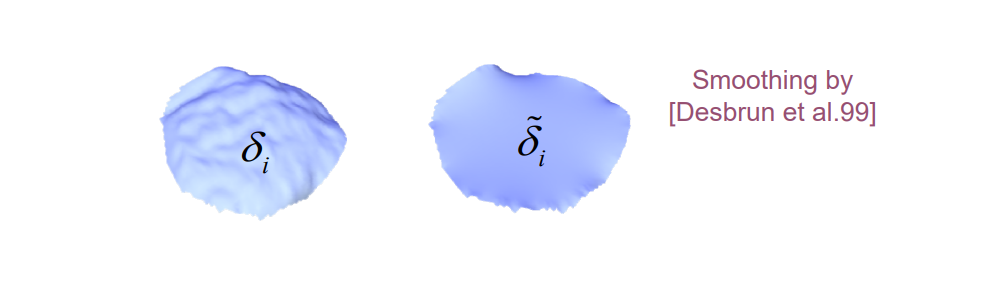
$$ \xi _i=\delta _i-\tilde{\delta } _i $$
第三步:Changing local frames:
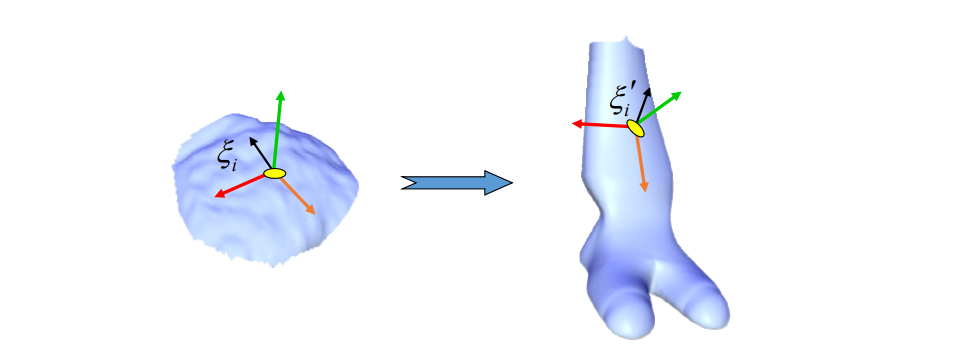
第四步:Reconstruction of target surface from: \(\delta _{target}\)
$$ \delta _{target} ={\delta}' _i+{\xi}' _i $$
Examples
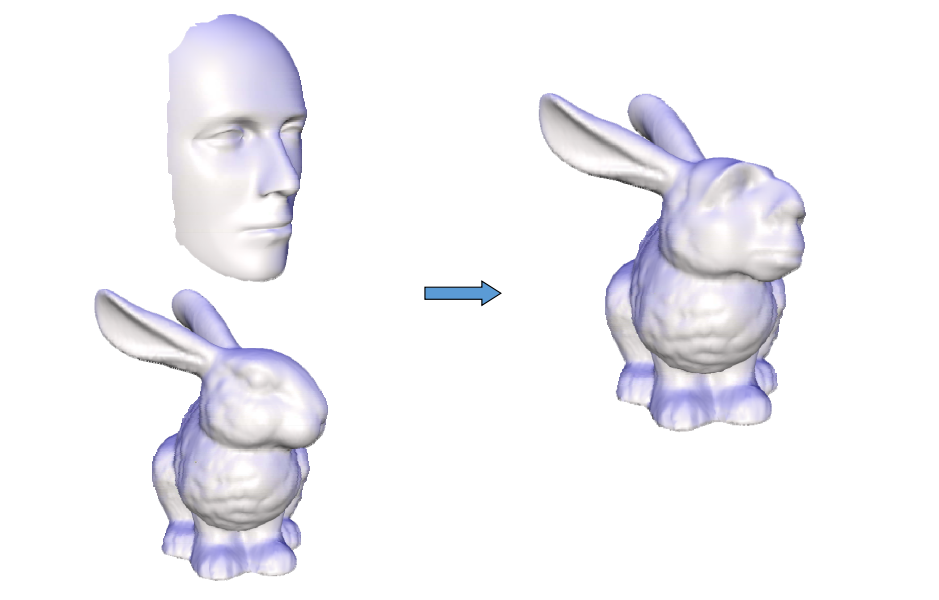
Mixing Laplacians
• Taking weighted average of \(\delta _i\) and \(\delta ^‘_i\)
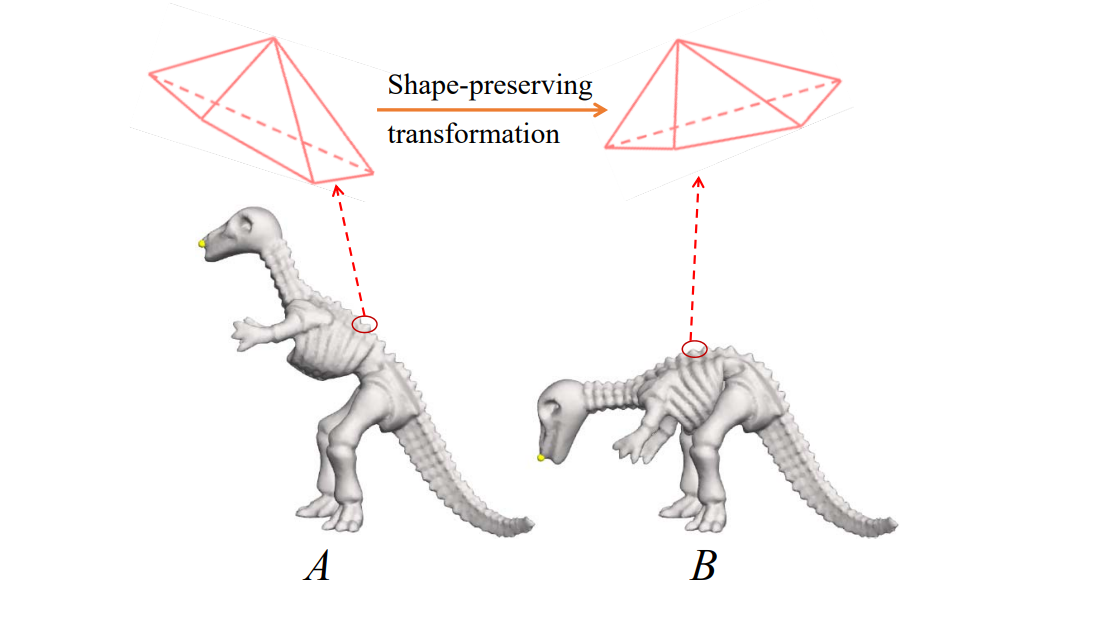
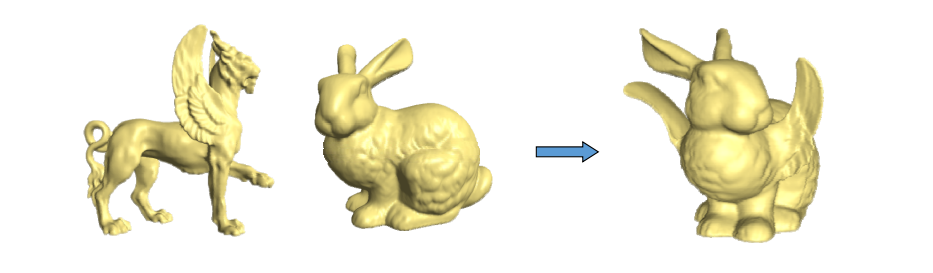
Mesh transplanting
- The user defines
• Part to transplant
• Where to transplant
• Spatial orientation and scale - Topological stitching
- Geometrical stitching via Laplacian mixing
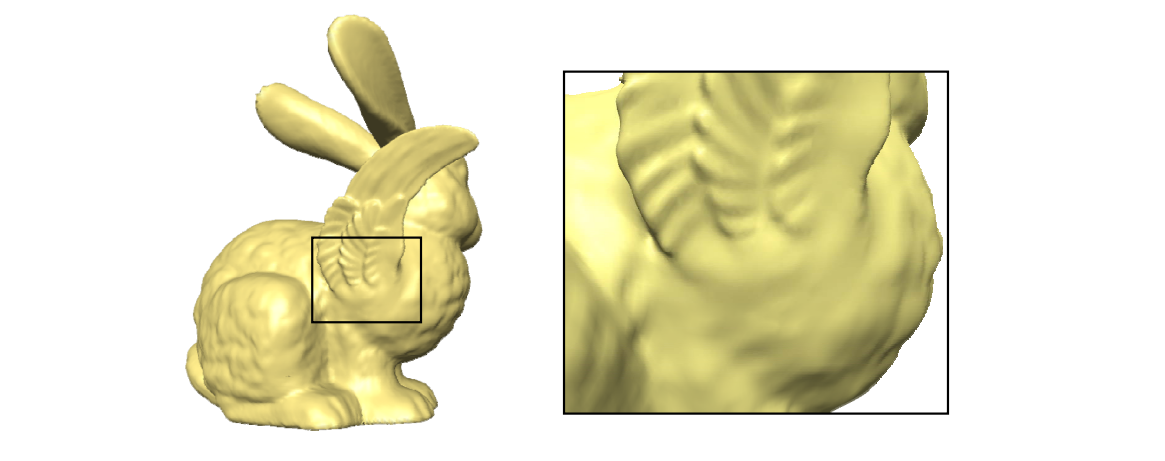
• Details gradually change in the transition area
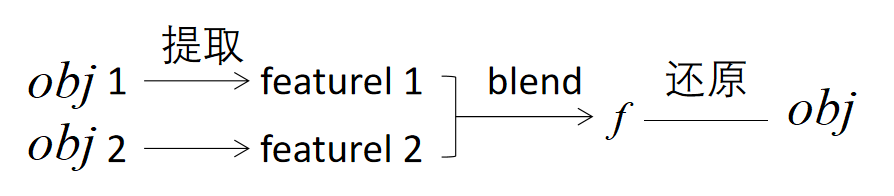
提取与还原即 Encoder& Decoder.Laplace 是手工方法,E&D是AI方法。
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/