准备数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100)
X = x. reshape(-1, 1)
y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100)
使用polynomialFeatures为原数据升维
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
poly.fit(X)
X2 = poly.transform(X)
输入:X2.shape
输出:(100, 3)
输入:X2[:5,:]
输出:
array([[ 1. , -1.34284888, 1.80324311],
[ 1. , -0.18985858, 0.03604628],
[ 1. , -1.58563134, 2.51422675],
[ 1. , 1.2149354 , 1.47606802],
[ 1. , -2.05874706, 4.23843944]])
输入:X2[:5,:]
输出:
array([[-1.34284888],
[-0.18985858],
[-1.58563134],
[ 1.2149354 ],
[-2.05874706]])
X2中第一列是1,第二列是原数据,第三列是原数据的平方
使用scikit-learn中的线性回归算法
这一部分与8-1相同
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lin_reg2 = LinearRegression()
lin_reg2.fit(X2, y)
y_predict2 = lin_reg2.predict(X2)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(np.sort(x), y_predict2[np.argsort(x)], color='r')
plt.show()
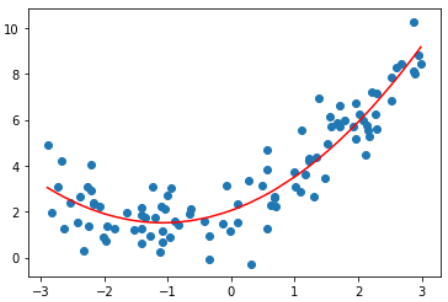
输入:lin_reg2.coef_
输出:array([0. , 1.01723515, 0.46407147])
0是对X2是第一列数据拟合的结果
输入:lin_reg2.intercept_
输出:2.1789150996943945
关于PolynomialFeatures
X = np.arange(1,11).reshape(-1, 2)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
poly.fit(X)
X2 = poly.transform(X)
输入:X.shape
输出:(5, 2)
输入:X
输出:array([[ 1, 2], [ 3, 4], [ 5, 6], [ 7, 8], [ 9, 10]])
输入:X2.shape
输出:(5, 6)
输入:X2
输出:
array([[ 1., 1., 2., 1., 2., 4.],
[ 1., 3., 4., 9., 12., 16.],
[ 1., 5., 6., 25., 30., 36.],
[ 1., 7., 8., 49., 56., 64.],
[ 1., 9., 10., 81., 90., 100.]])
第一列:1,即0次幂
第二列:x1,1次幂
第三列:x2,1次幂
第四列:x1^2,2次幂
第五列:x1*x2,2次幂
第六列:x2^2,2次幂
假设有x1, x2两个特征,PolynomialFeatures(degree=3),会得到多少项数据?

poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)
poly.fit(X)
X3 = poly.transform(X)
# X3.shape = (5, 10)
# array([[ 1., 1., 2., 1., 2., 4., 1., 2., 4., 8.],
# [ 1., 3., 4., 9., 12., 16., 27., 36., 48., 64.],
# [ 1., 5., 6., 25., 30., 36., 125., 150., 180., 216.],
# [ 1., 7., 8., 49., 56., 64., 343., 392., 448., 512.],
# [ 1., 9., 10., 81., 90., 100., 729., 810., 900., 1000.]])
Pipeline
使用pipeline把多项式特征、数据规一化、线性回归三步合在一起,就不需要在每一次调用时都重复这三步
sklearn没有直接提供多项式回归算法,但可以使用pipe很方便地创建一个多项式回归算法
x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100)
X = x. reshape(-1, 1)
y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100)
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
poly_reg = Pipeline([
("poly", PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)),
("std_scaler", StandardScaler()),
("lin_reg", LinearRegression())
])
poly_reg.fit(X, y)
y_predict = poly_reg.predict(X)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(np.sort(x), y_predict[np.argsort(x)], color='r')
plt.show()
