import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Linear Regression模型"""
self.coef_ = None
self.interception_ = None
self._theta = None
def _sigmoid(self, t):
return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-t))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters = 1e4):
"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train,使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], "the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
def J(theta, X_b, y):
y_hat = self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta))
try:
return np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat) + (1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat))
except:
return float('inf')
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):
return X_b.T.dot(self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta))-y) / len(X_b)
def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e4, epsilon=1e-8):
theta = initial_theta
i_iter = 0
while i_iter < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):
break
i_iter += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta)
self.interception_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
def predict_proba(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self.interception_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, "must fit before predict"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), "the feature number of X_predict must equal to X_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])
return self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(self._theta))
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self.interception_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, "must fit before predict"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), "the feature number of X_predict must equal to X_train"
proba = self.predict_proba(X_predict)
return np.array(proba>=0.5, dtype=int)
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集X_test, y_test确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "LogisticRegression()"
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X = X[y<2, :2] # 逻辑回归只能解决二分类问题,因此只选取其中两种花的数据
y = y[y<2]
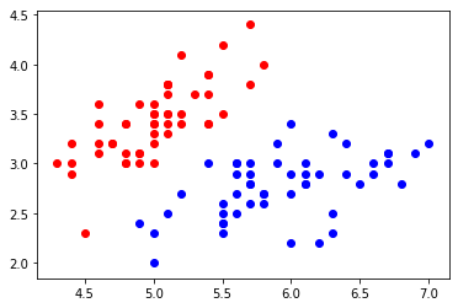
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1], color='red')
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1], color='blue')
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=666)
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
log_reg.score(X_test, y_test)
# 输出:1.0
log_reg.predict_proba(X_test)
# array([0.93292947, 0.98717455, 0.15541379, 0.01786837, 0.03909442,
# 0.01972689, 0.05214631, 0.99683149, 0.98092348, 0.75469962,
# 0.0473811 , 0.00362352, 0.27122595, 0.03909442, 0.84902103,
# 0.80627393, 0.83574223, 0.33477608, 0.06921637, 0.21582553,
# 0.0240109 , 0.1836441 , 0.98092348, 0.98947619, 0.08342411])
y_test
# array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
# 1, 1, 0])
log_reg.predict(X_test)
# array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
# 1, 1, 0])
