💡 旋转的表示比较独立,单独放在最后link,避免破坏整体的结构性。最后结论是混合式的积分方法。
P27
符号定义
角度
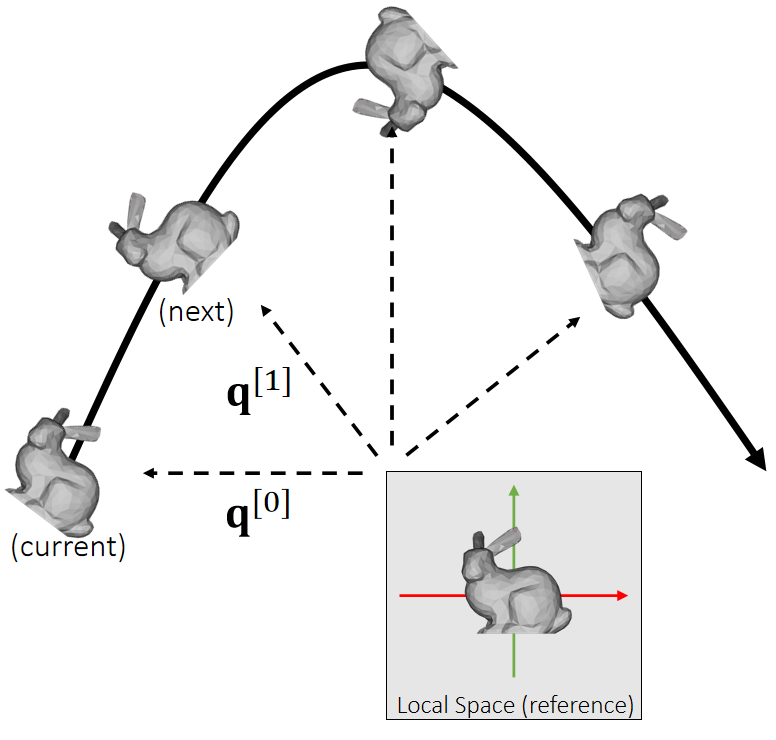
Now we choose quaternion q to represent theorientation, i.e., the rotation from the reference to the current.
角速度
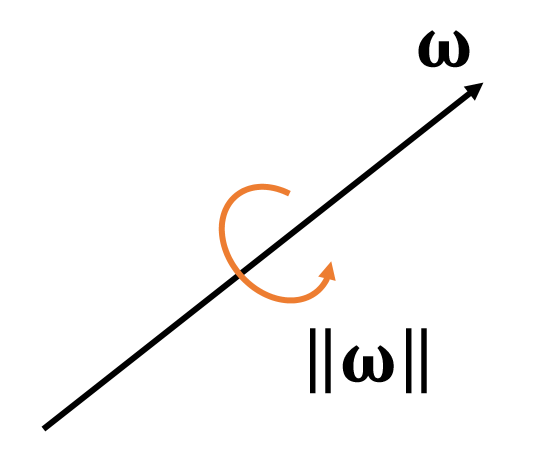
We use a 3D vector ω to denote angular velocity.
{The direction of ω is the axis.The magnitude of ω is the speed.
P3
力矩 torque
A torque is the rotational equivalent of a force. It describes the rotational tendency caused by a force.
✅ Torque:力矩,造成物体旋转的趋势。类比于Force:力,造成物体运动的趋势。
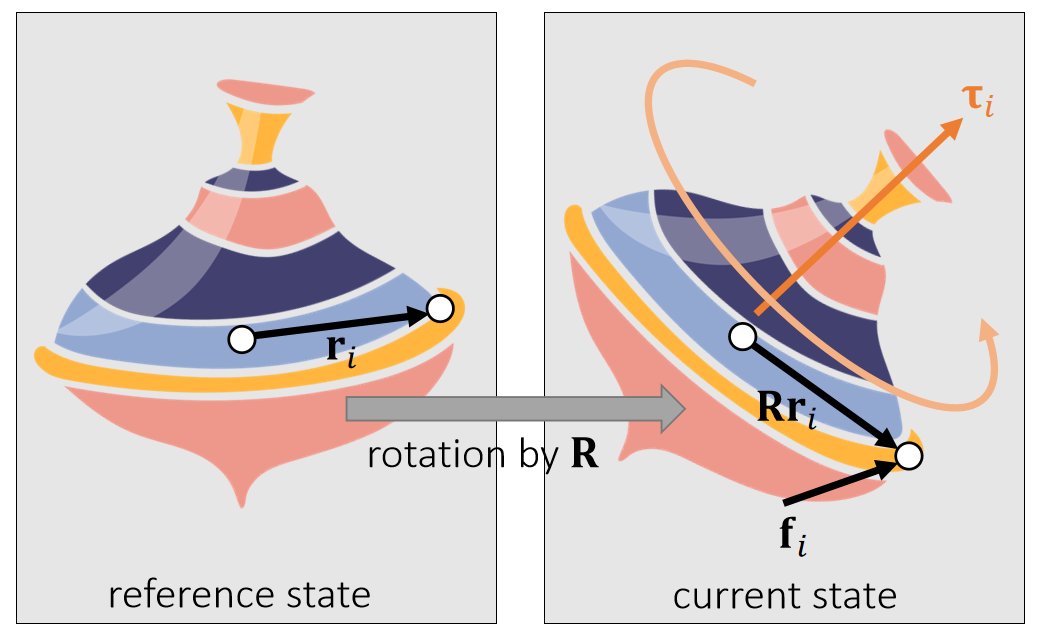
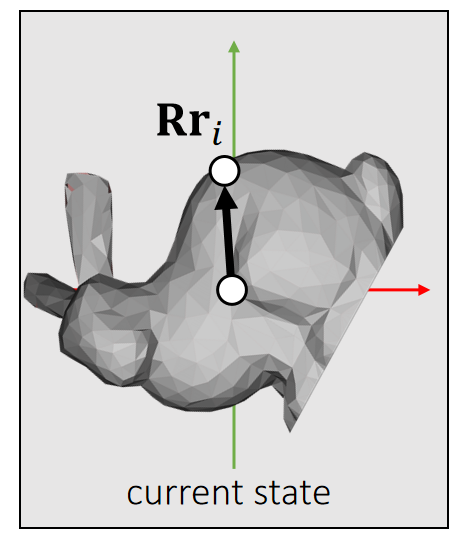
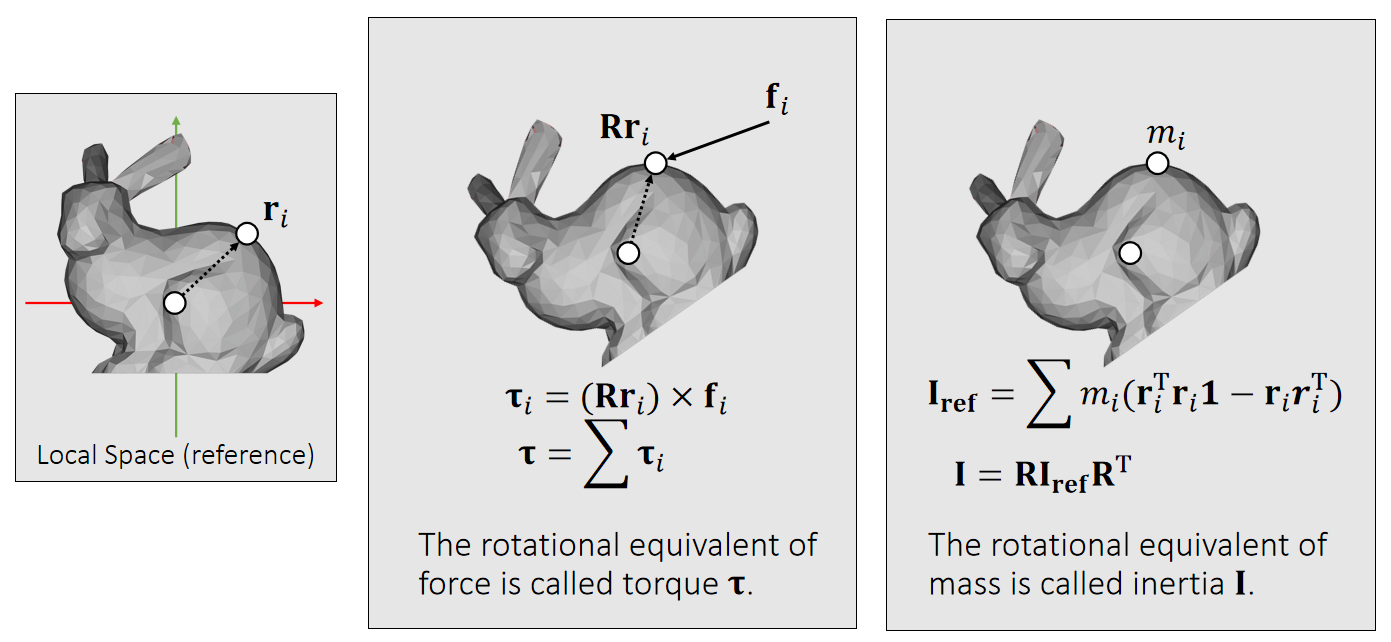
✅ Rri:当前状态下质心到作用点的向量
\mathbf{τ} _i is perpendicular to both vectors: \mathbf{Rr} _i and \mathbf{f} _i.
✅ 因此力矩的方向决定了旋转轴的方向,因此由叉差乘得到
\mathbf{τ} _i is porportional to ||\mathbf{Rr} _i|| and ||\mathbf{f} _i||.
\mathbf{τ} _i is porportional to \sin \theta.
(\theta is the angle between two vectors.)
✅ 力矩的大小决定旋转的快慢。
| \mathbf{τ} _i\longleftarrow (\mathbf{Rr} _i)\times \mathbf{f} _i |
|---|
P6
inertia tensor
Similar to mass, an inertia tensor describes the resistance to rotational tendency caused by torque. But different from mass, it’s not a constant.
✅ inertia 也与自身的状态相关
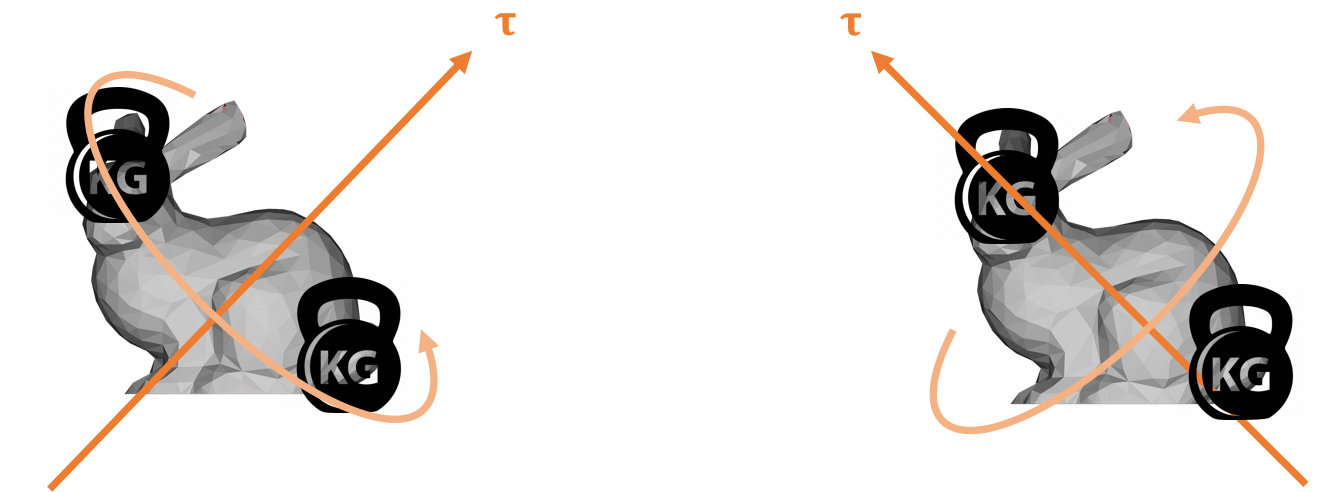
Which side receives greater resistance?
✅ 两图的力矩大小相同,但产生的旋转不同
inertia 看作是对运动的抵抗,其效果与力矩的方向有关,因此不是常数
P7
It’s a matrix! The mass inverse is the resistance (just like mass).
✅ 用于旋转的质量不再是实数,而是矩阵,称为 Inertia 矩阵,用 \mathbf{I} 来标记 Inertia 矩阵,其中 \mathbf{I}_{ref}为参考状态,\mathbf{I} 为当前状态,\mathbf{I} 是 3\times 3 矩阵。
| reference state | current state |
|---|---|
 |  |
| \mathbf{I} _{\mathbf{ref} }=\sum m_i(\mathbf{r} _i^\mathbf{T} \mathbf{r} _i\mathbf{1} −\mathbf{r} _i\mathbf{r} _i^\mathbf{T} ) \mathbf{1} is the 3-by-3 identity. | \mathbf{I} =\sum m_i(\mathbf{r} _i^\mathbf{T}\mathbf{R} ^\mathbf{T}\mathbf{Rr} _i\mathbf{1} −\mathbf{Rr} _i\mathbf{r} _i^\mathbf{T} \mathbf{R^T} ) \quad=\sum m_i(\mathbf{Rr} _i^\mathbf{T}\mathbf{r} _i\mathbf{1R} ^\mathbf{T} −\mathbf{Rr} _i\mathbf{r} _i^\mathbf{T} \mathbf{R^T} ) \quad=\sum m_i\mathbf{R}(\mathbf{r}_i^\mathbf{T}\mathbf{r}_i\mathbf{1}−\mathbf{r}_i\mathbf{r}_i^\mathbf{T} ) \mathbf{R^T} \quad=\mathbf{RI _{ref}R^T} |
✅ 不需要每次都根据当前状态计算,而是基于一个已经算好的ref状态的 inertia快速得出。
P29
更新法则
| Translational (linear) | Rotational (Angular) | |
|---|---|---|
| Updafe | 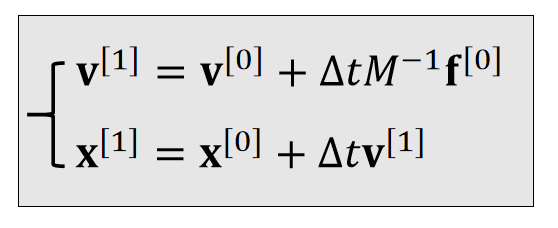 | 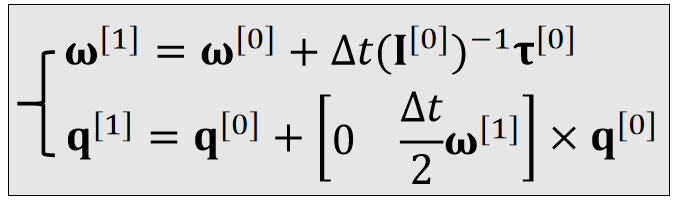 |
| states | Velocity \mathbf{v} Position \mathbf{x} | Angular velocity \mathbf{ω} Quaternion \mathbf{q} |
| Physical Quantities | Mass \mathbf{M} Force \mathbf{f} | Inertia \mathbf{I} Torque \mathbf{τ} |
✅ 平移: 加速度 = \frac{力}{质量} ,旋转: 加速度 =\frac{力矩}{\text{Inertia}}
✅ q是四元数,代表物体的旋转状态
✅ q_1\times q_2不是叉乘,而是四元数普通乘法
✅ \begin{bmatrix} 0 & \frac{\bigtriangleup t}{2} & w^{(1)} \end{bmatrix}是一个四元数,0为实部,后面为虚部
❗ 算完q^{[1]}的之后要对它 Normalize
🔎 由q^{[0]}到q^{[1]}的更新公式的推导过程见Affer Class Reading(Appendix B)
❓ 四元数相加有什么含义?
P30
Rigid Body Simulation Piplene
In practice, we update the same state variable \mathbf{s} ={\mathbf{v,x,\omega ,q}} over time.

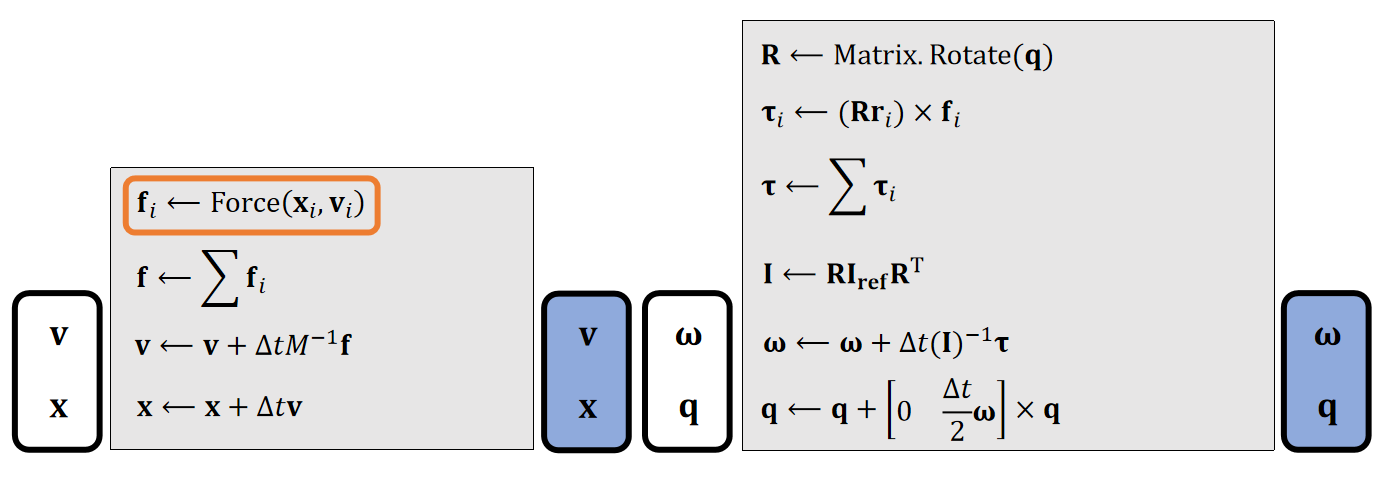
❗ Gravity doesn't cause any torque! lf your simulator does not contain any other force, there is no need to update \mathbf{\omega}.
P33
After-Class Reading (Before Collision)
P35
https://graphics.pixar.com/pbm2001
❓ 建议读其中的Rigid Body Dynamics部分
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。
https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES103_mdbook/