P32
Impact Zone Optimization
The goal of impact zone optimization is to optimize \(\mathbf{x}^{[1]}\) until it becomes intersection-free. (This potentially suffers from the tunneling issue, but it’s uncommon.)
tunneling issue 是指:\(\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}\) 离两个安全区都比较近。\(\mathbf{x} ^{[0]}\) 在其中一个安全区,而\(\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}\) 被优化到了另一个安全区。表现出的现象为穿透。
带约束优化问题
目标优化:
$$ \bar{\mathbf{x} }^{[1]}\longleftarrow \mathrm{argmin} _\mathbf{x} \frac{1}{2} ||\bar{\mathbf{x} }-\mathbf{x}^{[1]}||^2 $$
约束:
$$ \text{such that} \begin{cases} C(\mathbf{x} )=−(\mathbf{x} _3−b_0\mathbf{x} _0−b_1\mathbf{x} _1−b_2\mathbf{x} _1)\cdot \mathbf{N} ≤0 & \text{ For each detected vertex-triangle pair } \\ C(\mathbf{x} )=−(b_2\mathbf{x} _2+b_3\mathbf{x} _3−b_0\mathbf{x} _0−b_1\mathbf{x} _1)\cdot \mathbf{N}≤0 & \text{ For each detected edge-edge pair } \end{cases} $$
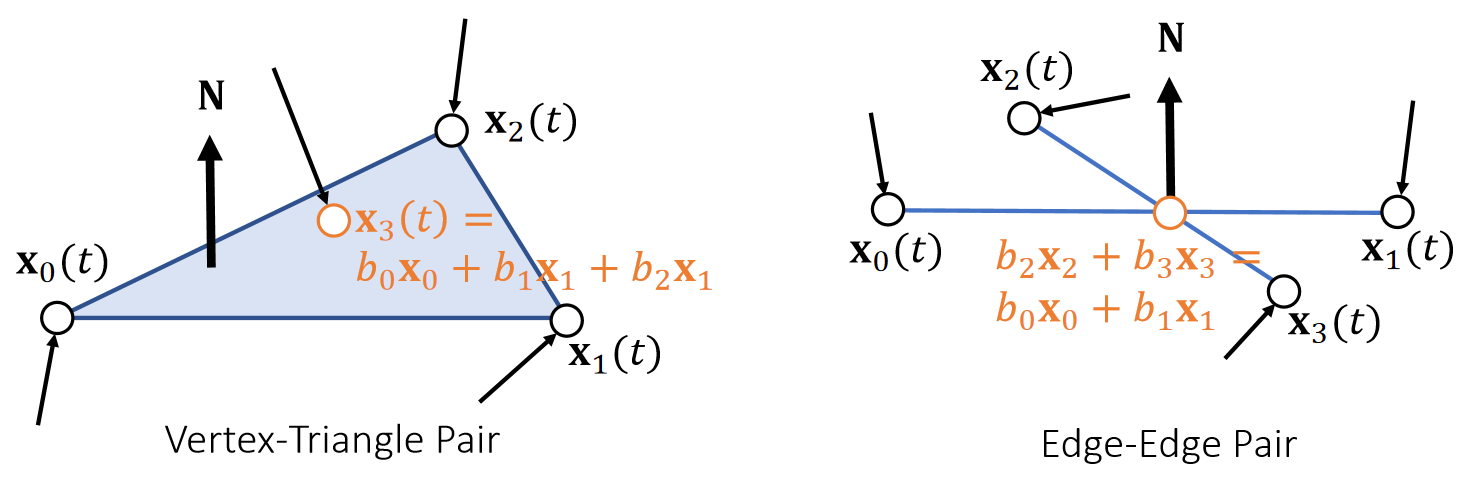
这是一个带约束优化问题。
带约束优化问题转为无约束优化问题
P36
We can then convert it into an unconstrained form:
$$\bar{\mathbf{x} } {[1]}\longleftarrow \text{argmin}_{x,λ}(\frac{1}{2} ||\mathbf{x} −\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}||^2+\frac{ρ}{2} ||\text{max}(\tilde{C} (\mathbf{x} ))||^2−\frac{1}{2ρ}||\mathbf{λ} ||^2) $$
$$ \tilde{C} (\mathbf{x})= \text{max}(\mathbf{C} (\mathbf{x} )+\mathbf{λ} /ρ) $$
Augmented Lagrangian:
\(\mathbf{x} ^{(0)} \longleftarrow \mathbf{x} ^{[0]}\)
\(\mathbf{λ \longleftarrow 0} \)
For \(k=0…K\)
$$\mathbf{x} ^{(k+1)} \longleftarrow \mathbf{x} ^{(k)}−α∇(\frac{1}{2} ||\mathbf{x} −\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}||^2+\frac{ρ}{2} ||\text{max}(\tilde{C} (\mathbf{x} ))||^2−\frac{1}{2ρ}||\mathbf{λ} ||^2)$$
\(λ\longleftarrow ρ\tilde{C} (\mathbf{x} )\)
\(\bar{\mathbf{x} } ^{[1]}\longleftarrow \mathbf{x} ^{(k+1)}\)
Tang et al. 2018. I-Cloth: Incremental Collision Handling for GPU-Based Interactive Cloth Simulation. TOG. (SIGGRAPH Asia)
P37
About Impact Zone Optimization
-
Fast per iteration
- Only have to deal with vertices in collision.
-
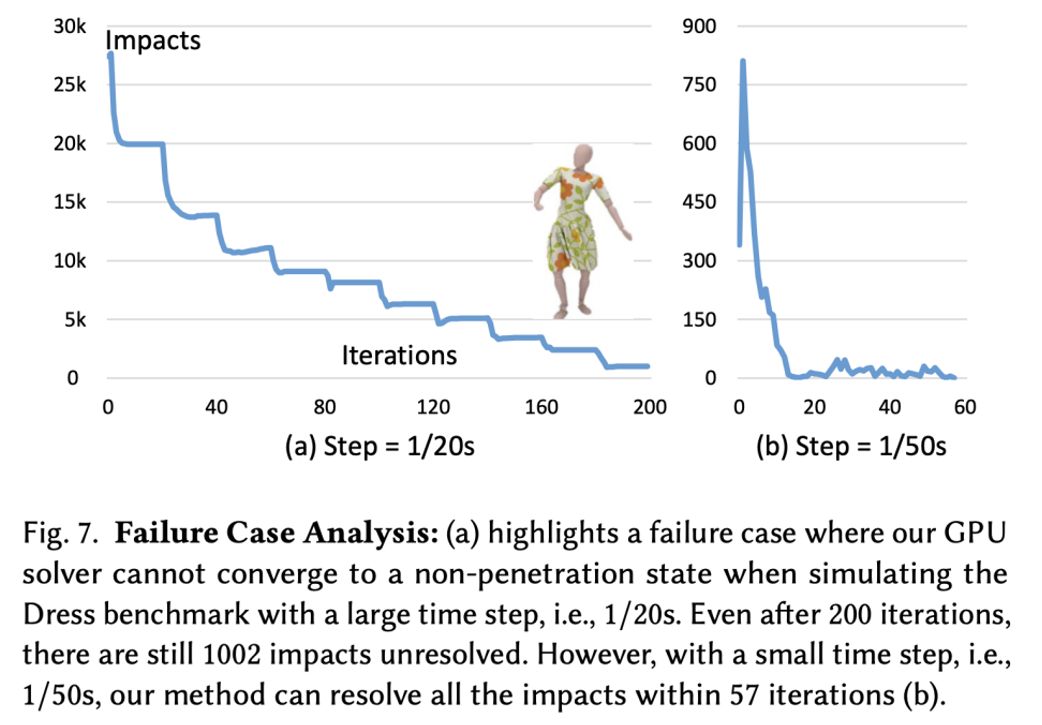
Convergence sensitive to \(||\mathbf{x} ^{[0]}−\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}||^2\), or the time step \(∆t\)
- Can take many iterations to, or never achieve intersection-free.
- Easy solution is to reduce \(∆t\), but that increases total costs.
P33
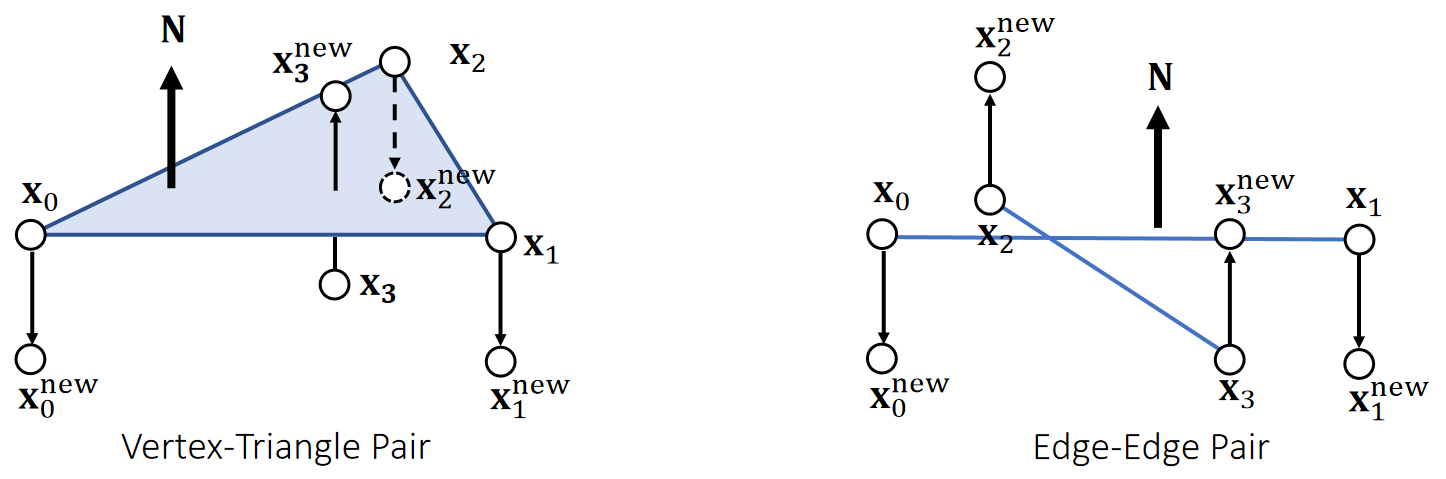
Every pair gives new positions to the involved vertices. We can combine them together in a Jacobi, or Gauss-Seidel fashion, just like position-based dynamics.
P34
After-Class Reading (Cont.)
Bridson et al. 2002. Robust Treatment of Collisions, Contact and Friction for Cloth Animation. TOG (SIGGRAPH).
Relative simple explicit integration of cloth dynamics
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。
https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES103_mdbook/