1. Local Simplification Strategies
Local error: Compare new patch with previous iteration
• Fast
• Accumulates error
• Memory‐less
大部分情况下local就够用了。
The Basic Algorithm
(1) Select the element with minimal error
(2) Perform simplification operation (remove/contract)
(3) Update error (local/global)
重复(1)-(3)Until mesh size / quality is achieved
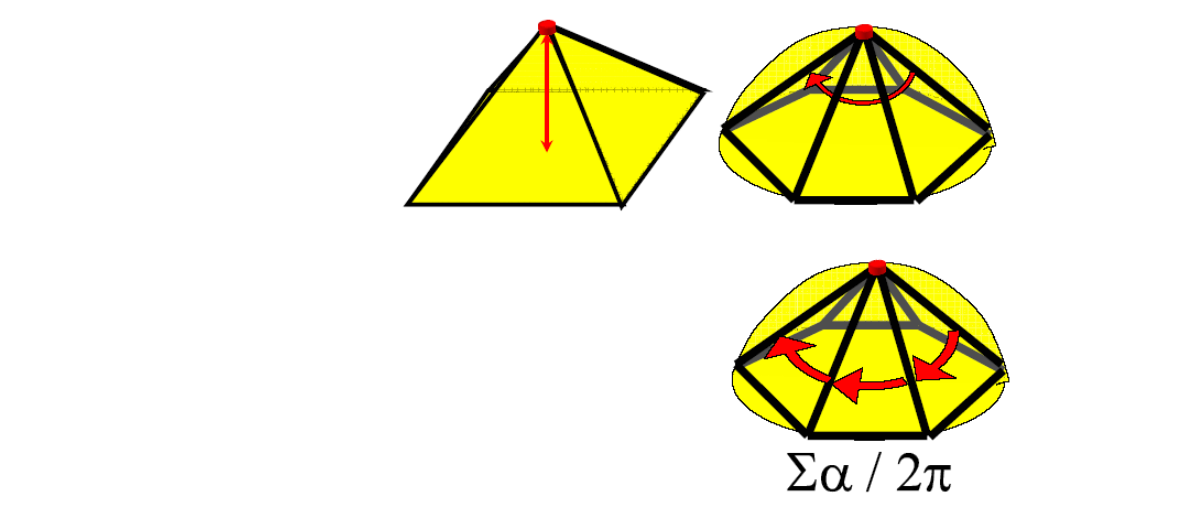
顶点删除的误差度量
点越尖锐越重要。(Laplace,一圈夹角等)
- Measures
• Distance to plane
• Curvature - Usually approximated
• Average plane
• Discrete curvature
边收缩的误差度量
Quadris Error Matrics(QEM), 二次误差度量
二次误差度量用于衡量“坍缩后的形状与坍缩前的接近程度”,使算法可以基于此标准选择要坍缩的边及确定坍缩点的位置。
用二次曲面拟合这条边。拟合得到系数矩阵,用矩阵性质度量扭曲。从直观上理解就是, 二次误差来度量[41:17] = new point 到 old edge(或old face) 的距离平方和。
(1) Choose point closest to set of planes (triangles)
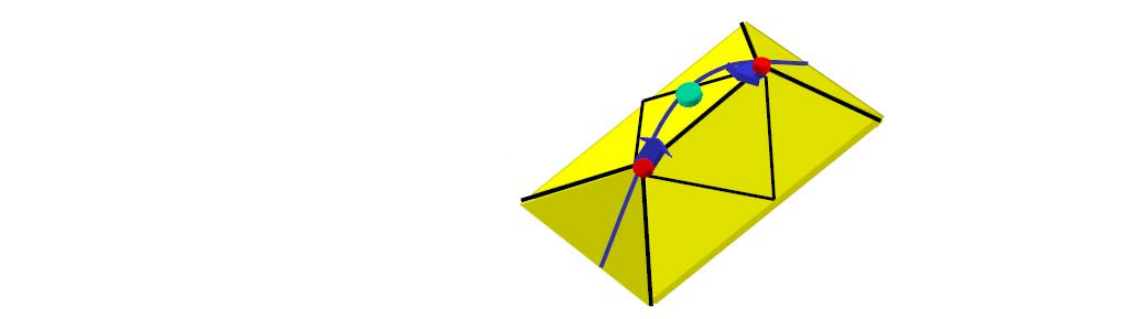
坍缩点的位置应该在使二次度量误差最小的地方。
找到坍缩点转化为一个优化问题。
(2) Sum of squared distances to set of planes is quadratic \(\Rightarrow\) has a minimum
把所有边都尝试坍缩,评估一下每条边如果要做坍缩并选择了最好的坍缩点位置,会得到多少误差。最后选择造成误差最少的边。
即:遍历-计算-排序-选择-坍缩
每次选择当前最优,这是贪心的思想。不一定最终是最优,但是至少效果可用。
用二次曲面来拟合,得到系数矩阵,用二次曲面性质来度量 [Garland & Heckbert 1997]
Given a plane, we can define a quadric Q
$$ Q=(A,b,c)=(nn^T,dn,d^2) $$
measuring squared distance to the plane as
$$ Q(V)=V^TAV+2b^TV+c $$
$$ Q(V)=\begin{bmatrix} x & y&z \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} a^2 &ab &ac \\ ab& b^2&bc \\ ac & bc &c^2 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} x\\ y\\ z \end{bmatrix}+2\begin{bmatrix} ad & bd &cd \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} x\\ y\\ z \end{bmatrix}+d^2 $$
Garland and Heckbert. Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics. Siggraph 1997.
- Sum of quadrics represents set of planes
$$ \sum _i(n_i^TV+d_i)^2=\sum _iQ_i(V)=\begin{pmatrix}\sum _iQ_i \end{pmatrix}(V) $$
- Each vertex has an associated quadric
• Error\((v_i) = Q_i (v_i)\)
• Sum quadrics when contracting \((v_i,v_j) \to v’\)
• Cost of contraction is \(Q(v’)\)
$$ Q=Q_i+Q_j=(A_i+A_j,b_i+b_j,c_i+c_j) $$
- Sum of endpoint quadrics determines v’
• Fixed placement: select \(v_1\) or \(v_2\)
• Optimal placement: choose v’ minimizing \(Q(v’)\)
$$ \nabla Q({V}' )=0\Rightarrow {V}' =-A^{-1}b $$
• Fixed placement is faster but lower quality
• But it also gives smaller progressive meshes
• Fallback to fixed placement if A is non‐invertible
Contracting Two Vertices
- Goal: Given edge e=(\(v_1, v_2\)), find contracted
\(v=(x, y, z)\) that minimizes \(\Delta(v)\):
$$ \partial \Delta / \partial x=\partial \Delta / \partial y=\partial \Delta / \partial z=0 $$
- Solve system of linear normal equations.
$$ \begin{bmatrix} q_{11} &q_{12} &q_{13} &q_{14} \\ q_{21} & q_{22} &q_{23} & q_{24}\\ q_{31} & q_{32} &q_{33} & q_{34}\\ 0& 0 & 0 &1 \end{bmatrix}V=\begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0\\ 0\\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$
If no solution - select the edge midpoint
Visualizing Quadrics
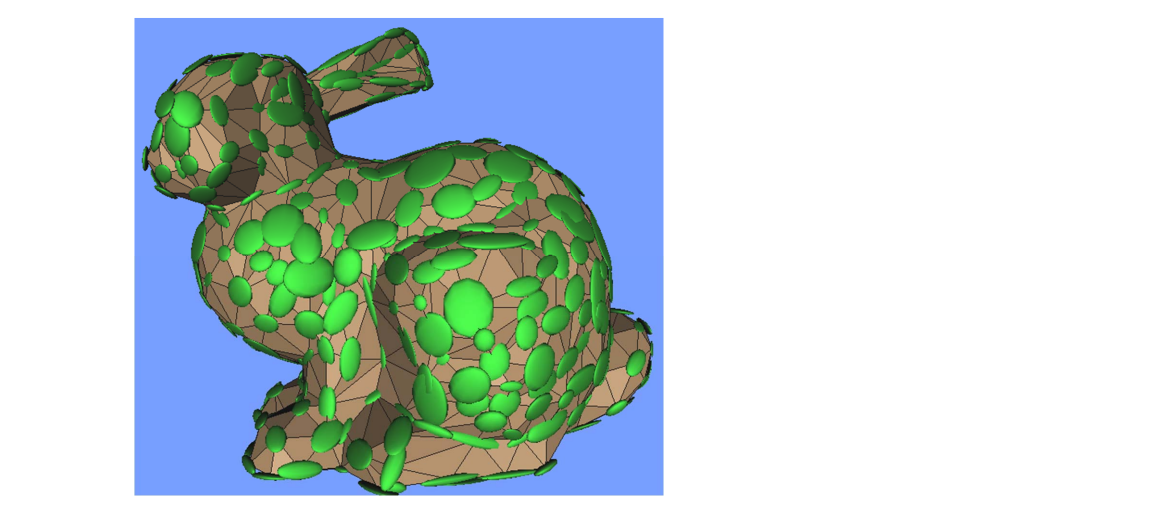
- Quadric isosurfaces
• Are ellipsoids (maybe degenerate)
• Centered around vertices
• Characterize shape
• Stretch in least‐curved directions
简化后的折叠、翻转现象
Selecting Valid Pairs for Contraction
- Edges:
{\((v_1, v_2):(v_1v_2)\). is in the mesh }
- Close vertices:
{\((v_1,v_2):||v_1-v_2||<T\)}
- Threshold T is input parameter

动态优先队列
计算一条边的坍缩点及坍缩误差是一个优化问题,用迭代法来解。因此“遍历-计算”是一个比较耗时的过程。
尤其是使用“遍历-计算-排序-选择-坍缩”的过程坍缩了一条边之后,坍缩过程对被坍缩的边周围的边造成影响,上一轮的“遍历-计算”的结果已经不适用了,不能直接基于此结果做排序和选择。
- 解决方法:
优先队列。动态更新受影响的边。
预处理:遍历-计算-生成队列
循环:取队列top - 坍缩 - 部分点重新计算 - 更新队列部分点
💡 计算出new point的位置后可以再调整一下old point的位置。
Algorithm
- Compute \(Q_v\) for all the mesh vertices
- Identify all valid pairs
- Compute for each valid pair (\(v_1, v_2\)) the contracted vertex \(v\) and its error \(\Delta(v)\)
- Store all valid pairs in a priority queue (according to \(\Delta(v)\))
- While reduction goal not met
• Contract edge (\(v_1, v_2\)) with the smallest error to \(v\)
• Update the priority queue with new valid pairs
Artifacts by Edge Collapse
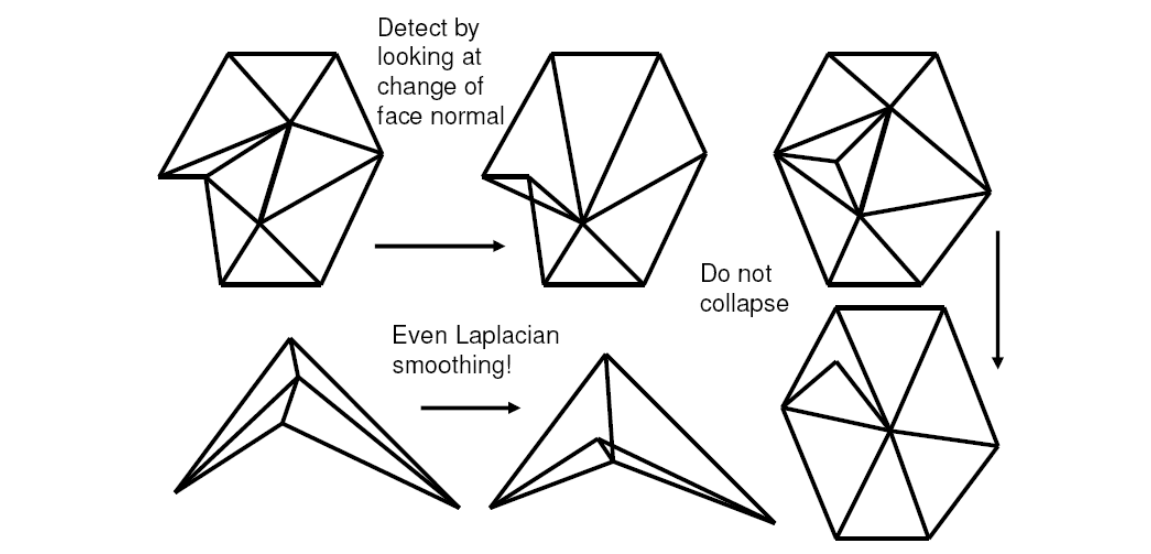
收缩后会出现边的翻转
Pros and Cons
- Pros
• Error is bounded
• Allows topology simplification
• High quality result
• Quite efficient - Cons
• Difficulties along boundaries
• Difficulties with coplanar planes
• Introduces new vertices not present in the original mesh
Appearance‐based metrics
- Generalization required to handle appearance properties
- color
- texture
- normals
- etc.
- Treat each vertex as a 6‐vector [x,y,z,r,g,b]
- Assume this 6D space is Euclidean
- Of course, color space is only roughly Euclidean
- Scale xyz space to unit cube for consistency
- Assume this 6D space is Euclidean
Generalized Quadric Metric
| Vertex | Dimension | |
|---|---|---|
| Color | [x y z r g b] | 6x6 quadrics |
| Texture | [x y z s t] | 5x5 quadrics |
| Norma | [x y z u v w] | 6x6 quadrics |
| Color+Normal | [x y z r g b u v w] | 9x9 quadrics |
$$ Q(V)=V^TAV+2b^TV+C $$
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/