ROC:Receiver Operation Characteristic Curve
ROC曲线描述TPR和FPR之间的关系。
TPR = recall = TP / (TP + FN) # true positive rate FPR = FP / (FP + TN) # false positive rate
TPR和FPR的关系如图:

TPR和FRP呈现相一致的趋势
代码
回顾前面学过的代码
def TN(y_true, y_predict):
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict)
return np.sum((y_true == 0) & (y_predict==0)) # 注意这里是一个‘&’
def FP(y_true, y_predict):
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict)
return np.sum((y_true == 0) & (y_predict==1))
def FN(y_true, y_predict):
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict)
return np.sum((y_true == 1) & (y_predict==0))
def TP(y_true, y_predict):
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict)
return np.sum((y_true == 1) & (y_predict==1))
def confusion_matrix(y_true, y_predict):
return np.array([
[TN(y_true, y_predict), FP(y_true, y_predict)],
[FN(y_true, y_predict), TP(y_true, y_predict)]
])
def precision_score(y_true, y_predict):
tp = TP(y_true, y_predict)
fp = FP(y_true, y_predict)
try:
return tp / (tp + fp)
except: # 处理分母为0的情况
return 0.0
def recall_score(y_true, y_predict):
tp = TP(y_true, y_predict)
fn = FN(y_true, y_predict)
try:
return tp / (tp + fn)
except:
return 0.0
TPR和FPR
def TPR(y_true, y_predict):
tp = TP(y_true, y_predict)
fn = FN(y_true, y_predict)
try:
return tp / (tp + fn)
except:
return 0.0
def FPR(y_true, y_predict):
fp = FP(y_true, y_predict)
tn = TN(y_true, y_predict)
try:
return fp / (fp + tn)
except:
return 0.0
加载测试数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
digits = datasets.load_digits()
X = digits.data
y = digits.target.copy()
y[digits.target==9] = 1
y[digits.target!=9] = 0
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=666)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
绘制TFP和FRP的曲线,即ROC
decision_scores = log_reg.decision_function(X_test)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fprs = []
tprs = []
thresholds = np.arange(np.min(decision_scores), np.max(decision_scores), step=0.1)
for threshold in thresholds:
y_predict = np.array(decision_scores >= threshold, dtype='int')
fprs.append(FPR(y_test, y_predict))
tprs.append(TPR(y_test, y_predict))
plt.plot(fprs, tprs)
plt.show()

sklearn中的ROC曲线
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
fprs, tprs, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, decision_scores)
plt.plot(fprs, tprs)
plt.show()
 我们通常关注这条曲线下面的面积。面积越大,说明分类的效果越好。
我们通常关注这条曲线下面的面积。面积越大,说明分类的效果越好。
ROC score
ROC score代码曲线下面的面积。
auc = area under curl
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
roc_auc_score(y_test, decision_scores)
输出:0.9830452674897119
总结
对于有偏数据,观察它的精准率和召回率是非常有必要的。
但是ROC曲线对有偏数据并不敏感,它主要用于比较两个模型的孰优孰劣。
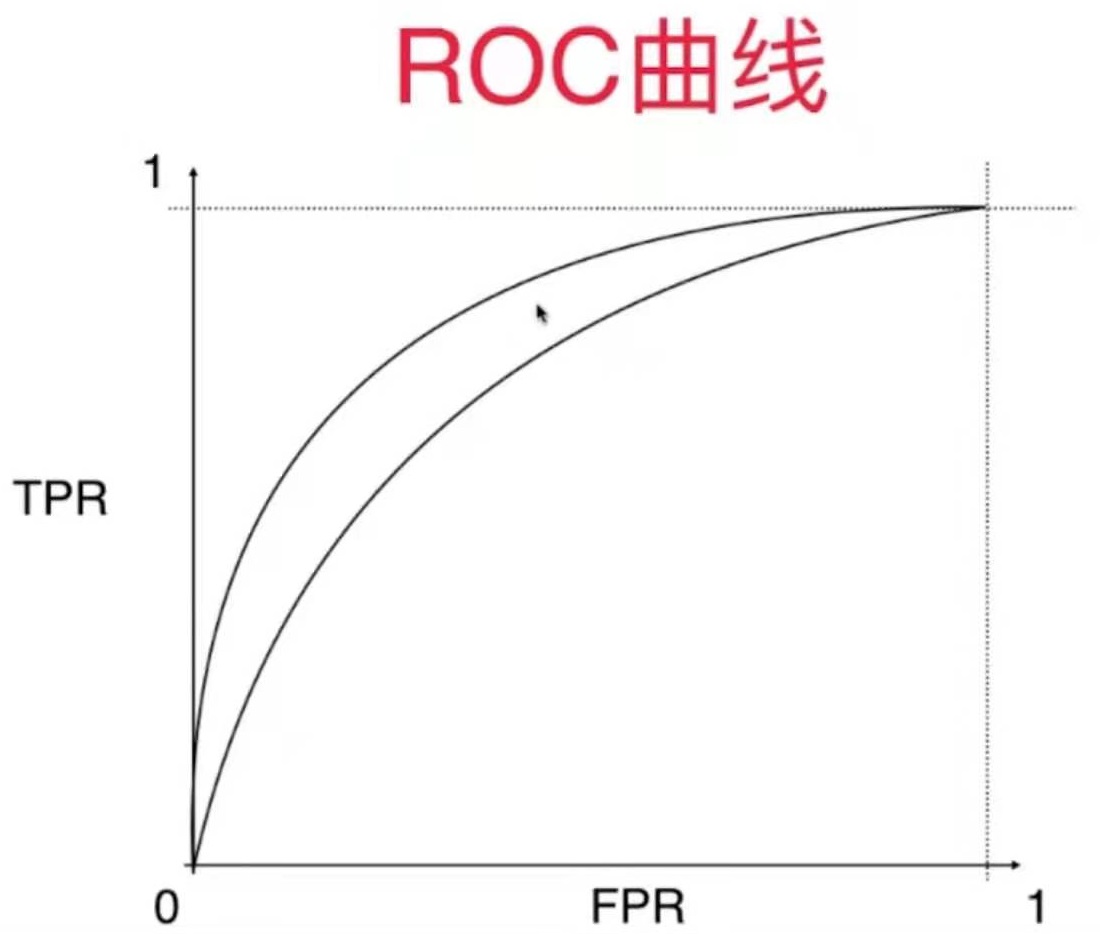
如果两根曲线分别代码两个模型的ROC曲线,在这种情况下我们会选择外面那根曲线对应模型。