P39
Shape Matching
先让每个粒子独立仿真,也不需要考虑弹簧力。
将每个面片的变形程度构建为能量,通过优化能量的方式使 Mesh 减少形变,所有面片以统一的方式进行优化,因此是一种全局优化方法。
所有方法最后都归结为一个分式:
$$ \psi(x)=k||x-y||_m^2+E(x) $$
关键是如何定义,以及非线性方程如何求解
P40
量化形变
The basic idea is to define a quadratic energy based on the rotated reference element. To do so, we split transformation into deformation + rotation.

P41

P42
计算能量
We can then define the quadratic energy as:
$$ E (\mathbf{x} )=\frac{1}{2}||\mathbf{F−R} ||^2 $$
(\(\mathbf{R}\) is the rotation inside of \(\mathbf{F}\). This energy tries to penalize the existence of \(\mathbf{S}\)).
Assuming that \(\mathbf{R}\) is constant, this \(E(\mathbf{x})\) becomes a quadratic function. We can then derive the force and the Hessian.
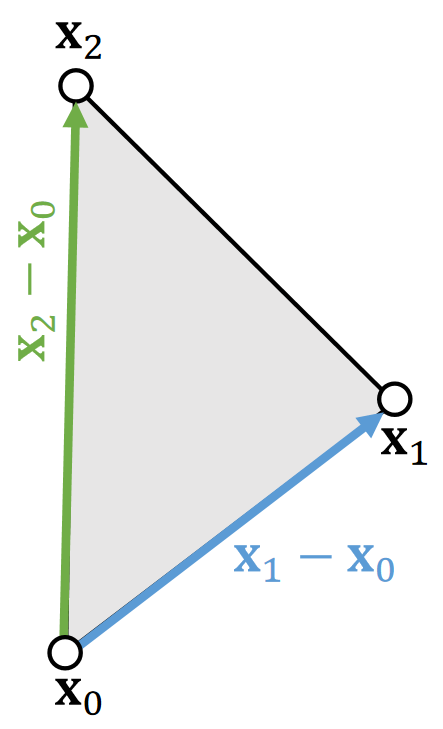
$$ E(\mathbf{x} ) =\frac{1}{2} ||\begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{x} _1-\mathbf{x} _0 &\mathbf{x} _2-\mathbf{x} _0 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{r} _1-\mathbf{r} _0 &\mathbf{r} _2-\mathbf{r} _0 \end{bmatrix}^{−1}−\mathbf{R}||^2 $$
P24
Shape Matching
这是用 \(PD\) 来优化优化问题的另一个例子。原 \(PD\) 算法用于长度保持约束,而这里把它用于形状保持约束。
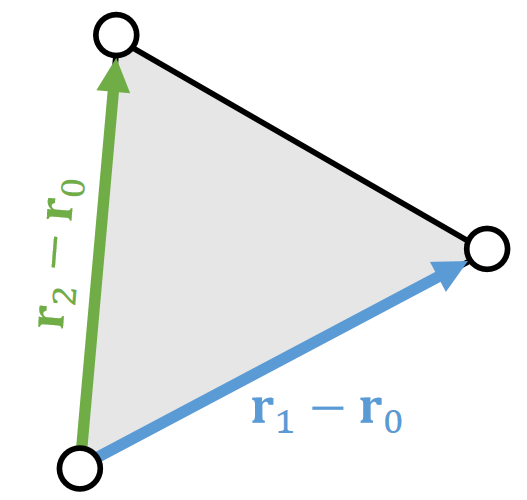
Shape matching is also projective dynamics, if we view rotation as projection:
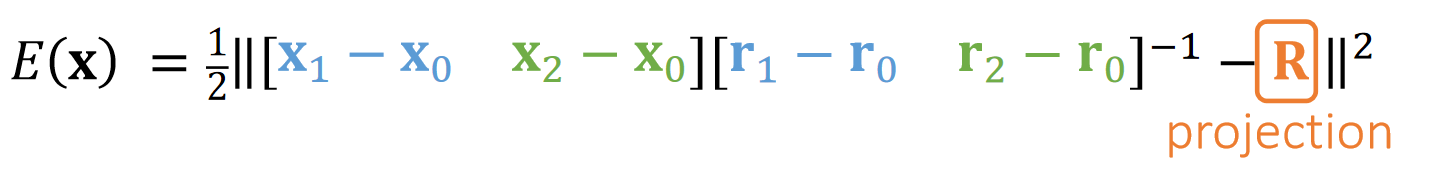
| The 2D Space | The 3D Space |
|---|---|
 |  |
Assuming that \(\mathbf{{\color{Orange} R} }\) is constant,
$$
\begin{matrix}
\mathbf{f} _0=−\nabla_0E(\mathbf{x} )\\
\mathbf{f} _1=−\nabla_1E(\mathbf{x} ) \\
\mathbf{f} _2=−\nabla_2E(\mathbf{x} )\\
\mathbf{H} =\frac{∂E^2(\mathbf{x} )}{∂x^2} \quad \text{is a constant !}
\end{matrix}
$$
P25
Simulation by Projective Dynamics
-
According to implicit integration and Newton’s method, a projective dynamics simulator looks as follows, with matrix \(\mathbf{A} =\frac{1}{∆t^2}\mathbf{M+}\mathbf{H} \) being constant.
-
We can use a direct solver with only one factorization of A.
Pipeline
Initialize \(\mathbf{x} ^{(0)}\), often as\( \mathbf{x} ^{[0]} \)or \(\mathbf{x} ^{[0]} +∆t\mathbf{v} ^{[0]} \)
For \(k=0\dots K\)
\(\quad\) Recalculate projection
\(\quad\) Solve \((\frac{1}{∆t^2}\mathbf{M} +\mathbf{H} )∆\mathbf{x} =−\frac{1}{∆t^2}\mathbf{M} (\mathbf{x} ^{(k)}−\mathbf{x} ^{[0]}−∆t\mathbf{v} ^{[0]})+\mathbf{f} (\mathbf{x} ^{(k)})\)
\(\quad\) \(\mathbf{x} ^{(k+1)}\longleftarrow \mathbf{x} ^{(k)}+∆\mathbf{x} \)
\(\quad\) If \(||∆\mathbf{x}||\) is small \(\quad\) then break
\(\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}\longleftarrow \mathbf{x} ^{(k+1)}\)
\(\mathbf{v} ^{[1]}\longleftarrow (\mathbf{x} ^{[1]}-\mathbf{x} ^{[0]})/∆t\)
P27
Pros and Cons of Projective Dynamics
Pros
- By building constraints into energy, the simulation now has a theoretical solution with physical meaning.
- Fast on CPUs with a direct solver. No more factorization!
✅ Fast on CPU,因为它只作一次\(\mathbf{LU}\)分解。
- Fast convergence in the first few iterations.
Cons
- Slow on GPUs. (GPUs don’t support direct solver wells.)
✅ Slow on GPU,因为\(\mathbf{LU}\)分解不适用于 \(\mathbf{GPU}\)
- Slow convergence over time, as it fails to consider Hessian caused by projection.
- Still suffering from high stiffness
- Cannot easily handle constraint changes.
- Contacts
- Remeshing due to fracture, etc.
✅ constraint changes: 网格关系改变导至弹簧结构改变,原来的\(\mathbf{H}\)将不再适用。
本文出自CaterpillarStudyGroup,转载请注明出处。
https://caterpillarstudygroup.github.io/GAMES103_mdbook/