P11
粒子碰撞检测 --- SDF
Signed Distance Function
A signed distance function \(\phi (\mathbf{x} )\) defines the distance from \(\mathbf{x}\) to a surface with a sign. The sign indicates on which side \(\mathbf{x}\) is located.
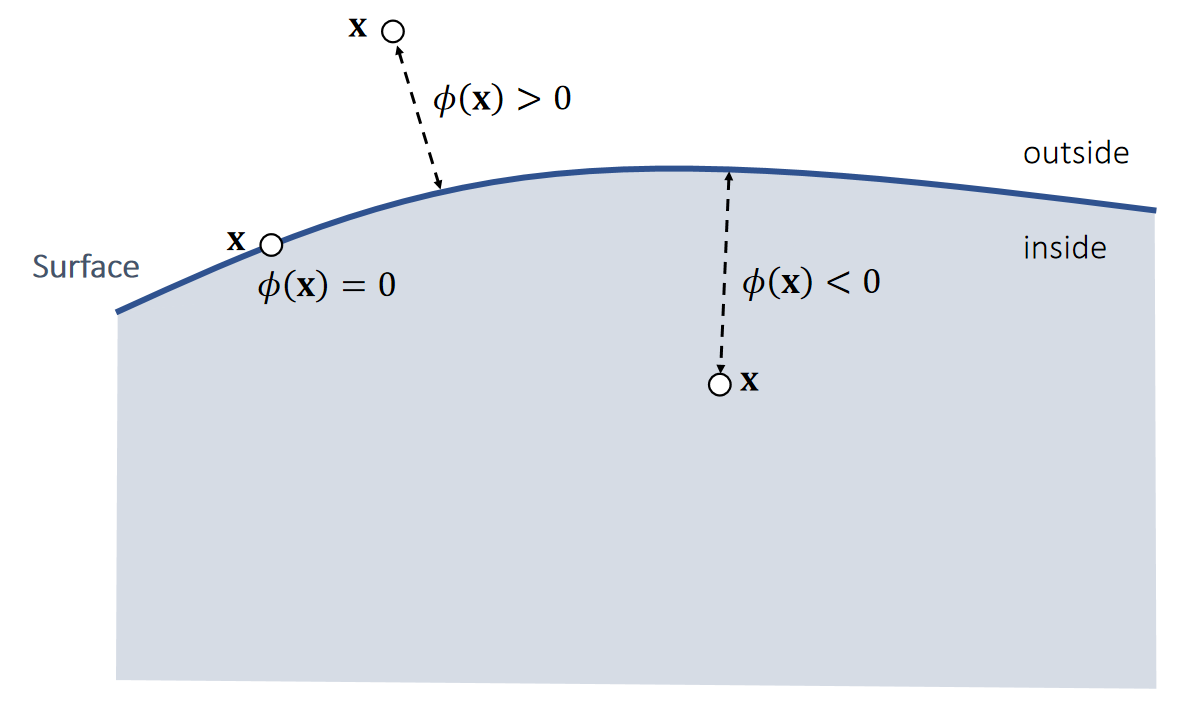
P12
Signed Distance Function Examples
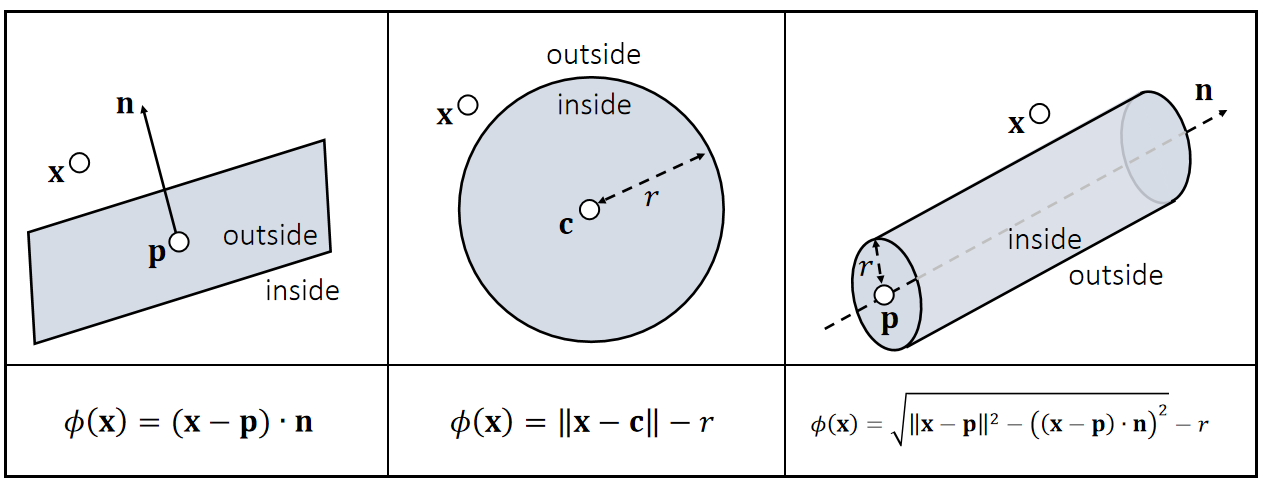
✅ 圆柱SDF基于勾股定理,\(\sqrt{\cdot }\) 内第一项为斜边长, 第二项为底边长,得出点到中轴的距离。
P13
Intersection of Signed Distance Functions
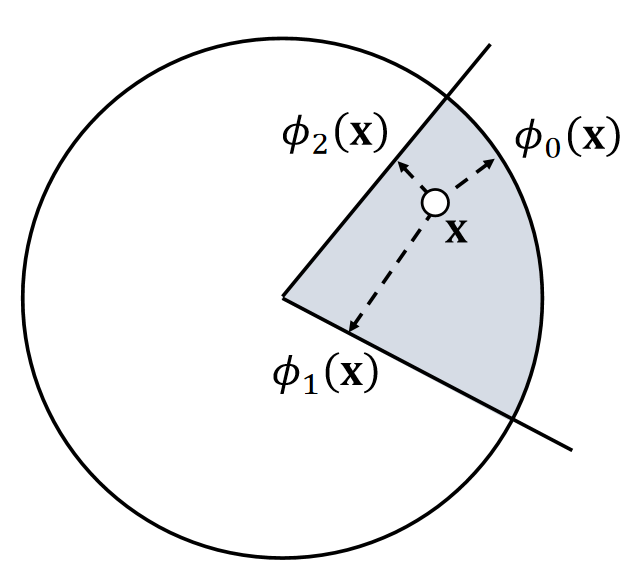
If \(\phi _0(\mathbf{x} )<0\) and \(\phi_1(\mathbf{x} )<0\) and \(\phi_2(\mathbf{x} )<0\)
then inside
\(\quad \phi (\mathbf{x} )\)=max \((\phi_0(\mathbf{x}),\phi_1(\mathbf{x}),\phi_2(\mathbf{x}))\)
Else outside
\(\quad \phi (\mathbf{x})=?\)
P14
Union of Signed Distance Functions
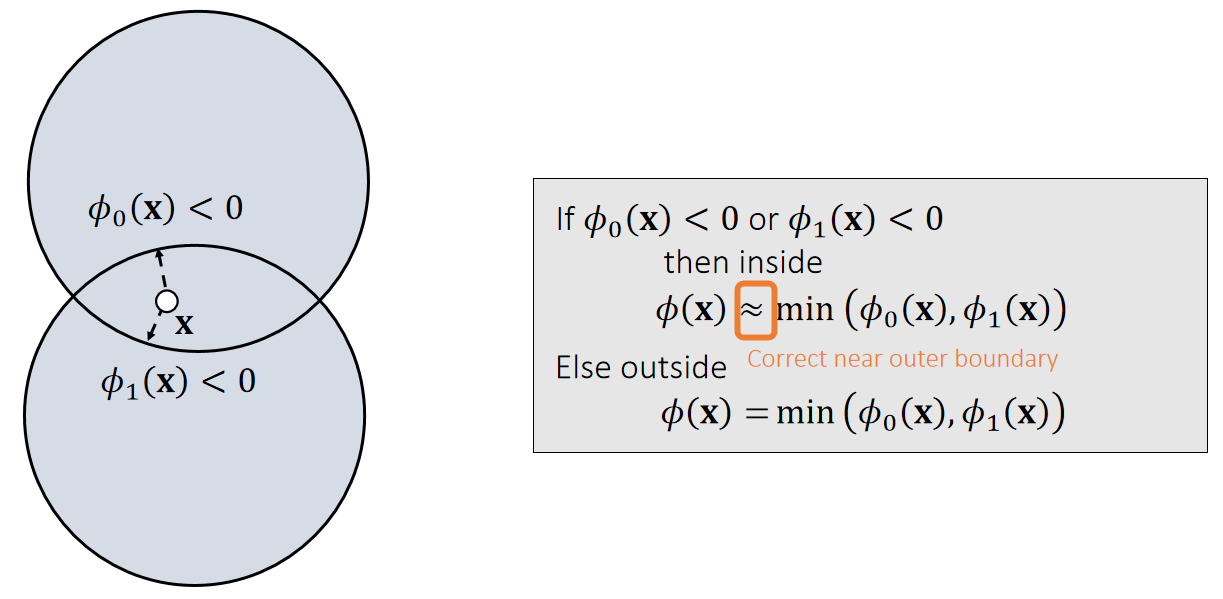
✅ 有时候此公式不成立,例如图中\(\mathbf{x}\) 点
Intuitively, we can consider collision detection with the union of two objects as collision detection with two separate objects.
P15
穿透检测
$$ \phi (x(t))=0 $$
解出 \(t\)
如果 \(t\) 在所检测的时间范围内有解,则说明存在穿透 \(t\) 为穿透时刻。
粒子碰撞响应 —— Penalty Method
碰撞解除
SDF 常用于代表静态物体,这种物体不响应力和碰撞,所以所有的碰撞响应都发生在粒子上。
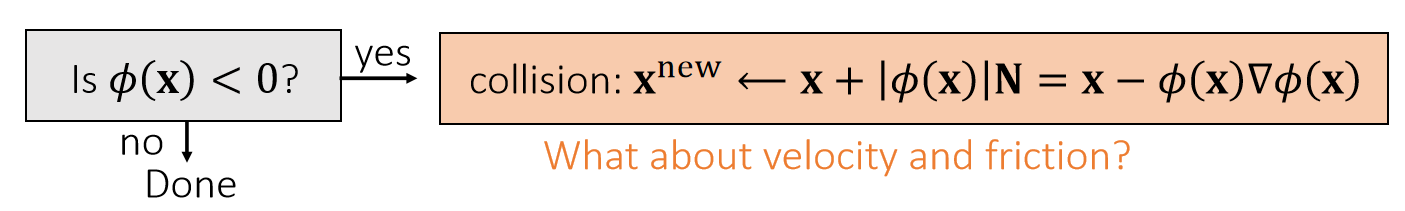
✅ 更新方向:N方向。更新距离:穿入的距离。
状态更新
Quadratic Penalty Method
A penalty method applies a penalty force in the next update. When the penalty potential is quadratic, the force is linear.
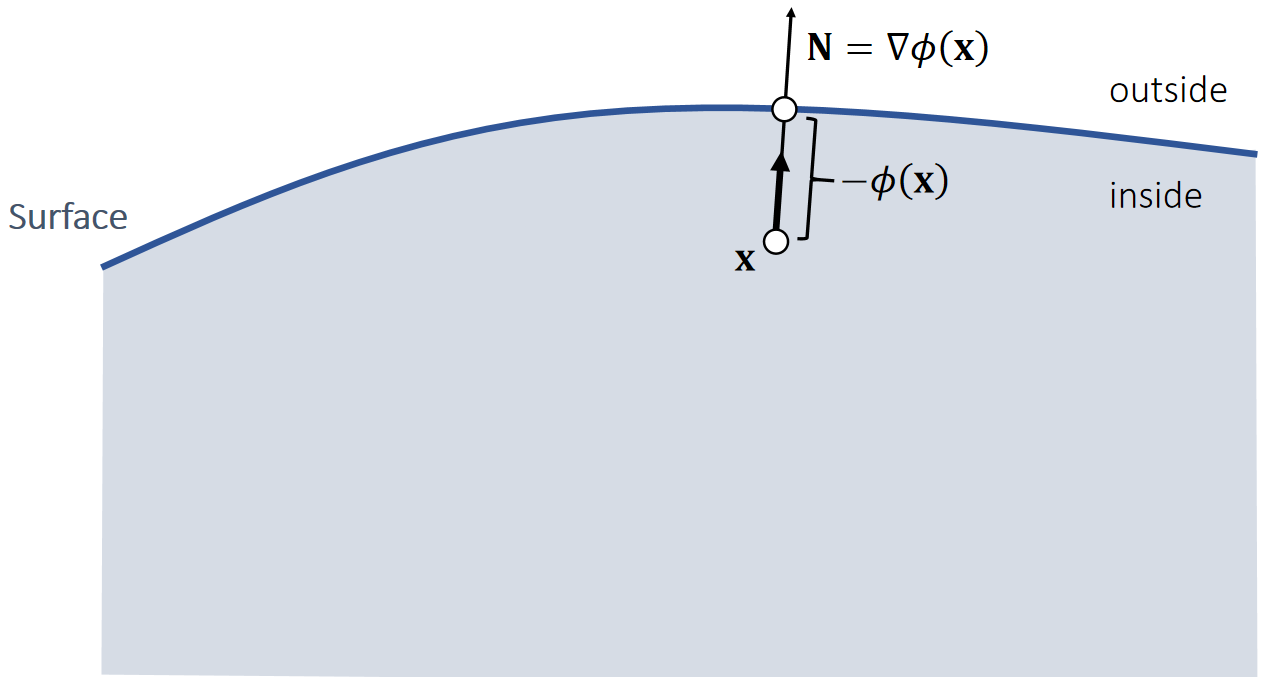
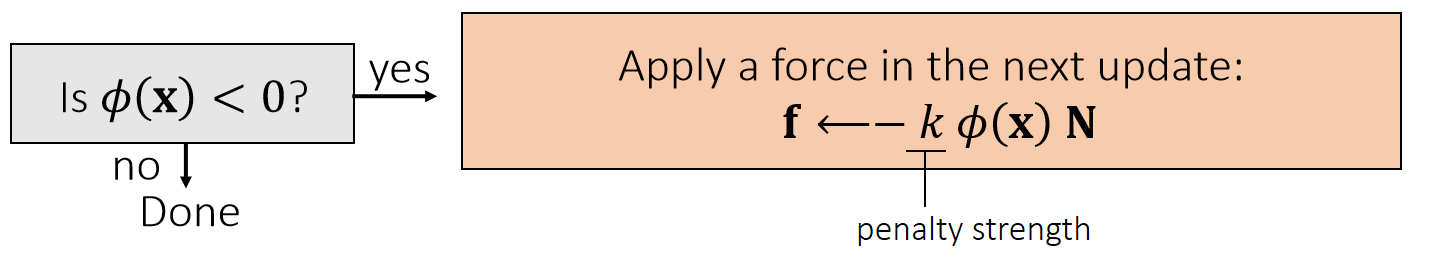
当粒子进入物体内部后,就会产生一个向外的推力。
✅ 力的大小与距离有关,方向为normal
✅ 存在的问题:只有\(\mathbf{x}\) 进入 mesh 内部了,才会有力,但此时穿透的 artifacts 已经产生了。解决方法:使用buffer
P16
粒子的运动状态发生变化确实是由于力的作用。但对力的大小的假设均不合理。
力的大小确实与穿透深度有关,因为:
穿透深 → 相对速度大 → 碰撞速度和反弹速度都大 → 速度改变大 → 力大
Quadratic Penalty Method with a Buffer
A buffer helps lessen the penetration issue. But it cannot strictly prevent penetration, no matter how large \(k\) is.
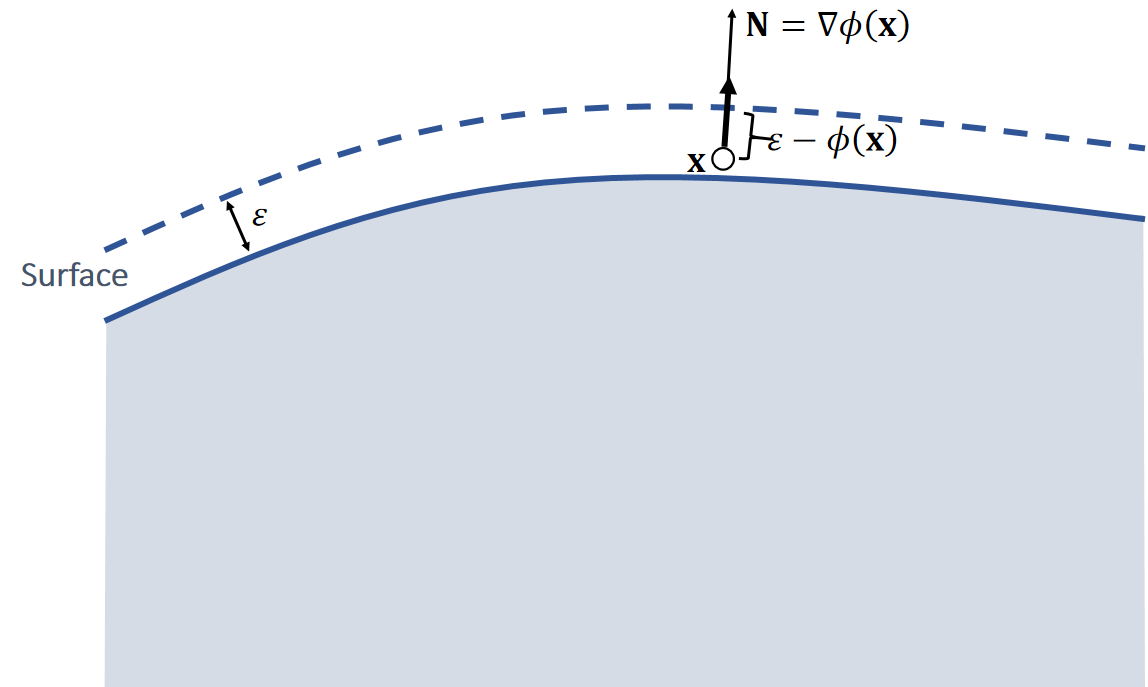
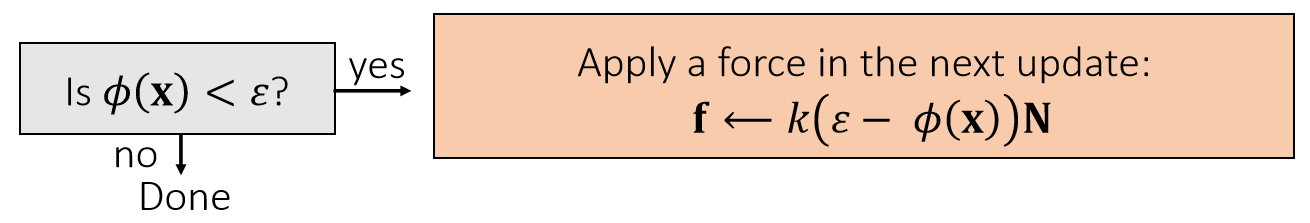
✅ 存在的问题:
如果 \(k\) 太小,快速的碰撞仍会产生 artifacts
如果 \(k\) 太大,碰撞的反弹过于强烈(overshooting)
解决方法:不用常数 \(k\) ,而是 \(k\) 与距离相关
P17
Log-Barrier Penalty Method
A log-barrier penalty potential ensures that the force can be large enough. But it assumes \(\phi (\mathbf{x} ) < 0\) will never happen!!! To achieve that, it needs to adjust \(\Delta t\).
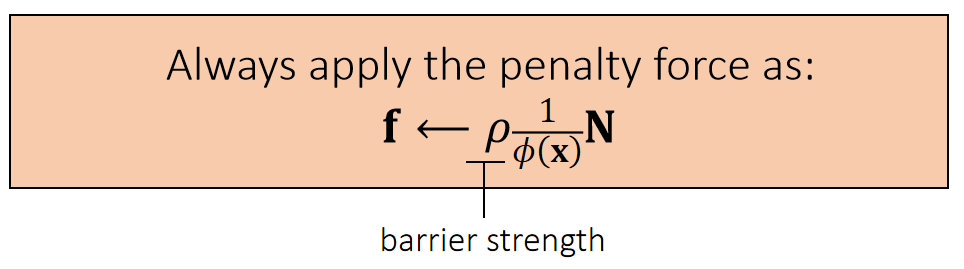
✅ 用倒数关系代替线性关系。
✅ 存在的问题:
1.当\(\mathbf{x}\) 靠近物体表面时,仍然会 overshooting
2.\(\mathbf{x}\) 穿透表面后,会越陷越深。
3.本算法如果要求保证穿透永远不会发生,因此要仔细调节 \(\Delta t\).
P18
A Short Summary of Penalty Methods
-
The use of step size adjustment is a must.
- To avoid overshooting.
- To avoid penetration in log-barrier methods.
-
Log-barrier method can be limited within a buffer as well.
- Li et al. 2020. Incremental Potential Contact: Intersection- and Inversion-free Large Deformation Dynamics. TOG.
- Wu et al. 2020. A Safe and Fast Repulsion Method for GPU-based Cloth Self Collisions. TOG.
-
Frictional contacts are difficult to handle.
✅ 缺点:
(1) 难以模拟摩擦。
(2) 碰撞 → 施加力 → 调整,因此效果是滞后的。
优点:易实现
P19
Particle Collision Response —— Impulse Method
An impulse method assumes that collision changes the position and the velocity all of sudden.
✅ Penalty 方法是碰撞 → 力 → 下一时刻的速度和位置,效果滞后。
✅ Impulse方法碰撞时立即更新速度和位置
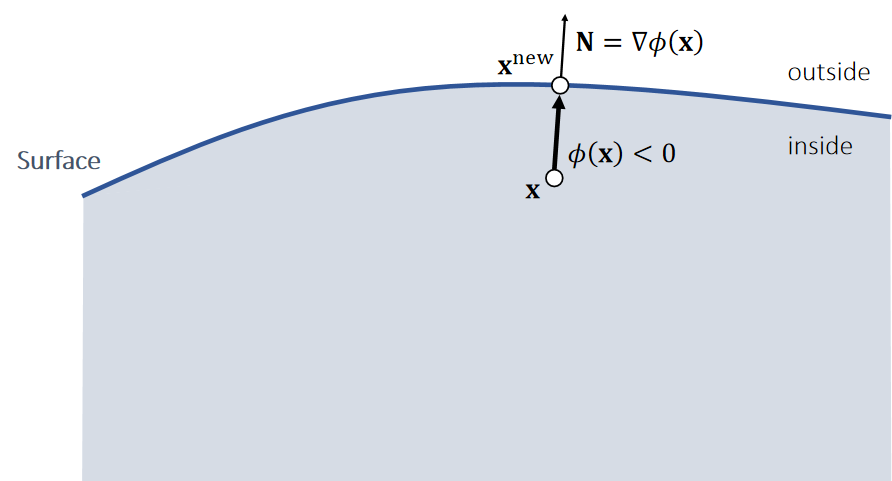
✅ lmpulse 省去了力这一步,直接更新刚体状态。方法要求已经有一个比较好的\(\phi (x)\)
✅ 关键区别不在于是否使用力,而是位置是怎样计算出来的,前者的位置由力和速度,这个计算出来的(不管是作为下一时刻还是这一时刻)的位置,都不能保证一定能以物体内部推出来,但后者直接求出当前置对应的表面位置的点,并更新上去,因此能立即生效。
更新速度
P20
Changing the position is not enough, we must change the velocity as well.
✅ \(\mathbf{v}\cdot \mathbf{N}\ge 0\):当前速度想要让物体越陷越深, 这种情况下才需要更新速度
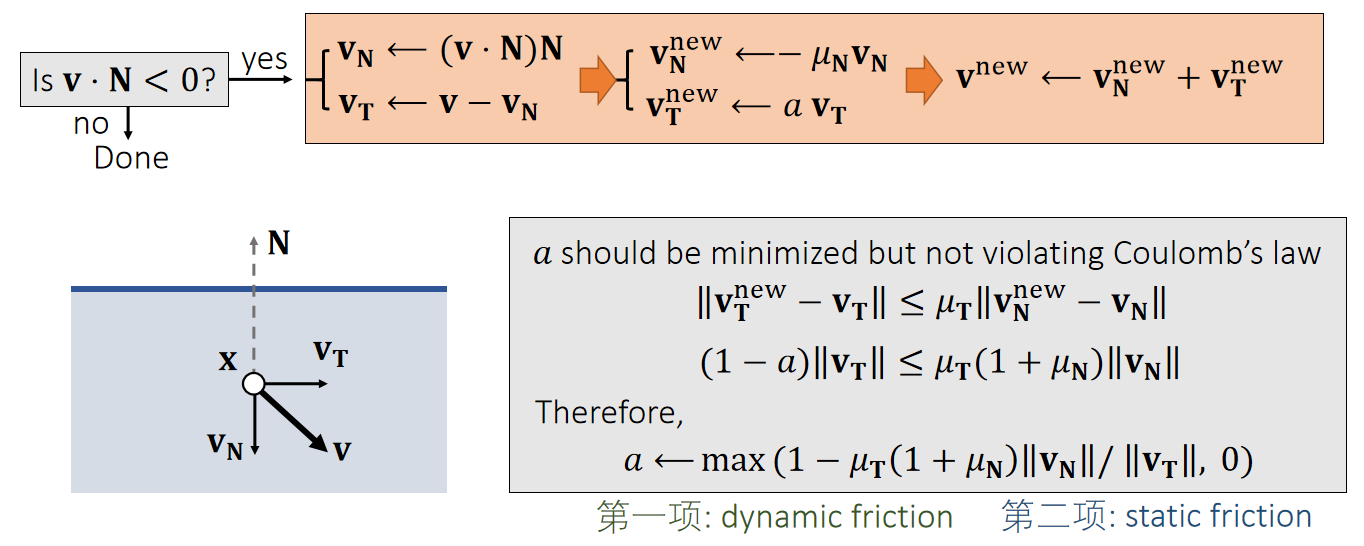
✅ 把\(\mathbf{v}\)分解为\(\mathbf{v_T}\)(切线方向的速度)和\(\mathbf{v_N}\)(法线方向的速度).
✅ \(\mathbf{v_N}\)方向速度反弹, \(\mu _\mathbf{N}\) 为反弹系数。\(\mathbf{v_N}\)方向不变或由于摩擦而衰减
✅ a的约束:(1)越小越好,尽量把速度衰减掉(2)满足库仑定律(切方向的速度改变不应大于法线方向的速度改变)(3)切方向速度不能反转,即a不能为负
Impulse方法总结
✅ 优点:可以精确控制摩擦力和反弹位置。缺点:计算比 Penalty 复杂
✅ 刚体常见于 Impulse; 弹性体常见于Penalty.
| 速度大小 | 速度方向 | |
|---|---|---|
| Penalty | 碰撞深度->力的大小 | 表面方向 |
| Impulse | 相对速度 * decay | 反弹方向+惯性方向 |
粒子与 Mesh
相交检测
检测粒子是否在 Mesh 的内部
射线法:粒子从自身出发,发出一条射线,判断射线是与 Mesh 上的面片相交。
相交次数为奇数,则在 Mesh 内
相交次数为偶数,则在 Mesh 外
穿透检测
碰撞响应
粒子与 SDF 的碰撞响应在此处同样适用
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。
https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES103_mdbook/