Shape Morphing
要解决的问题
给定头尾模型,生成中间的模型,常用于做关键帧动画。

- Input: two meshes source & target
• Frames at \(t_0\) and \(t_n\) - Output: sequence of intermediate meshes
• Frames \(t_1\) to \(t_{n‐1}\)
• For each point on source/target model specify location at time \(t_i\) consistent with source & target
Wraping VS Morphing
- Warping: Unary Op
• Given Object A and F(t), find Object B
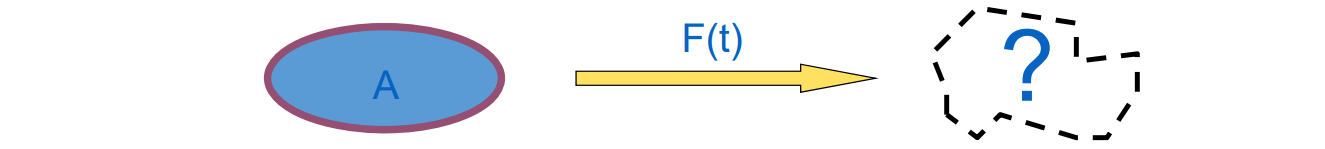
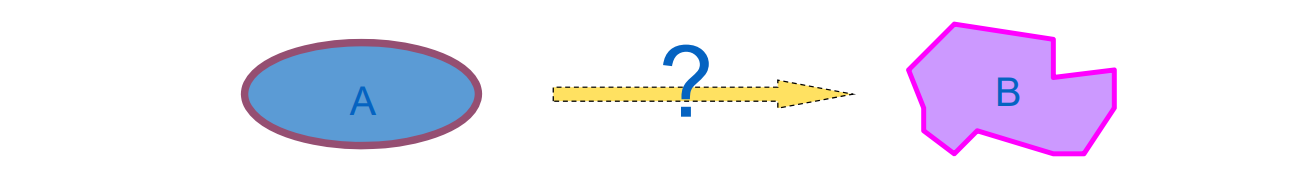
- Morphing: Binary Op
• Given Object A and Object B, find F(t)
Rules for Good Morphing
- Natural
- Keep as much as possible of the two shapes during the transformation
- Volume, curvature, area, etc...
- Subjective aesthetic criteria
- Keep as much as possible of the two shapes during the transformation
- User control
- intuitive
- not too heavy
- can be adapted to user's knowledge
Two Sub‐Problems
-
Correspondence problem
- Compatible meshes
- For each point on source/target meshes find corresponding point on second mesh = Parameterization

-
Path problem
- Inbetween shapes
- Specify trajectory in time for each point
- For mesh – specify vertex trajectory
1. Vertex Correspondence
目标
Each vertex on source mesh mapped to vertex on target (and vice versa)
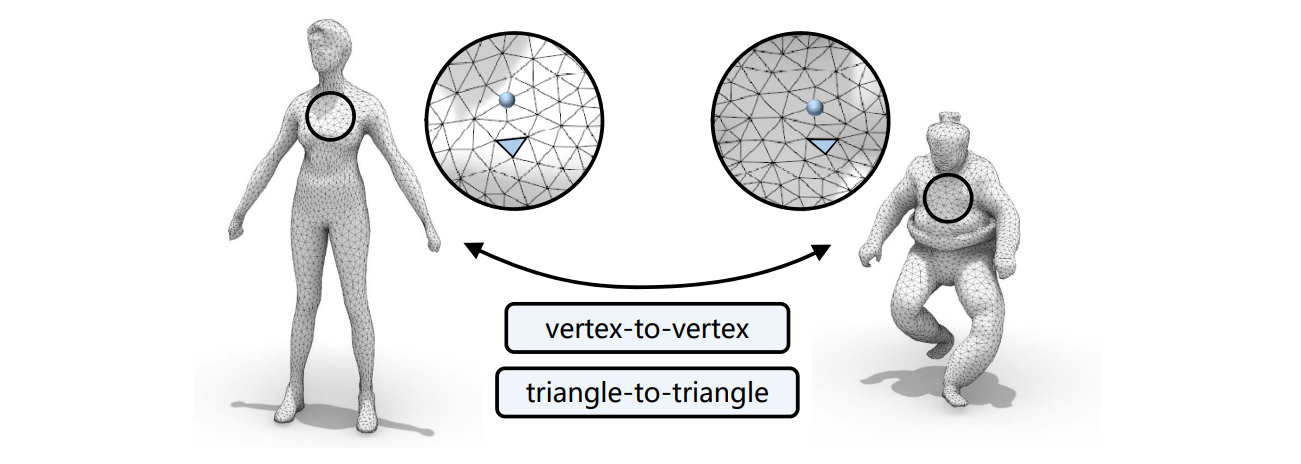
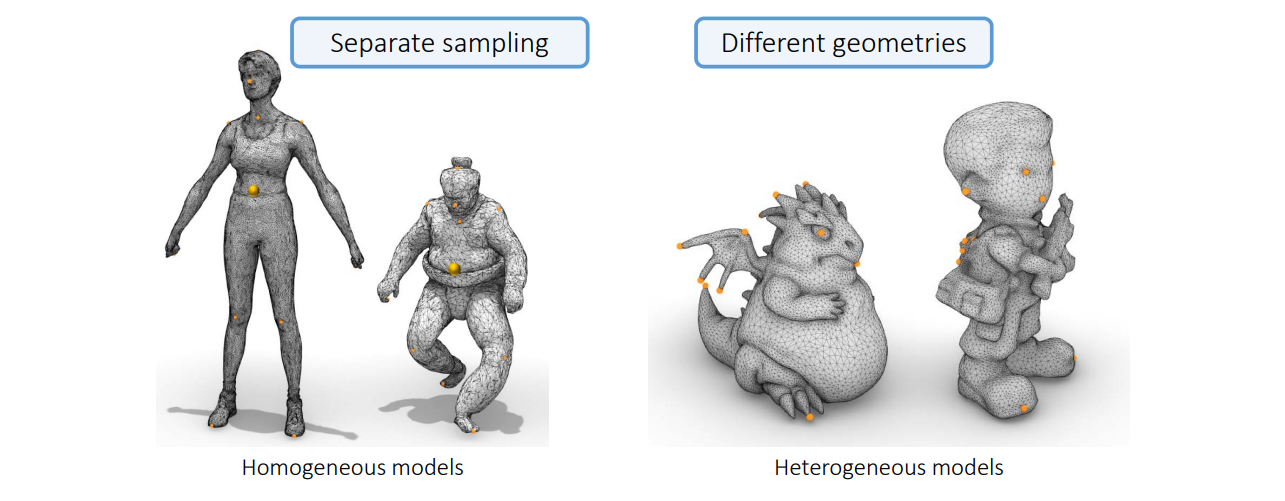
挑战

1.1 Parameterization
To compute map between source mesh S and target mesh T parameterize both on common domain D:
$$ F_s:S \to D\\ F_t:S \to D\\ F_{st}:F_t^{-1} F_s $$
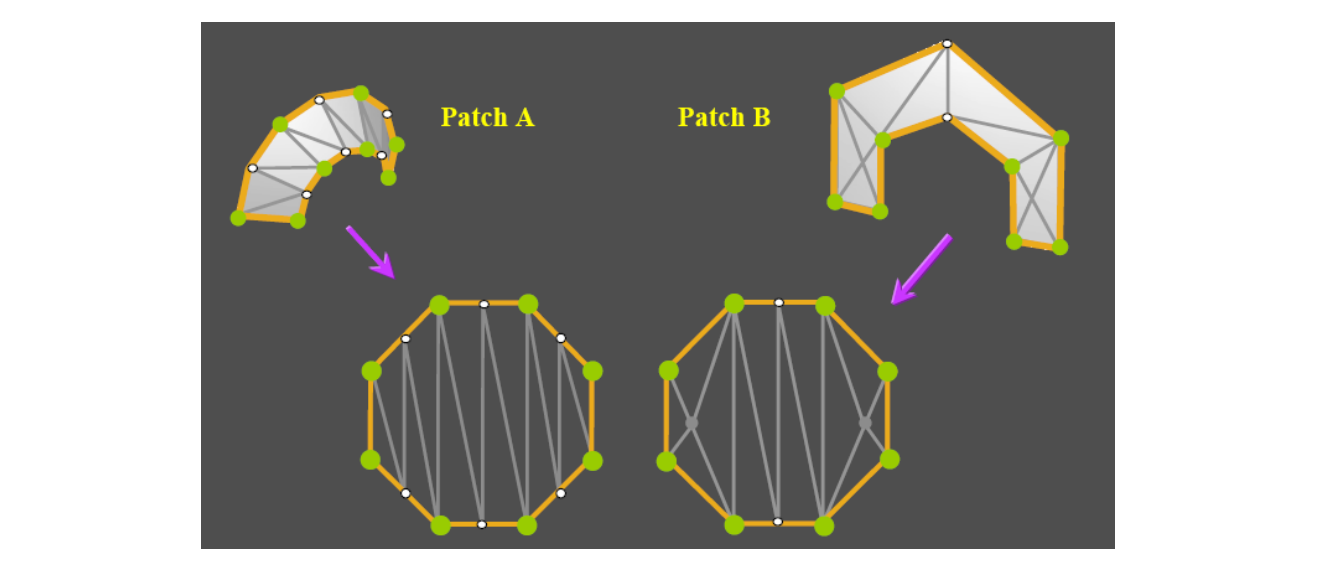
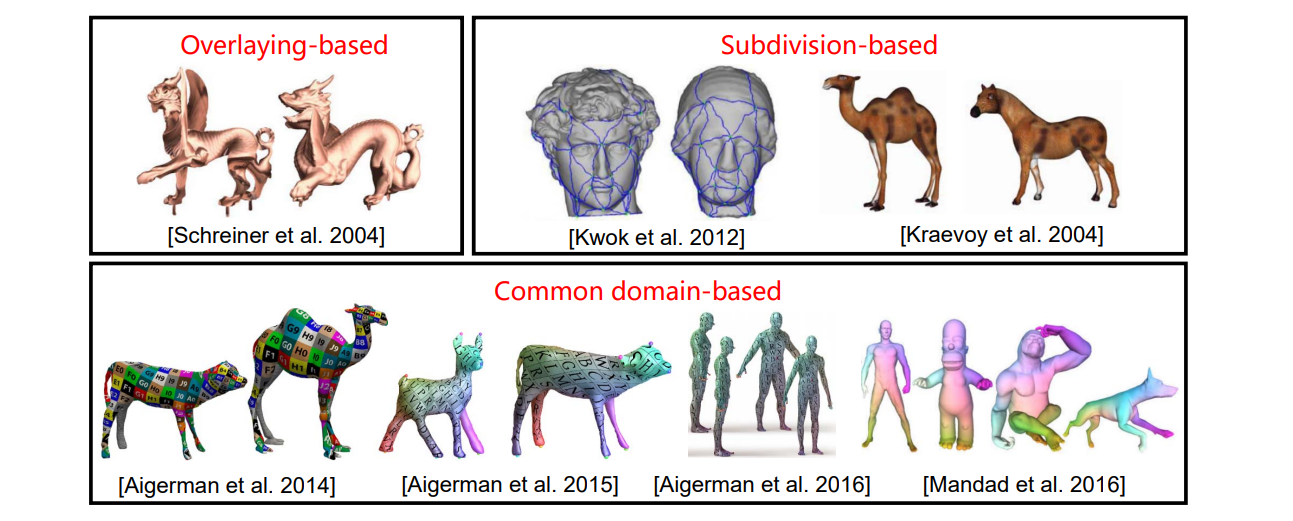
Common domain options
- 2D patch(es) – works for genus 0 + boundary
- Use convex boundary (why?)
 | 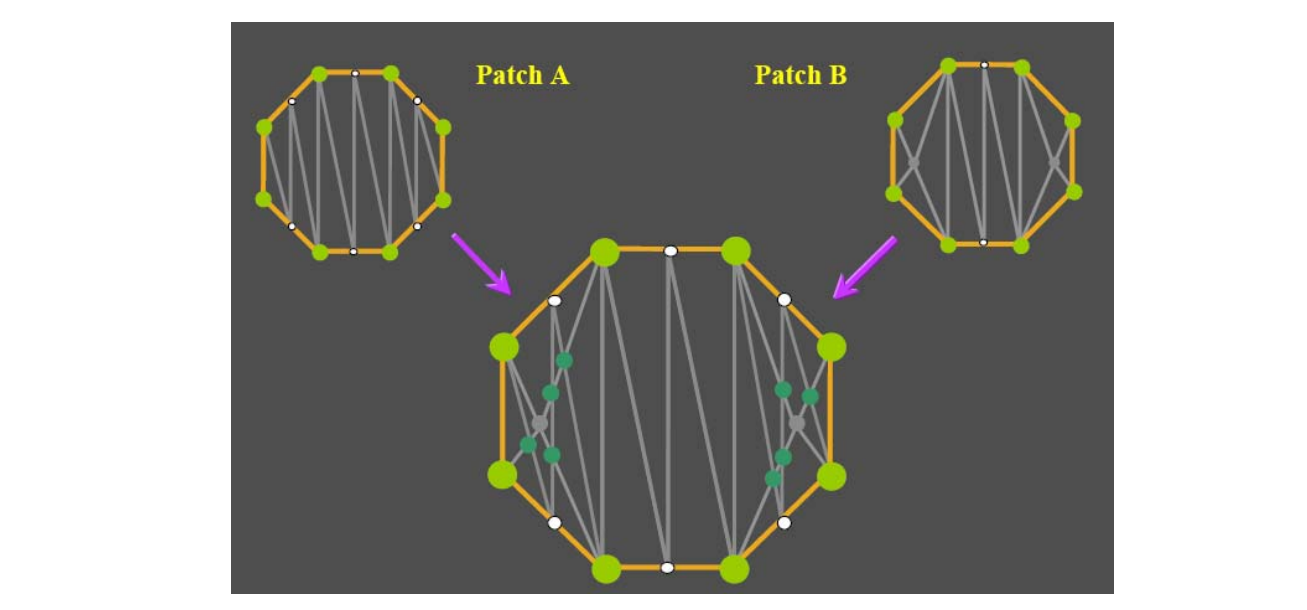 |  |
- Sphere
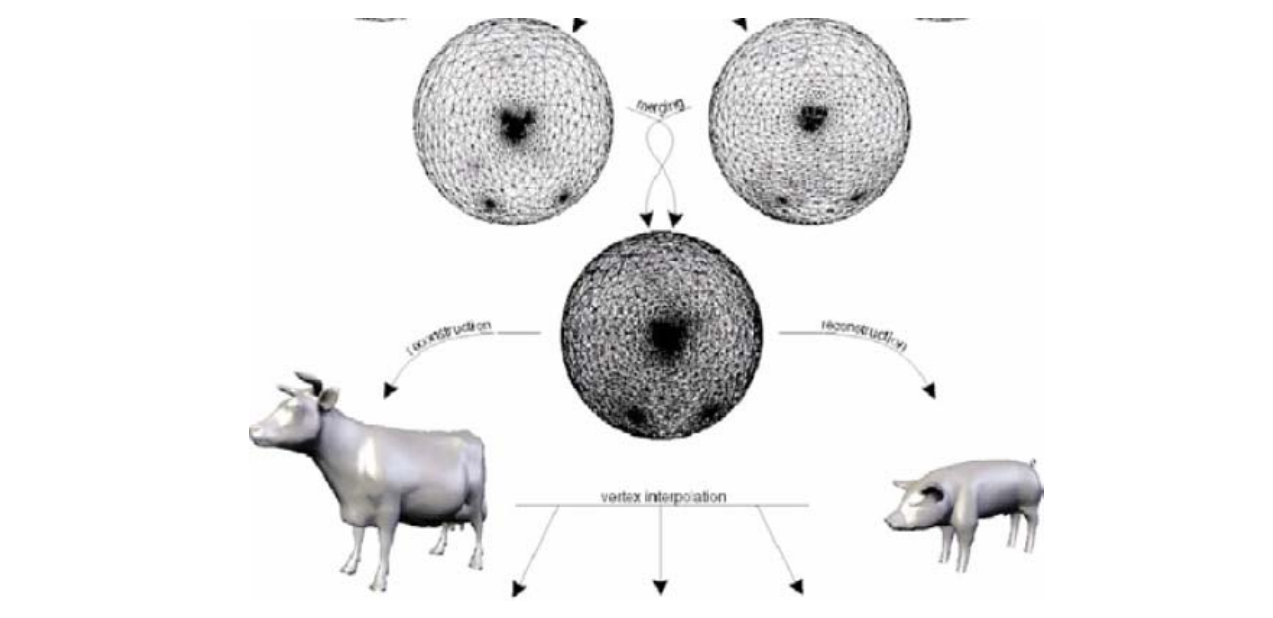
- Base mesh
Lee et al. 1999
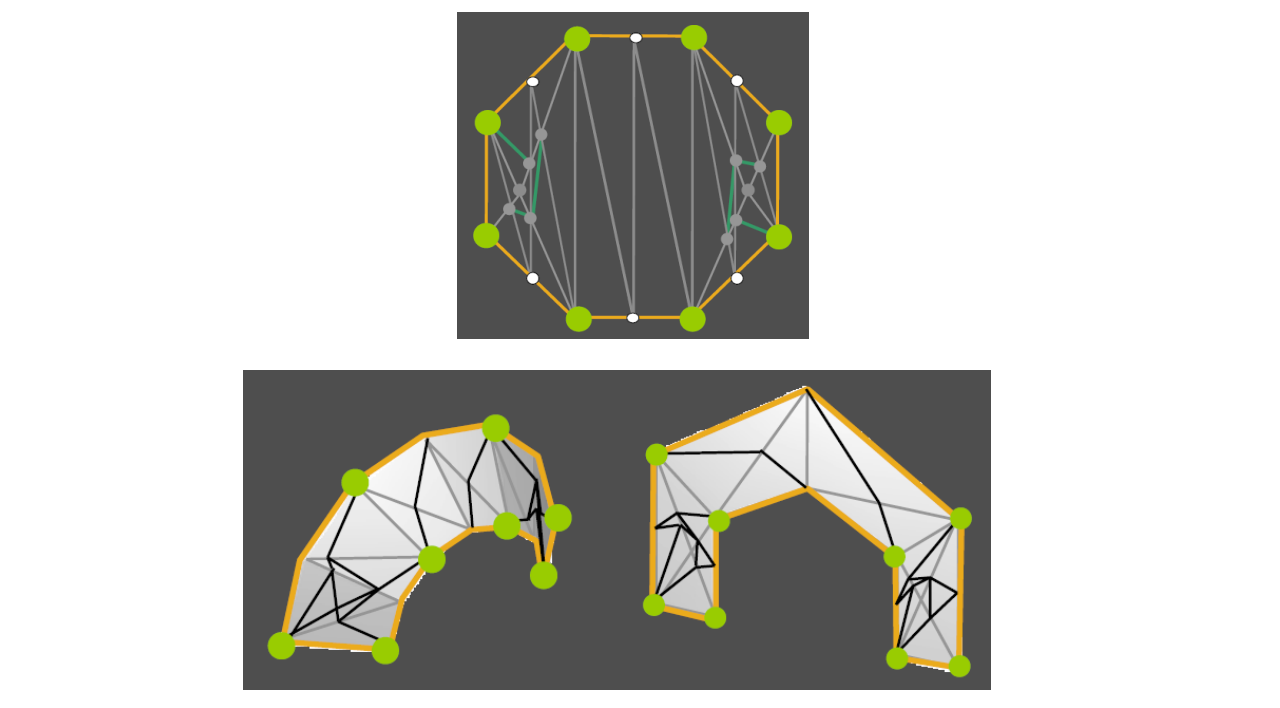
1.4 Decomposition Based
[Shlafman et al. 2002]
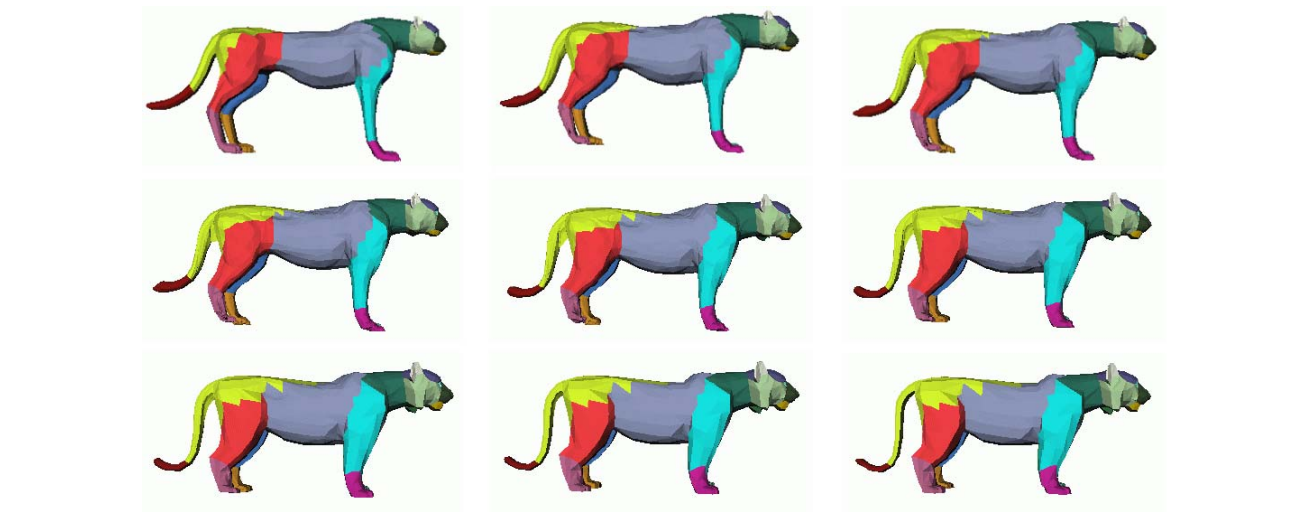
分解成部分,每个部分分别对应。
大问题分解成小问题
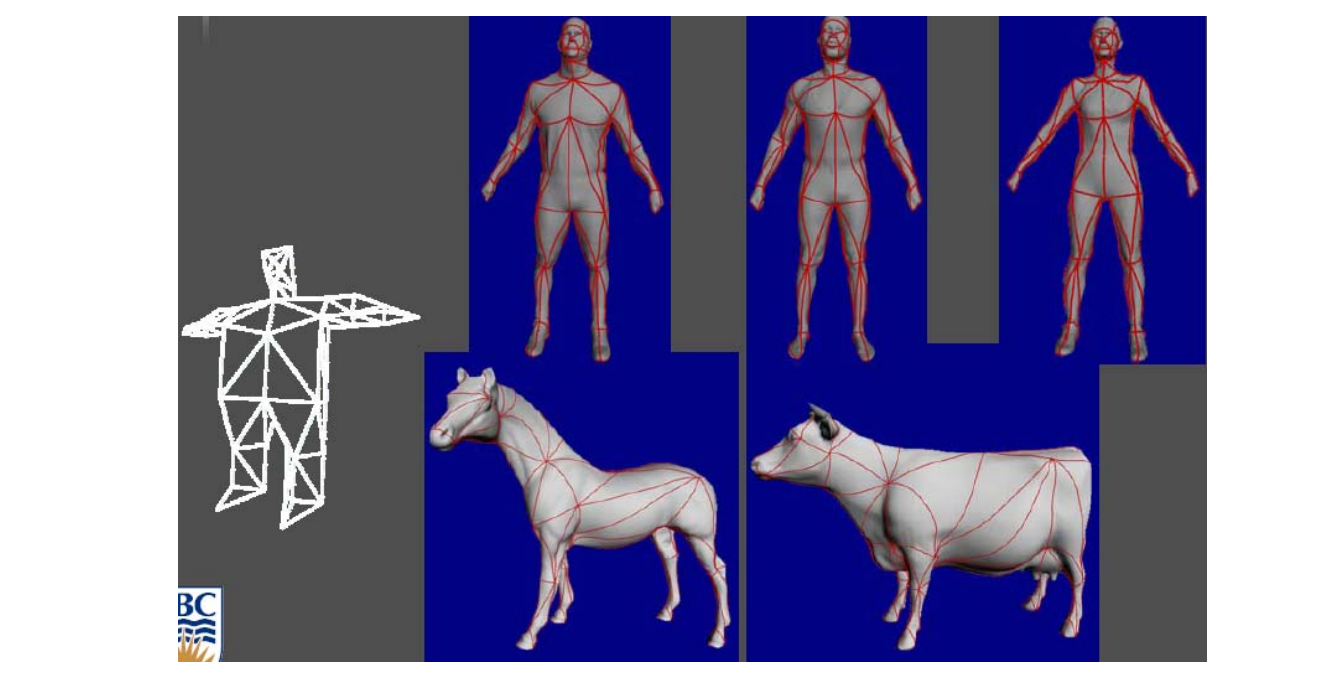
1.5 Component Based
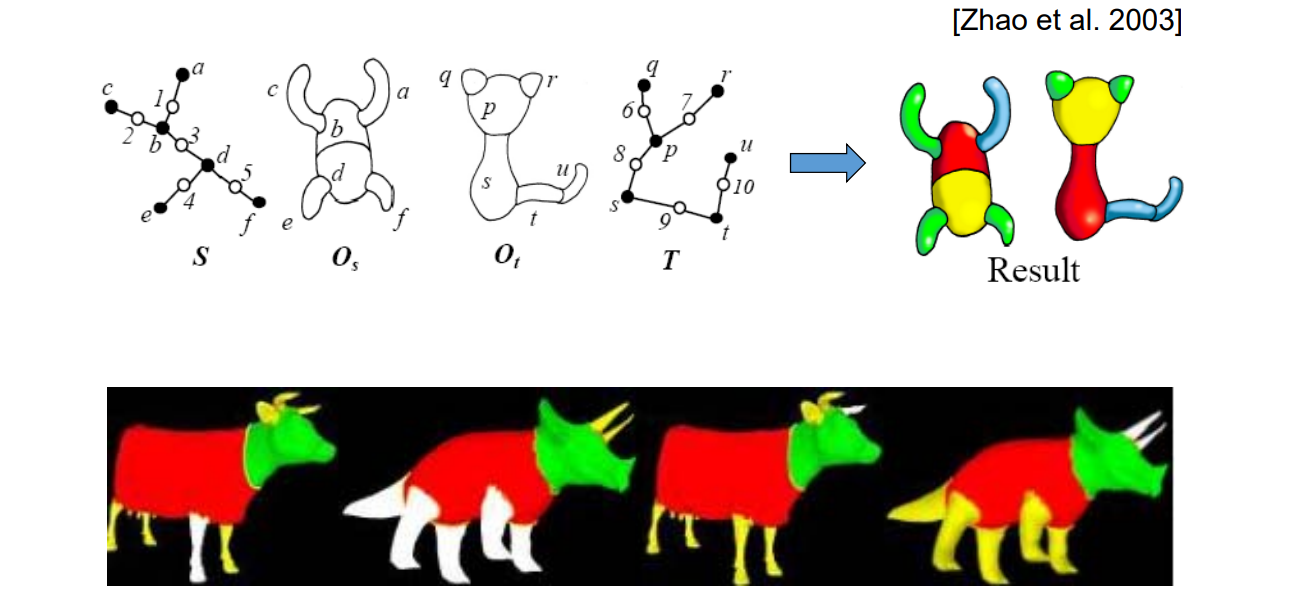
1.6 Many Recent Works
mapping问题,网络A映射到网络B,使得映射后扭曲极小
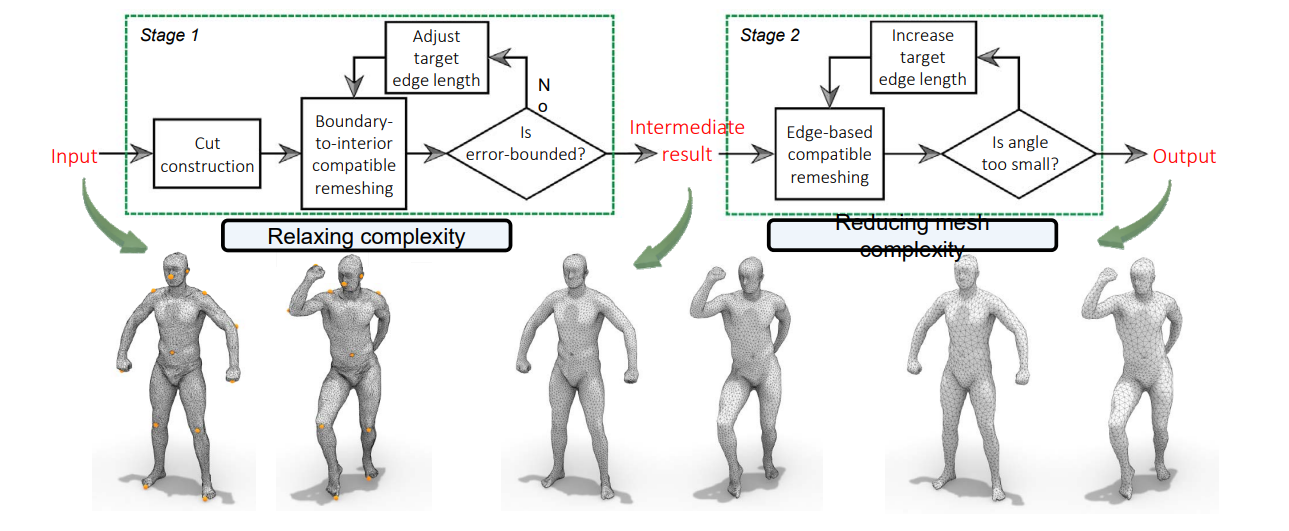
1.7 Error‐Bounded Compatible Remeshing
Yang et al. Error‐Bounded Compatible Remeshing. Siggraph 2020.
• Optimization based method
1.8 Different Topologies
[DeCarlo et al. 1996]
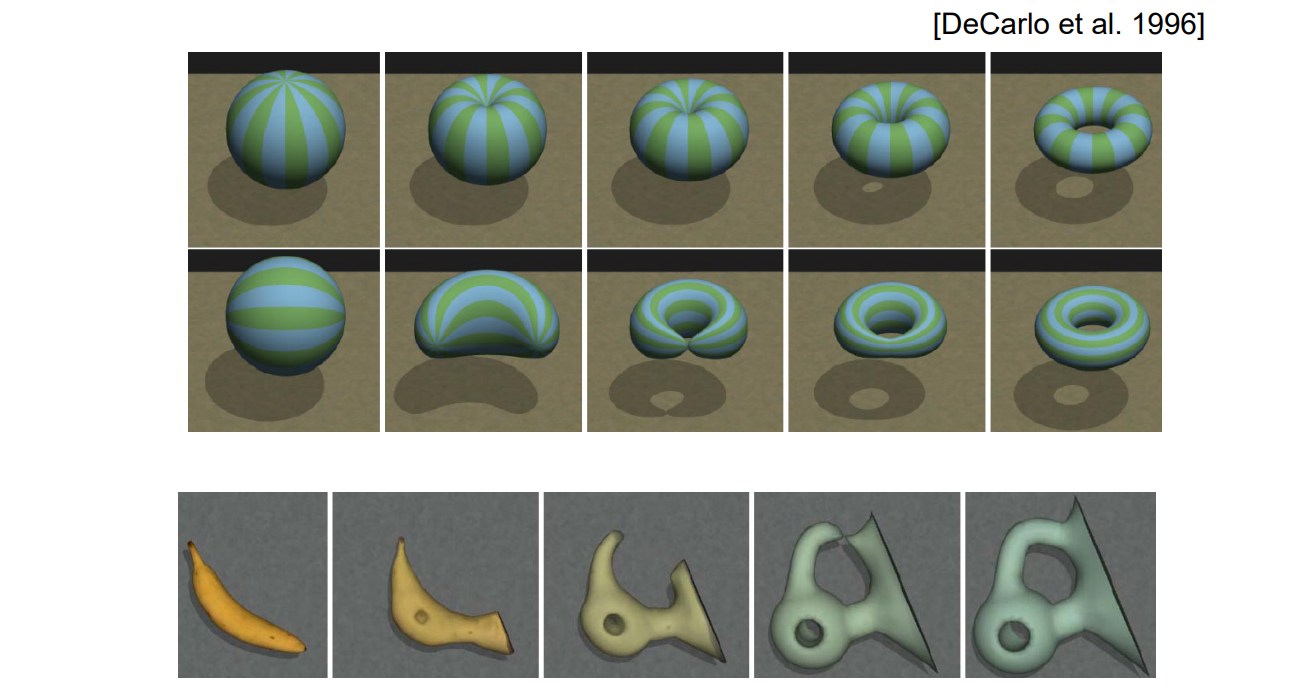
More: Correspondences between planar shapes – Matching
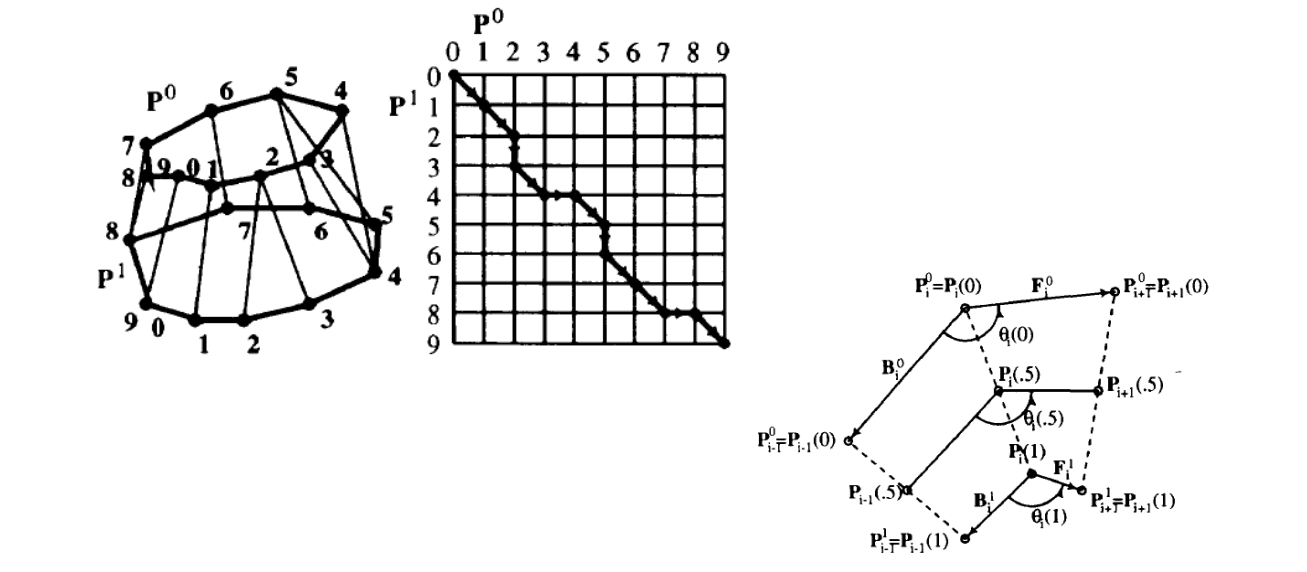
• Physically Based Method [Sederberg et al. 1992]
• Curve Aligning [Sebastian et al. 2003]
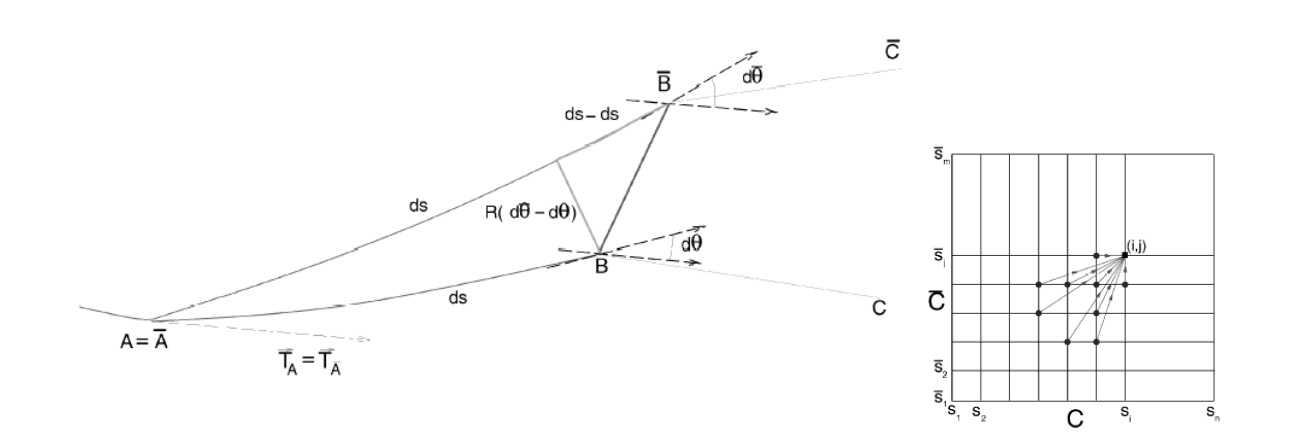
$$ \mu[g]=\int_{C}\left|\frac{\partial}{\partial s}(\bar{C}(\bar{s})-C(s))\right|^{2} d s+R \int_{C}(\kappa(s)-\bar{\kappa}(\bar{s}))^{2} d s $$
• Perceptually Based Method [Liu et al. 2004]
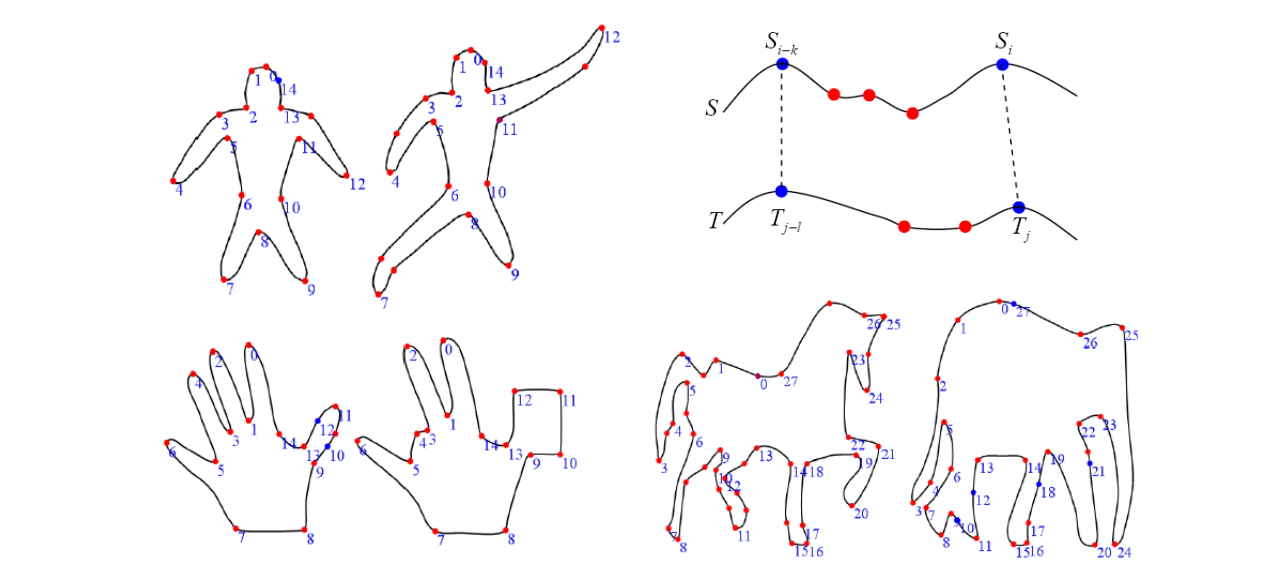
2. Vertex Path (Trajectory)
-
Input:
• All vertices on source & target have one‐to‐one correspondence with each other
• Each vertex has two 3D coords vFc1 (source) and vFc2 (target) -
Output: generate the intermediate shapes from two shapes

Simplest Method: Linear Interpolation
- Linear interpolation between corresponding points
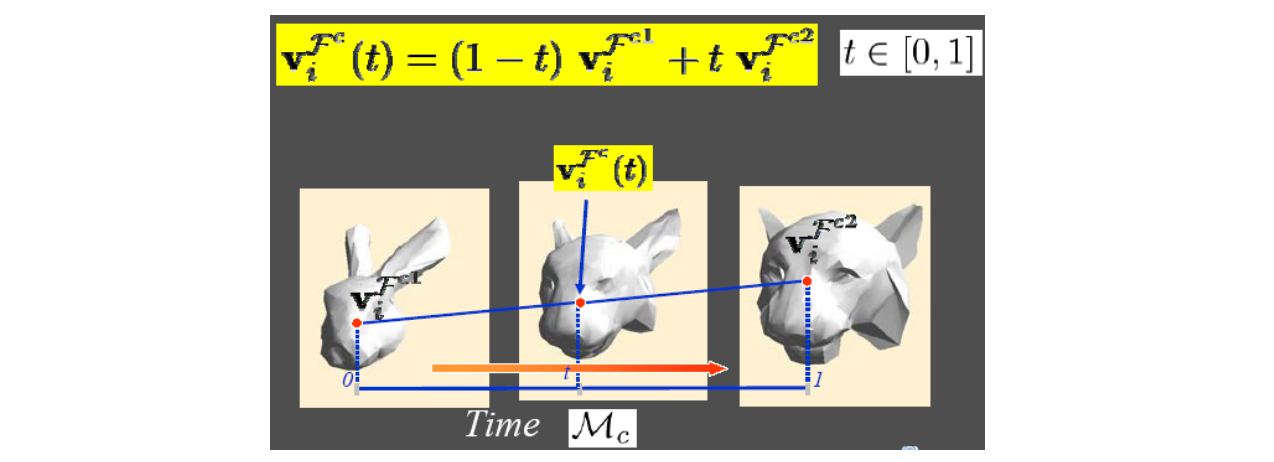
优点:Work well for many cases,Simple and easy
缺点:Shrinkage
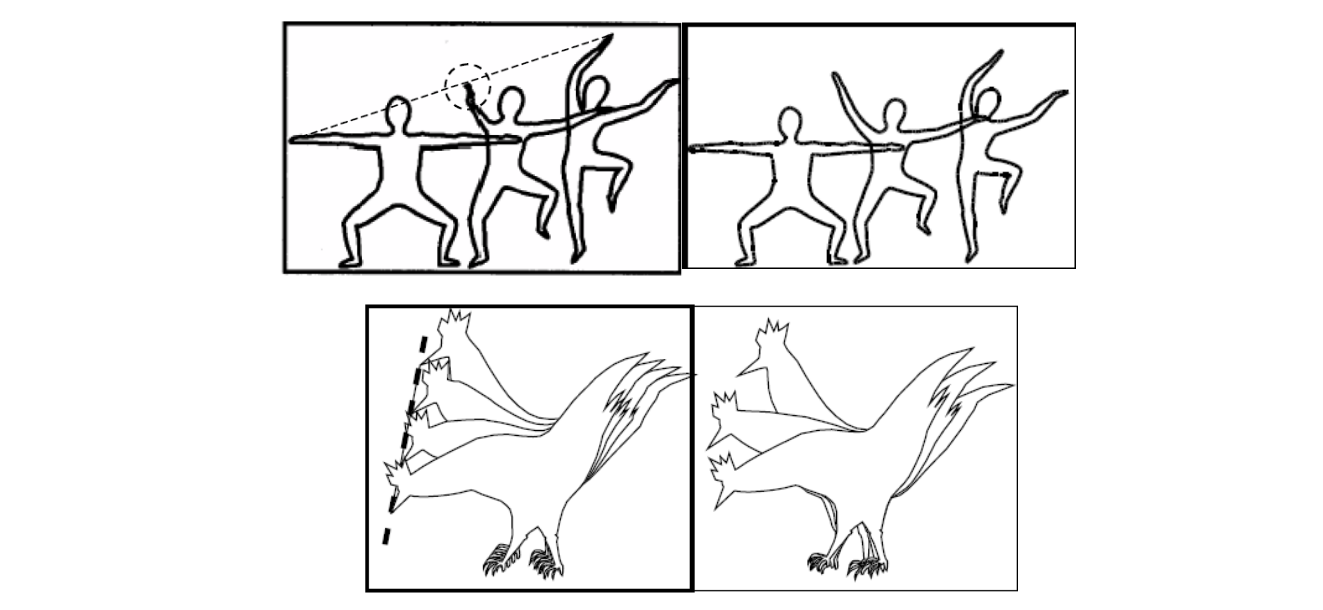
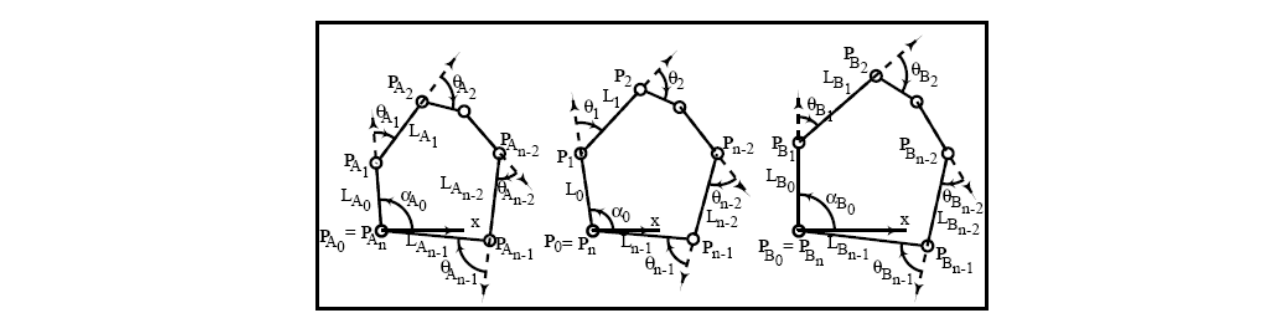
Intrinsic Approach
Sederberg et al. 1993
不插值顶点,而是插值多边形的边长和夹角
Fourier Approach
插件付里叶系数
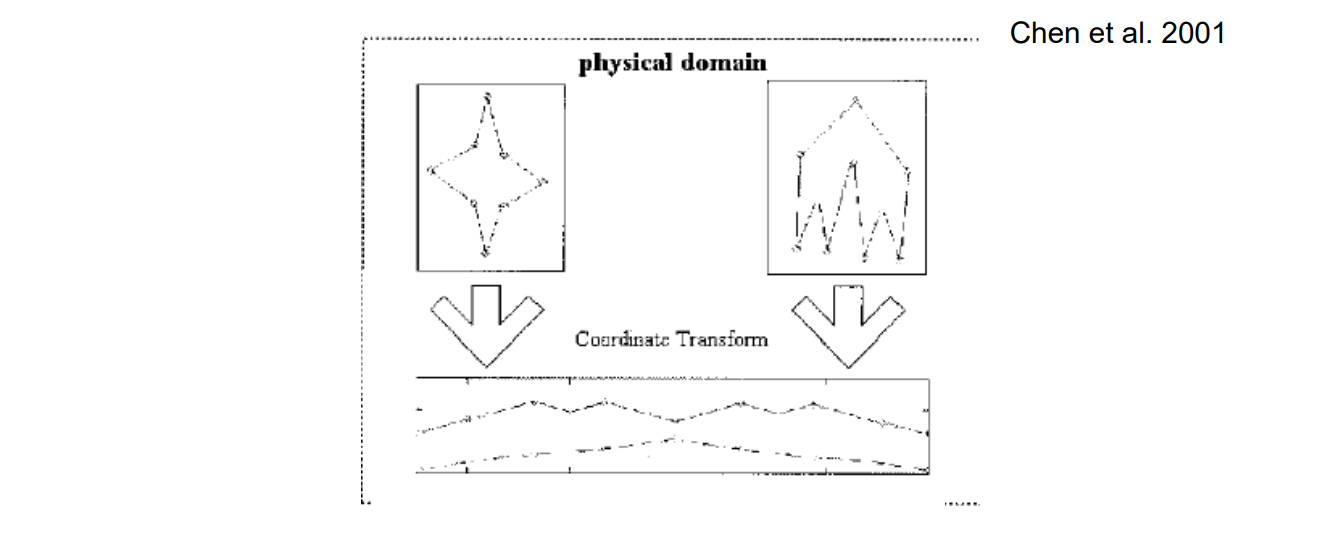
$$ \begin{array}{l} \begin{bmatrix}x(t) \\y(t) \end{bmatrix} \\ =\begin{bmatrix}a_0 \\c_0 \end{bmatrix}+ {\textstyle \sum_{k=1}^{\infty }} \begin{bmatrix} a_k &b_k \\ c_k &d_k \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}\cos(2\pi kt) \\ \sin(2\pi kt) \end{bmatrix} \ \end{array} $$
Wavelet Approach
Zhang et al. 2000
• Wavelet decomposition
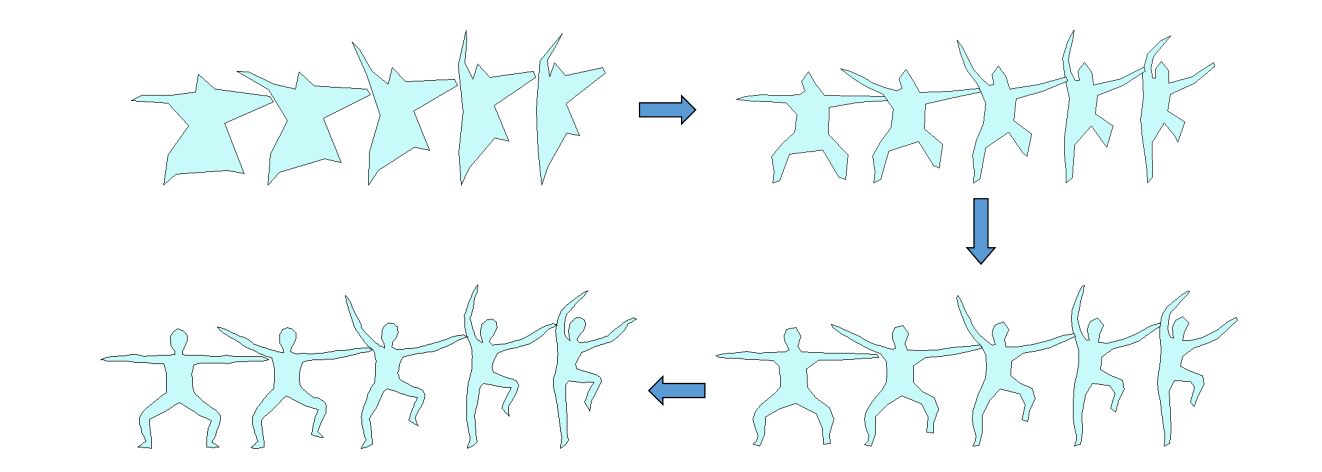
Star Skeleton Representation
[Shapira et al. 1995]
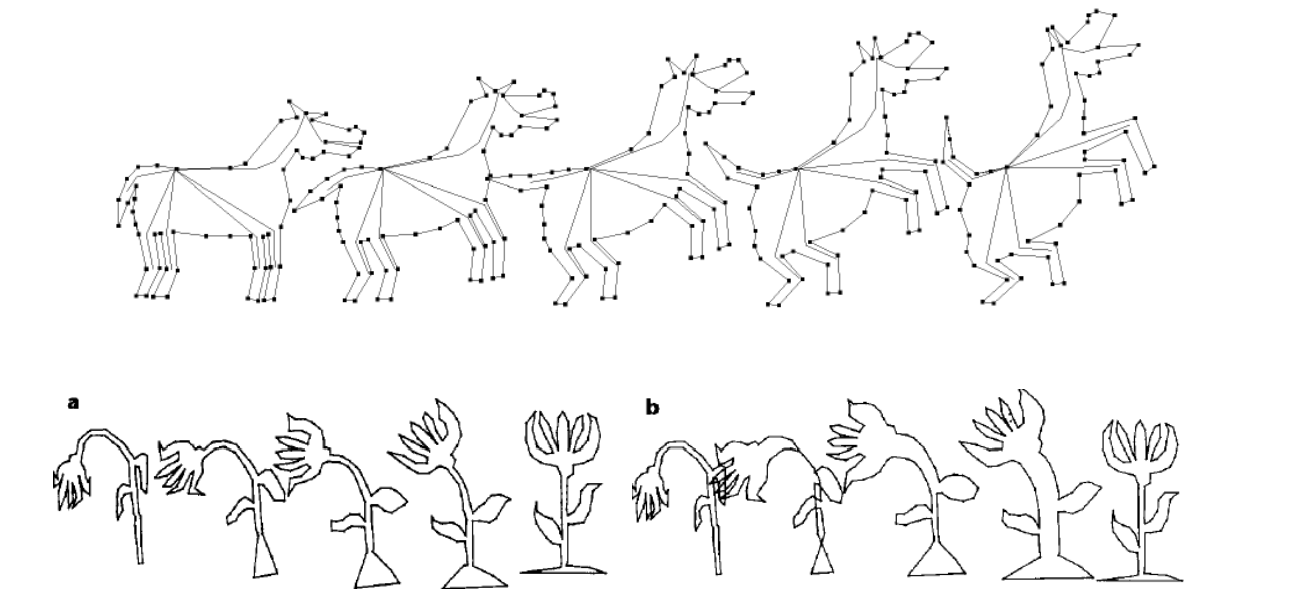
Interior Based Approach
不插值顶点,而是插值三角形的仿射变换(旋转和平移)
好处是能同时进行纹理的插值
- Based on compatible triangulation
• [Gotsman and Surazhsky, 1999‐2001]
• As‐rigid‐as‐possible [Alexa et al. 2000]
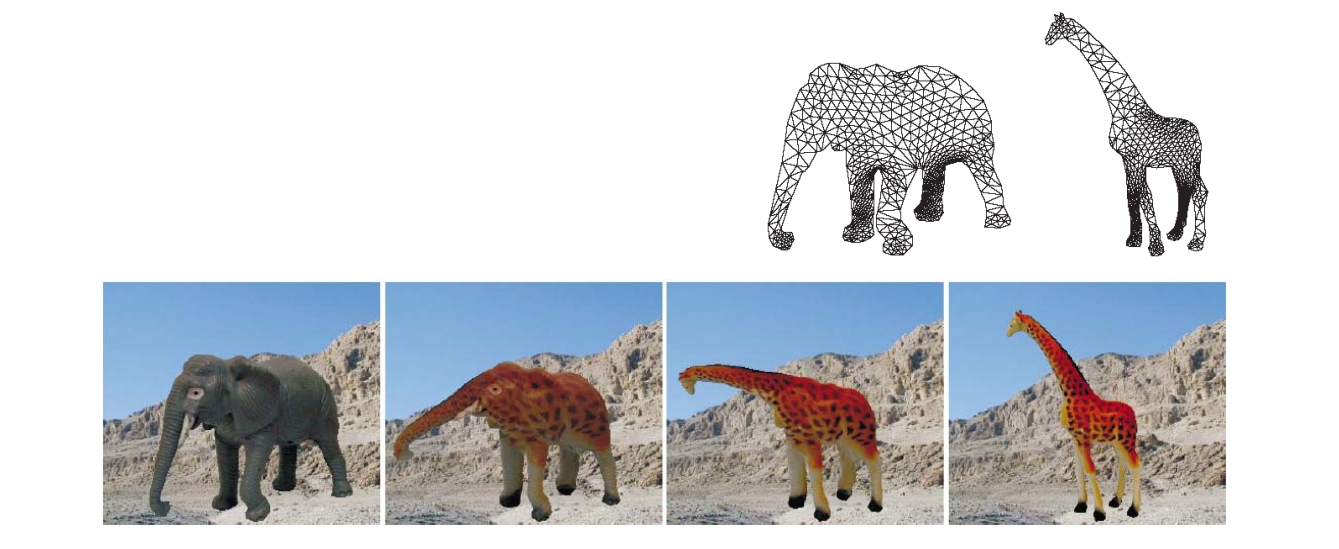
Morphing between Different Topologies
Liu et al. 2005

Implicit Approaches
Construct a 4D function which interpolates two shapes (with iso‐value 0 and 1 respectively)
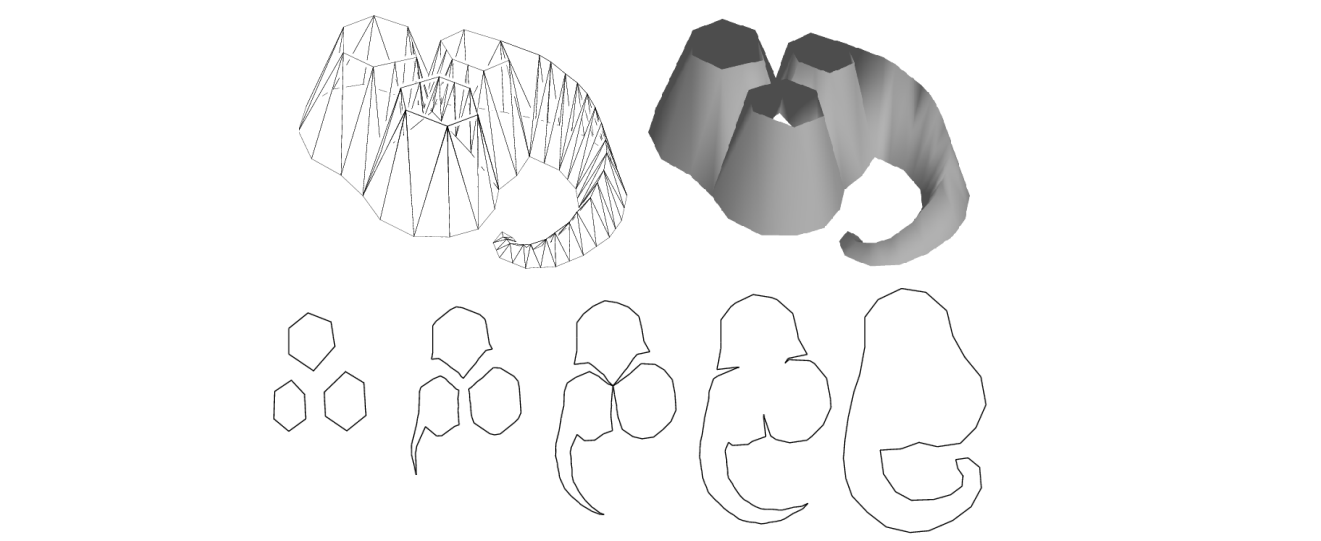
截面就是插值结果
优点是不需要找对应关系
缺点是不可控制
Distance Field
[Cohen-Or et al. 1998]
• Distance field of a shape
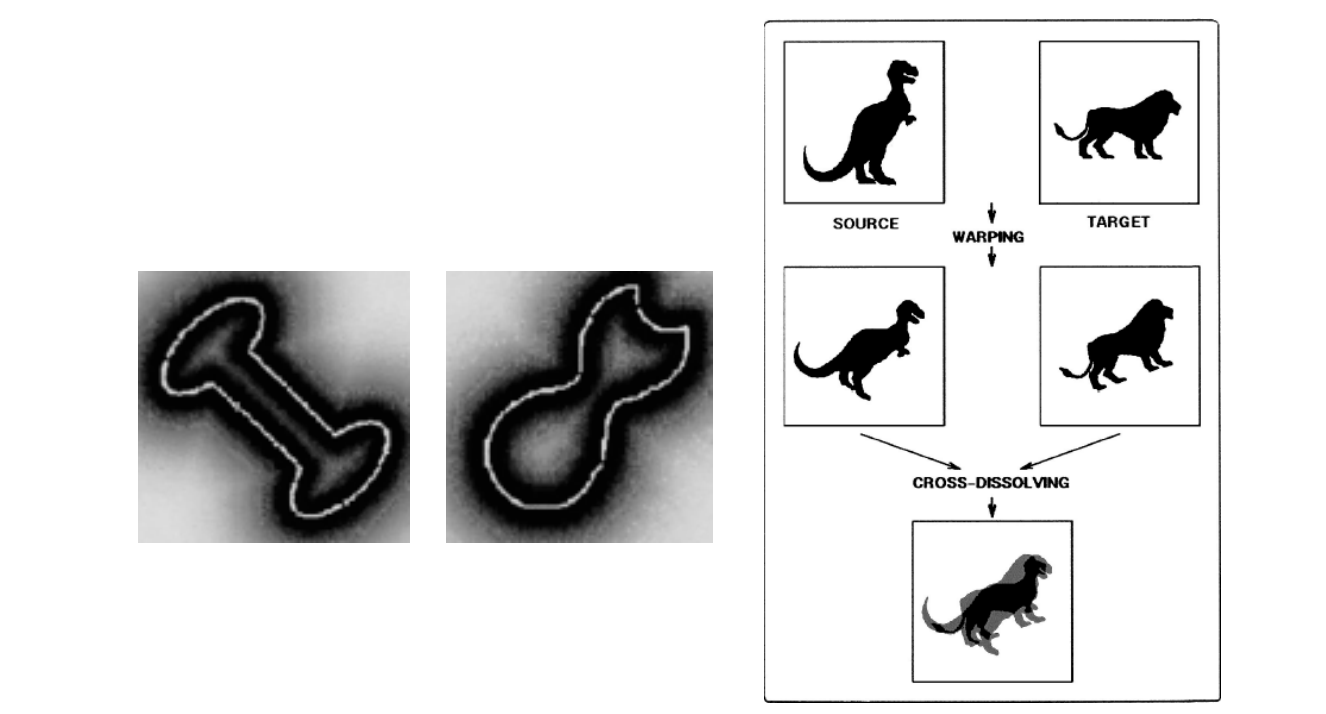
Variational Implicit Function
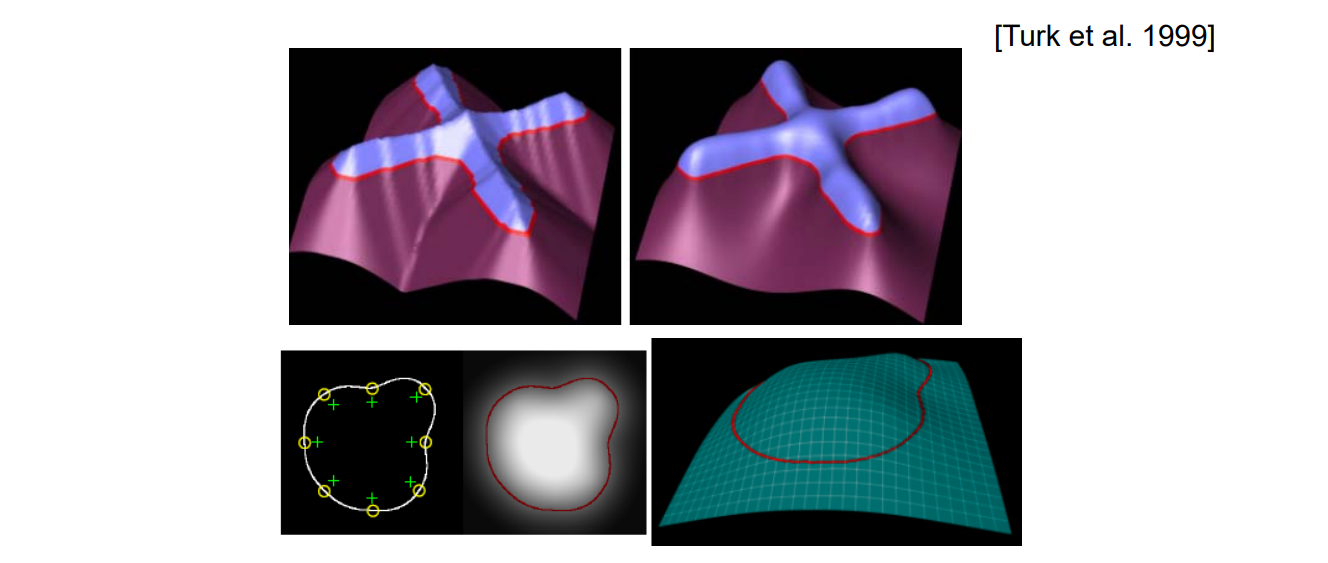
$$ f(X)=\sum_{j=1}^{n} d_j\phi (X-C_j)+P(X) $$
用RBF构造插值函数
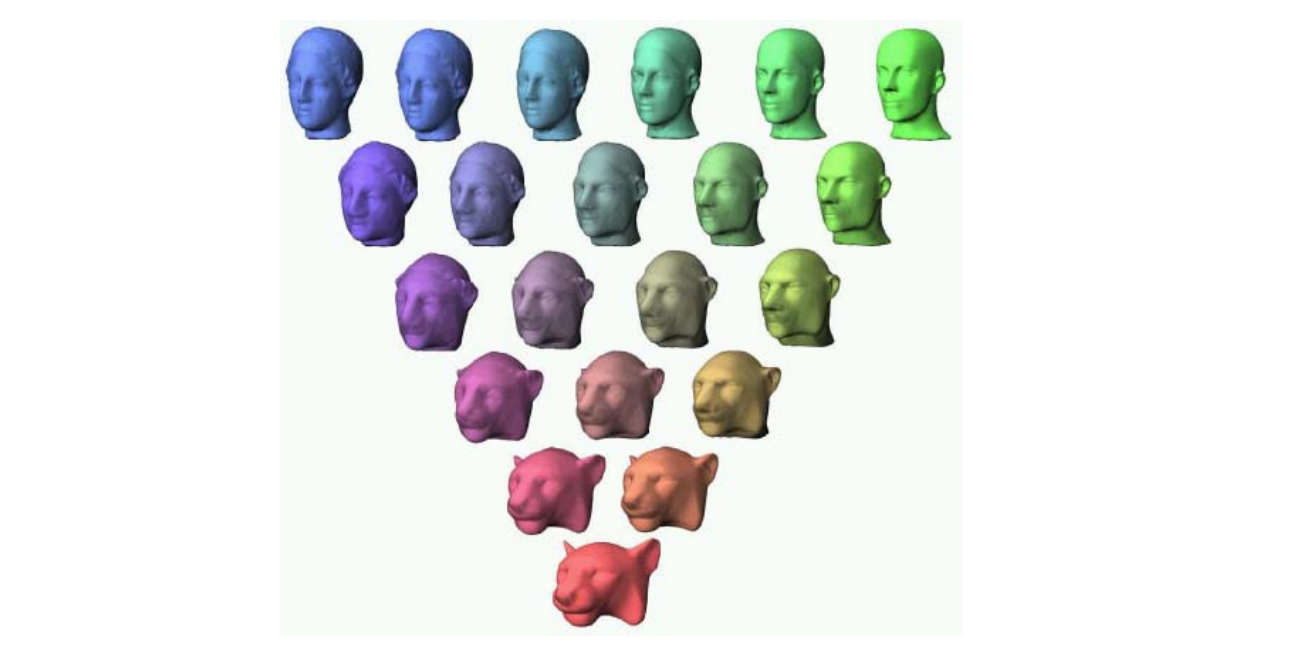
Polymorph: Morphing between multiple shapes
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。 https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES102_mdbook/