P42
Basic Concepts
1st-Order Derivatives
值是实数,变量是矢量
If \(f(\mathbf{x} )\in \mathbf{R} \), then \(df=\frac{∂f}{∂x}dx+\frac{∂f}{∂y}dy+\frac{∂f}{∂z}dz=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{∂f}{∂x} & \frac{∂f}{∂y} &\frac{∂f}{∂z} \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} dx \\ dy\\ dz \end{bmatrix}\).
$$
\frac{∂f}{∂x}=\begin{bmatrix}
\frac{∂f}{∂x} & \frac{∂f}{∂y} &\frac{∂f}{∂z}
\end{bmatrix}
$$
$$ \mathrm{ or } $$
| \(\nabla f(\mathbf{x} )=\begin{bmatrix}\frac{∂f}{∂x} \\ \frac{∂f}{∂y}\\\frac{∂f}{∂z}\end{bmatrix}\) gradient |
|---|
✅ \(\nabla f(x)=(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x} )^T\), 重要!!!
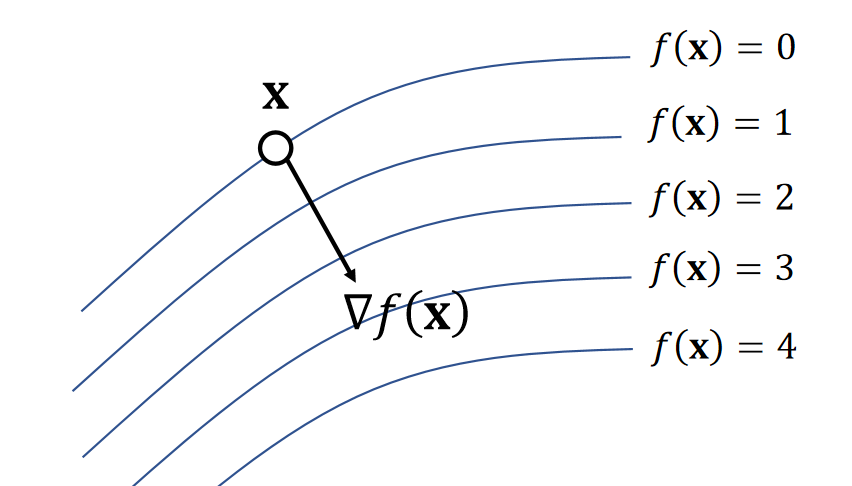
Gradient is the steepest direction for increasing \(f\). It’s perpendicular to the isosurface.
✅ isosurface:等高面
P43
值是矢量,变量是是矢量
If \(f(\mathbf{x} )=\begin{bmatrix} f(\mathbf{x} ) \\ g(\mathbf{x} )\\ h(\mathbf{x} ) \end{bmatrix}\in \mathbf{R} ^3\),then:
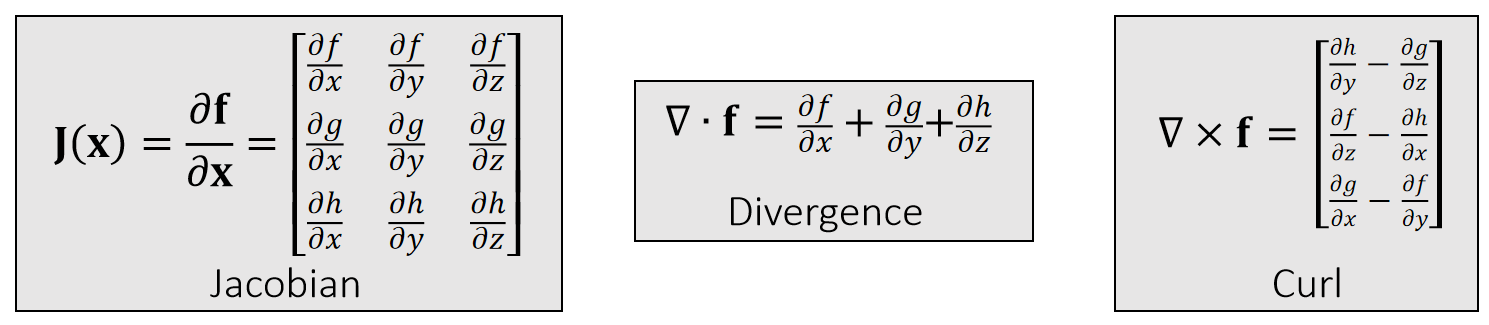
✅ Divergence:散度,也是\(\mathbf{J}(\mathbf{x})\)的 trace
✅ Curl:旋度。
✅ 怎么理解 curl?把微分算子\(\nabla \)看作是个向量,让它与 \(\mathbf{f}\) 做叉乘、在流体模拟中常用。
P44
2nd-Order Derivatives
If \(f\mathbf{(x)\in R} \),then:
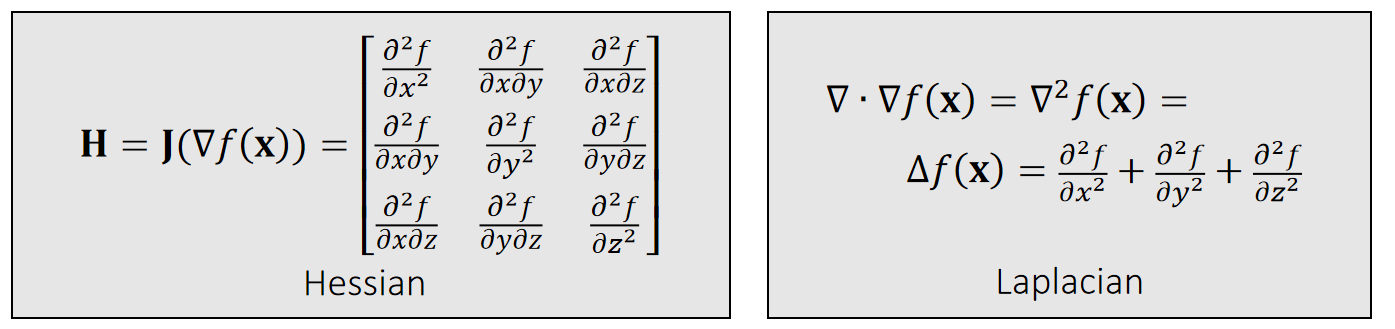
✅ 求导顺序不影响求导结果,因此 \(\mathbf{H}\) 是对称的
\(\mathbf{H}\)的trace称为Laplace
泰勒展开
①\(x\in R,f(x)\in R\)
$$
f(x)=f(x_0)+{f}' (x_0)(x-x_0)+\frac{1}{2} {f}'' (x_0)(x-x_0)^2+\cdots
$$
②\(x\in R^n,f(x)\in R\)
$$ f(x)=f(x_0)+\nabla {f}' (x_0)\cdot (x-x_0)+\frac{1}{2}(x-x_0)^TH(x-x_0)+\cdots $$
✅ 当\(\mathbf{H}\)正定时, \(f(\mathbf{x})\)满足一些特殊的性质
P45
Quiz:
\(\frac{∂||\mathbf{x}||}{∂\mathbf{x}} = ?\)
$$ \frac{∂||\mathbf{x}||}{∂\mathbf{x} } = \frac{∂(\mathbf{\mathbf{x^Tx} } )^{1/2}}{∂\mathbf{x} }=\frac{1}{2}(\mathbf{x^{T}x} )^{−1/2} \frac{∂(\mathbf{x^Tx} )}{∂\mathbf{x} }=\frac{1}{2||\mathbf{x} ||}2\mathbf{x^T} =\frac{\mathbf{x^T} }{||\mathbf{x} ||} $$
| $$\frac{∂(\mathbf{\mathbf{x^Tx} } )}{∂\mathbf{x} }=\frac{∂(x^2+y^2+z^2)}{∂\mathbf{x} }= \begin{bmatrix}2x& 2y &2z \end{bmatrix}= 2\mathbf{x^T}$$ |
|---|
✅ 向量梯度的物理意义:向量沿什么方向变化能最快地变短/长?答:沿它自己的当前方向。
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。
https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES103_mdbook/