P27
相交解除
P39
A Practical System Summary
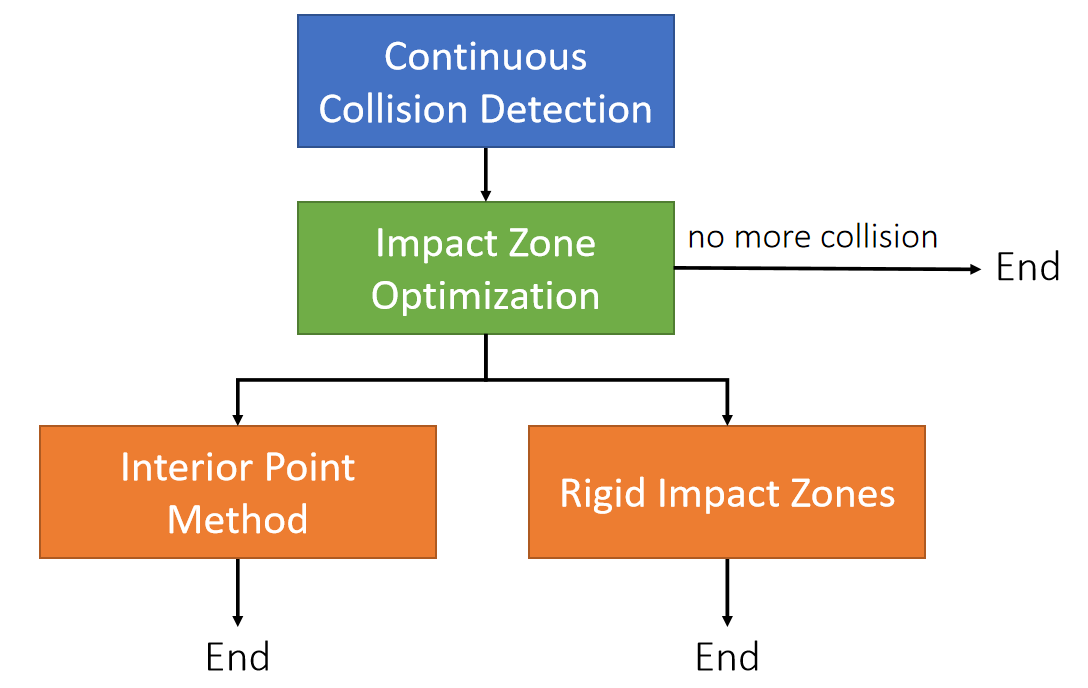
✅ 有碰撞,先做 Impact Zone. 因为这个快、不能解决再用后面方法、计算量不允许则选择 Rigid Impact.
P28
Interior Point Methods and Impact Zone Optimization
✅ 这是两个大的套路,不是具体的方法。
Given the calculated next state \(\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}\), we want to update it into \(\bar{\mathbf{x} } ^{[1]}\), such that the path from \(\mathbf{x} ^{[0]}\) to \(\bar{\mathbf{x} } ^{[1]}\) is intersection-free.
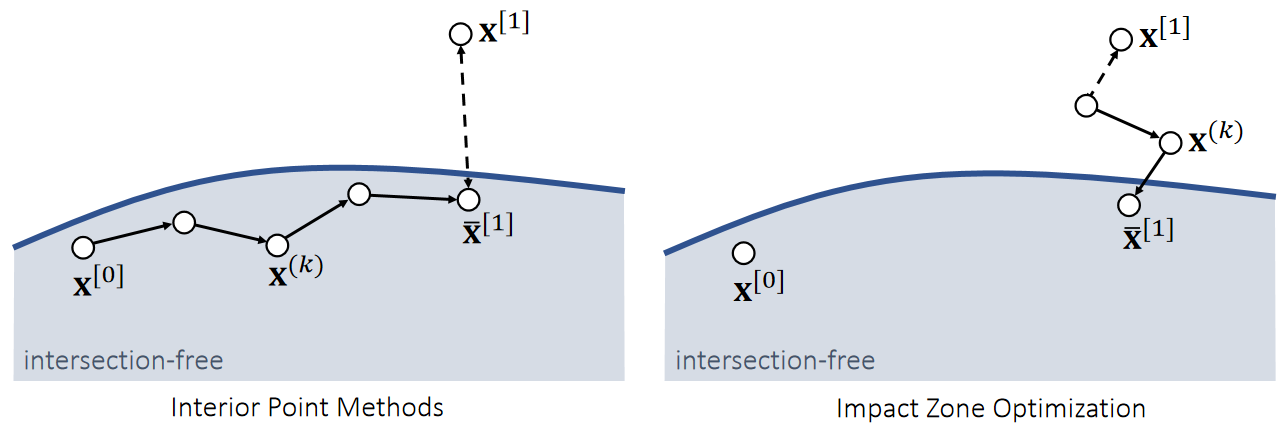
✅ 整个图代表刚体的状态空间而不是位置空间。
✅ 每个小圆点代表一个刚体状态,而不是一个粒子。
✅ \(\mathbf{x} \) 是刚体状态的表示符,至少包含质心的状态和旋转信息。
| 内点法 | Impact Zone 法 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ 从\(\mathbf{x}^{[0]}\)出来,朝\(\mathbf{x}^{[1]}\)走,并永远保证只在安全区域走,直到不能走为止。 | ✅ 从\(\mathbf{x}^{[1]}\)出发,反复优化结果(投影),直到回到安全区域为止。 | ✅ 蓝色区域为安全区域 | |
| 优点 | Always succeed | Fast. 1. Close to solution. 2. Only vertices in collision (impact zones). 3. Can take large step sizes. | ✅ Impact Zone:1. \(\mathbf{x}^{[1]}\)通常离安全区域不太远,且优化时只针对 Impact Zone 优化,因此快。 2. 只有\(\mathbf{x}\)不在安全区域时才需要做。 ✅ 内点:哪怕\(\mathbf{\bar{x}}^{[1]}\)最终没有到最佳位置,但能保证一定在安全区域,因此一定成功。 |
| 局限性 | Slow. 1. Cautiously by small step sizes. 2. Far from solution. 3. All of the vertices. | May not succeed. | ✅ 内点:1. 为保证每一步安全,步长不能太大,因此慢。 2. \(\mathbf{x}^{[0]}\)和\(\mathbf{x}^{[1]}\)可能比较远,也导致慢。 3. 每一次都必须要做 |
P47
A Summary For the Day
-
Collision handling involves two steps: collision detection and collision response.
-
Collision detection contains two phases: broad-phase culling and narrow-phase test.
-
There are two types of collision detection tests: discrete and continuous.
-
Similarly, there are discrete and continuous collision responses.
-
For continuous collision responses, we must update the state to become collisionfree state. There are two approaches: interior point method and impact zone optimization. Rigid impact zone is also a method, but it’s problematic.
-
For discrete collision responses, we allow intersections to stay and hope to remove them in long turn. Cloth-cloth intersections are difficult to handle.
✅ 如果考虑摩擦,通常把摩擦做为后处理,但这样结果不精确。如果同时处理摩擦和碰撞、会很复杂。
✅ Impulse方法的碰撞检测通常用SDF.但很多形变体无法使用SDF.
✅ Impulse响应方式是离散响应方式,无法处理穿透问题。
✅ 碰撞问题通常不使用物理方法,因为使用物理方法需要小步长,效率非常低。
✅ 碰撞开源代码:bullet. physics X
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。
https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES103_mdbook/